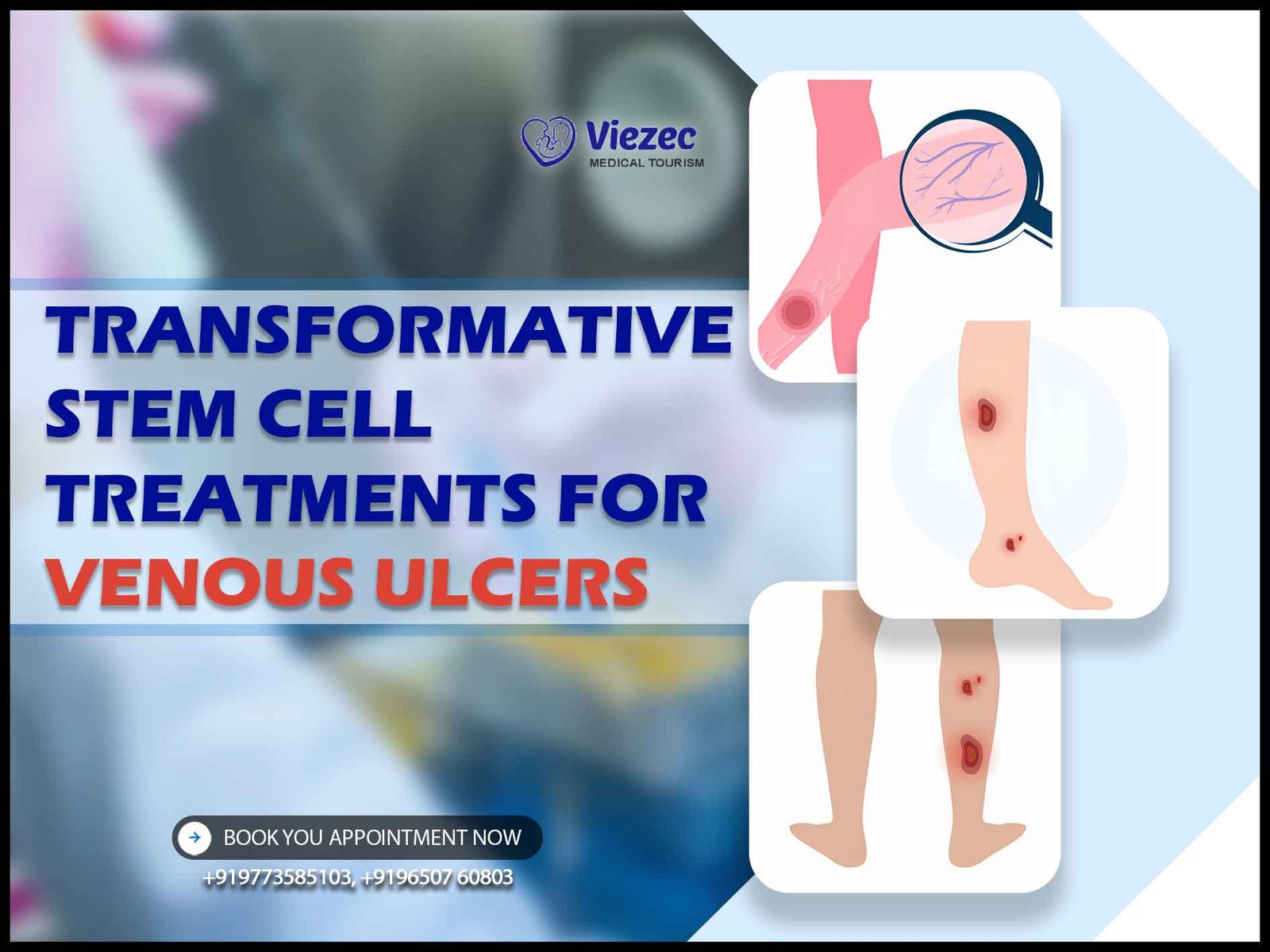
Venous ulcers are debilitating wounds that arise from venous insufficiency, a condition where the veins fail to adequately return blood from the legs to the heart. These ulcers typically manifest as open sores, often on the lower extremities, and can be challenging to manage due to their chronic nature.
Understanding Venous Ulcers: Causes and Symptoms
Venous ulcers develop when persistent venous hypertension leads to tissue damage and impaired wound healing. The hallmark symptoms include pain, swelling, and skin changes such as discoloration and thickening, culminating in the formation of non-healing wounds.
Impact of Venous Ulcers on Quality of Life
The impact of venous ulcers extends beyond physical discomfort, significantly affecting patients’ quality of life. Chronic pain, limited mobility, and social isolation are common consequences, leading to psychological distress and diminished overall well-being.
Current Treatment Landscape
Despite advancements in wound care, the management of venous ulcers remains a clinical challenge, often requiring long-term therapy and frequent interventions.
Conventional Therapies for Venous Ulcers
Conventional treatments focus on wound debridement, compression therapy, and topical dressings to promote healing and prevent infection. While effective to some extent, these approaches often fail to address the underlying venous insufficiency, resulting in high recurrence rates.
Limitations of Existing Treatments
The limitations of conventional therapies underscore the need for innovative interventions capable of addressing both the symptoms and the root cause of venous ulcers. Emerging evidence suggests that stem cell therapy holds promise in revolutionizing the treatment paradigm.
Promise of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy offers a paradigm shift in the management of venous ulcers by harnessing the regenerative potential of stem cells to promote tissue repair and angiogenesis.
Overview of Stem Cell Technology
Stem cells possess the unique ability to differentiate into various cell types and modulate the local microenvironment, making them ideal candidates for regenerative medicine applications. In the context of venous ulcers, stem cell therapy aims to accelerate wound healing and restore tissue integrity.
Mechanisms of Action in Stem Cell Therapy
The therapeutic mechanisms underlying stem cell therapy involve paracrine signaling, immunomodulation, and differentiation into specialized cell lineages. By releasing growth factors, cytokines, and extracellular vesicles, stem cells orchestrate a cascade of events conducive to wound healing and tissue regeneration.
Types of Stem Cells Utilized
Several types of stem cells have been investigated for their potential in treating venous ulcers, each offering unique advantages and challenges.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in Venous Ulcer Treatment
MSCs, derived from various sources such as bone marrow and adipose tissue, have emerged as frontrunners in clinical trials for venous ulcer therapy. These multipotent cells possess anti-inflammatory properties and promote angiogenesis, facilitating wound closure and tissue regeneration.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs) for Wound Healing
iPSCs, reprogrammed from somatic cells, hold immense therapeutic potential due to their pluripotent nature and unlimited proliferative capacity. While still in the experimental stages, iPSC-based approaches offer personalized treatment strategies tailored to individual patient needs.
Preclinical Studies and Experimental Models
Preclinical studies using animal models have provided valuable insights into the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapy for venous ulcers, laying the groundwork for clinical translation.
Efficacy Demonstrated in Animal Models
Animal studies have demonstrated the ability of stem cells to promote wound healing and improve tissue perfusion in venous ulcer models. These preclinical findings support the rationale for advancing stem cell-based interventions into human trials.
Insights from Preclinical Trials
Preclinical trials have elucidated the optimal cell dosing, delivery routes, and adjunctive therapies to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of stem cell treatments. These experimental findings inform the design and execution of subsequent clinical trials.
Clinical Trials and Evidence
The transition from preclinical research to clinical application represents a critical milestone in evaluating the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapy for venous ulcers.
Phase I Trials: Safety and Feasibility
Phase I trials primarily focus on assessing the safety profile of stem cell treatments and establishing the feasibility of administration. Initial studies have demonstrated the safety of MSC infusion and provided valuable data on dosing regimens and adverse event monitoring.
Phase II Trials: Efficacy and Dosing Optimization
Phase II trials aim to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of stem cell therapy in a larger cohort of patients. These studies explore optimal dosing strategies, patient selection criteria, and outcome measures to inform the design of subsequent pivotal trials.
Phase III Trials: Large-scale Validation
Phase III trials represent the final stage of clinical development, aiming to validate the efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy in a diverse patient population. Large-scale randomized controlled trials are essential for regulatory approval and widespread adoption of stem cell treatments.
Patient Selection and Considerations
Effective patient selection is crucial for maximizing the therapeutic benefits of stem cell therapy while minimizing potential risks and complications.
Criteria for Patient Selection in Stem Cell Therapy
Patient selection criteria encompass factors such as wound characteristics, comorbidities, and overall health status. Multidisciplinary assessment involving wound care specialists, vascular surgeons, and regenerative medicine experts is essential to identify suitable candidates for treatment.
Potential Risks and Complications
Despite the therapeutic potential of stem cell therapy, certain risks and complications must be considered, including immune rejection, tumorigenesis, and ectopic tissue formation. Close monitoring and adherence to established protocols are essential to mitigate these risks.
Mechanistic Insights and Pathways
Understanding the underlying mechanisms of stem cell-mediated wound healing is essential for optimizing treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes.
Understanding the Regenerative Mechanisms
Stem cells exert their therapeutic effects through a multifaceted interplay of paracrine signaling, cell differentiation, and immunomodulation. By modulating the local microenvironment, stem cells promote tissue repair and regeneration, leading to accelerated wound healing.
Angiogenesis and Tissue Repair Pathways
Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, plays a central role in wound healing by restoring perfusion and oxygenation to the injured tissue. Stem cells stimulate angiogenic pathways through the release of proangiogenic factors, facilitating neovascularization and tissue remodeling.
Combining Stem Cells with Adjunct Therapies
Synergistic combinations of stem cells with adjunctive therapies hold promise for enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of venous ulcer treatments.
Enhancing Efficacy through Combination Therapies
Combining stem cells with growth factors, biomaterials, and advanced wound care modalities can enhance tissue regeneration and improve wound closure rates. These synergistic approaches address multiple aspects of wound healing, leading to superior clinical outcomes.
Synergistic Effects with Growth Factors and Biologics
Growth factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) synergize with stem cells to promote angiogenesis and tissue repair. Biologic scaffolds and extracellular matrix components provide structural support and enhance cell engraftment, further augmenting the regenerative capacity of stem cell therapy.
Optimizing Delivery Methods
The choice of delivery method significantly influences the efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy for venous ulcers.
Comparing Different Delivery Routes
Intravenous infusion, local injection, and tissue-engineered constructs are among the various delivery routes explored for stem cell administration. Each approach offers unique advantages and challenges, requiring careful consideration based on the specific clinical context and patient characteristics.
Innovative Delivery Systems for Targeted Therapy
Advancements in biomaterial engineering and nanotechnology have led to the development of innovative delivery systems for targeted stem cell delivery. Hydrogels, microparticles, and 3D-printed scaffolds enable controlled release and spatial localization of stem cells, optimizing their therapeutic impact.
Long-term Outcomes and Follow-up
Long-term monitoring and follow-up are essential aspects of ensuring the sustained efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy for venous ulcers.
Monitoring Patient Progression Post-Treatment
Regular follow-up evaluations allow clinicians to assess wound healing progression, monitor for adverse events, and adjust treatment strategies as needed. Patient-reported outcomes and quality of life assessments provide valuable insights into the subjective experiences and functional improvements following stem cell therapy.
Assessing Long-term Safety and Durability
Longitudinal studies are necessary to evaluate the long-term safety and durability of stem cell treatments, including potential risks such as ectopic tissue formation and neoplastic transformation. Post-marketing surveillance and registry databases facilitate ongoing monitoring of real-world outcomes and adverse event reporting.
Economic Considerations and Cost-effectiveness
The economic implications of stem cell therapy must be carefully evaluated to ensure its sustainability and accessibility within the healthcare system.
Evaluating the Economic Impact of Stem Cell Therapy
Cost-effectiveness analyses compare the upfront expenses of stem cell treatment with long-term savings attributable to reduced hospitalizations, complications, and disability. Factors such as reimbursement policies, healthcare infrastructure, and technology adoption rates influence the economic viability of stem cell therapies.
Cost-benefit Analysis and Healthcare Resource Allocation
Balancing the potential benefits of stem cell therapy against its costs requires a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis accounting for both direct and indirect healthcare expenditures. Efficient resource allocation and strategic investment in regenerative medicine technologies are essential for maximizing societal welfare and patient outcomes.
Regulatory Framework
Navigating the regulatory landscape is critical for advancing stem cell therapies from bench to bedside and ensuring patient safety.
Current Regulatory Landscape for Stem Cell Therapies
Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA provide oversight and guidance on the development, approval, and post-market surveillance of stem cell-based products. Regulatory pathways, including expedited approvals and orphan drug designations, facilitate the translation of promising therapies into clinical practice.
Patient Perspectives and Case Studies
Patient perspectives and real-life experiences offer valuable insights into the impact of stem cell therapy on individuals’ lives and highlight the importance of patient-centered care.
Real-life Experiences of Patients Undergoing Stem Cell Treatment
Patient testimonials provide firsthand accounts of the challenges associated with venous ulcers and the transformative effects of stem cell therapy on wound healing and quality of life. These narratives underscore the significance of personalized medicine approaches tailored to individual patient needs and preferences.
Patient-reported Outcomes and Quality of Life Measures
Incorporating patient-reported outcomes and quality of life measures into clinical trials and real-world studies enhances our understanding of the holistic impact of stem cell therapy beyond traditional clinical endpoints. Patient-centered care strategies prioritize patient preferences, values, and goals, fostering meaningful therapeutic partnerships and optimizing treatment outcomes.
In conclusion, transformative stem cell treatments hold immense promise for addressing the unmet needs of patients suffering from venous ulcers. By leveraging the regenerative potential of stem cells, clinicians and researchers are poised to revolutionize wound care and improve the quality of life for millions worldwide. Through interdisciplinary collaboration, rigorous scientific inquiry, and patient-centered innovation, the future of regenerative medicine is brighter than ever before.