Stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising avenue in regenerative medicine, offering potential solutions for treating various medical conditions, including back injuries. The fundamental basis of stem cell therapy lies in the unique properties of stem cells themselves — their ability to differentiate into different cell types and promote tissue regeneration. This article explores the application of stem cell therapy specifically in the context of healing back injuries.
Understanding Stem Cells
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that have the remarkable potential to develop into many different cell types in the body during early life and growth. In adults, stem cells act as a repair system for the body, replenishing specialized cells and tissues. Their ability to self-renew and differentiate into specific cell types makes them invaluable in medical treatments.
Types of Stem Cells Used in Therapy
In stem cell therapy for back injuries, several types of stem cells are employed, including embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and adult stem cells such as mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Each type has its own unique properties and potential applications in regenerative medicine.
Mechanism of Stem Cell Therapy
The mechanism behind stem cell therapy involves harnessing the regenerative capabilities of stem cells to repair damaged tissue. When administered to the site of injury, stem cells can integrate into the damaged tissue, promote healing processes, reduce inflammation, and potentially restore function.
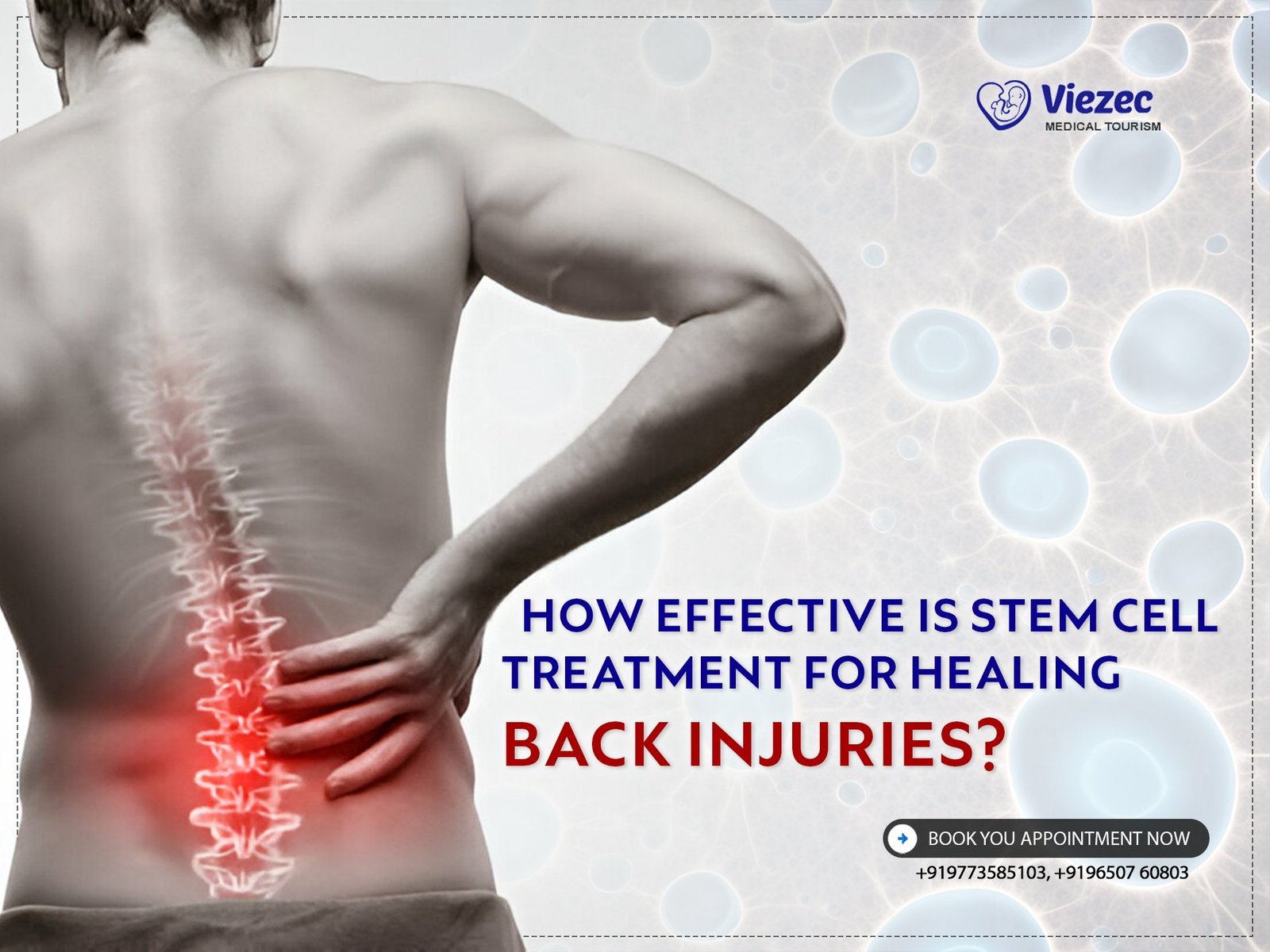
Back Injuries: Causes and Impact
Back injuries are prevalent and can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding the causes and implications of these injuries is crucial for appreciating the role of stem cell therapy in their treatment.
Common Types of Back Injuries
Back injuries encompass a range of conditions, from muscle strains and ligament sprains to more severe issues such as herniated discs, degenerative disc disease, and spinal fractures. These injuries can result from trauma, overuse, or degenerative changes in the spine.
Impact of Back Injuries on Quality of Life
The consequences of back injuries can be debilitating, affecting mobility, causing chronic pain, and limiting daily activities. Chronic back pain, in particular, can lead to psychological distress and reduced overall well-being, highlighting the need for effective treatment options.
Current Treatment Challenges
Traditional treatments for back injuries often focus on managing symptoms rather than promoting true tissue regeneration. Surgery may be necessary in severe cases, but it comes with risks and may not always provide long-term relief. Conservative treatments like physical therapy and pain management have their limitations in addressing underlying tissue damage.
Role of Stem Cells in Regenerative Medicine
Stem cells offer a promising alternative by addressing the root cause of tissue damage and promoting regeneration. Their unique regenerative potential makes them suitable candidates for treating various orthopedic conditions, including back injuries.
Regenerative Potential of Stem Cells
Stem cells have the ability to differentiate into bone, cartilage, and other connective tissues, making them ideal for repairing damaged spinal discs, vertebrae, and surrounding tissues. Their regenerative capabilities extend to modulating the immune response and promoting tissue healing.
Specific Applications in Orthopedics
In orthopedic practice, stem cell therapy has shown promise in treating conditions like osteoarthritis, tendon injuries, and spinal disorders. By targeting damaged tissues directly, stem cells can facilitate repair processes and potentially restore function in affected areas.
Scientific Basis for Using Stem Cells in Back Injury Treatment
Research into stem cell therapy for back injuries has demonstrated encouraging results, with studies showing improved pain relief, tissue regeneration, and functional outcomes in treated patients. Scientific understanding continues to evolve, driving advancements in treatment protocols and patient outcomes.
Clinical Applications of Stem Cell Therapy
Clinical trials and research findings provide valuable insights into the efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy in treating back injuries, paving the way for broader adoption and refinement of treatment protocols.
Overview of Clinical Trials and Research Findings
Clinical trials have explored the use of stem cells from various sources, including bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood, in treating back injuries. These studies have reported improvements in pain scores, mobility, and quality of life among participants.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Numerous case studies highlight the potential of stem cell therapy to achieve positive outcomes in patients with chronic back pain and spinal disorders. These success stories underscore the therapeutic benefits of stem cells in promoting tissue repair and functional recovery.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
Ensuring the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapies is paramount. Ongoing research aims to establish standardized protocols for harvesting, processing, and administering stem cells while monitoring long-term outcomes and potential adverse effects.
Procedure and Techniques in Stem Cell Treatment
The success of stem cell therapy relies on precise techniques for harvesting, isolating, and delivering stem cells to the injured site, tailored to optimize therapeutic outcomes.
Harvesting and Isolation Methods
Stem cells can be obtained from various sources, including bone marrow aspiration, adipose tissue extraction, and umbilical cord blood. Each method has its advantages and considerations regarding cell yield, purity, and suitability for specific applications.
Preparation and Cultivation of Stem Cells
Once harvested, stem cells undergo processing to isolate and concentrate viable cells for therapeutic use. Techniques such as cell culture and expansion may be employed to increase cell numbers and enhance their regenerative potential before administration.
Delivery Methods and Site-Specific Techniques
The route of stem cell administration varies depending on the injury type and location. Techniques such as direct injection into damaged tissues, guided by imaging technologies like ultrasound or fluoroscopy, aim to maximize cell retention and therapeutic efficacy.
Advantages of Stem Cell Therapy Over Traditional Treatments
Compared to traditional treatments for back injuries, stem cell therapy offers several distinct advantages in terms of effectiveness, safety, and long-term benefits.
Comparative Effectiveness Studies
Clinical studies comparing stem cell therapy with conventional treatments have shown comparable or superior outcomes in terms of pain relief, functional improvement, and reduced need for surgical intervention. Stem cells address underlying tissue damage, potentially offering more sustainable relief.
Reduced Risk of Complications
Unlike invasive surgeries, stem cell therapy is minimally invasive, reducing the risk of surgical complications such as infection, anesthesia-related issues, and prolonged recovery times. The use of autologous cells further minimizes immune rejection risks.
Long-Term Benefits and Healing Potential
Stem cell therapy aims not only to alleviate symptoms but also to promote tissue repair and regeneration, addressing the root cause of back injuries. By enhancing natural healing processes, stem cells may offer long-term benefits and improved quality of life for patients.
Patient Selection and Evaluation
Identifying suitable candidates for stem cell therapy involves careful evaluation based on medical history, diagnostic imaging, and specific criteria to optimize treatment outcomes.
Criteria for Eligibility
Candidates typically include individuals with chronic back pain, disc degeneration, or other orthopedic conditions refractory to conservative treatments. Factors such as age, overall health, and extent of tissue damage influence eligibility for stem cell therapy.
Pre-Treatment Assessment Protocols
Before undergoing stem cell therapy, patients undergo comprehensive evaluations, including physical examinations, imaging studies, and laboratory tests, to assess the extent of tissue damage and suitability for treatment.
Patient Education and Informed Consent
Educating patients about the benefits, risks, and expected outcomes of stem cell therapy is essential for informed decision-making. Informed consent ensures that patients understand the treatment process, potential outcomes, and any associated uncertainties.
Challenges and Future Directions
While promising, the widespread adoption of stem cell therapy for back injuries faces challenges related to scientific, regulatory, and ethical considerations.
Current Limitations and Research Gaps
Challenges include optimizing cell delivery methods, standardizing treatment protocols, and addressing variability in patient responses. Research continues to explore the ideal cell types, dosages, and timing of stem cell therapy for optimal clinical outcomes.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Regulatory frameworks govern the use of stem cell therapies, ensuring patient safety, ethical standards, and efficacy assessments. Compliance with regulatory guidelines and ethical principles is crucial for advancing clinical applications responsibly.
Emerging Trends in Stem Cell Research
Advancements in stem cell biology, tissue engineering, and biomaterial sciences are driving innovative approaches in regenerative medicine. Emerging technologies aim to enhance stem cell potency, improve delivery systems, and broaden treatment indications for back injuries.
Cost Considerations and Insurance Coverage
Understanding the financial implications of stem cell therapy and navigating insurance coverage are essential aspects for patients considering this treatment option.
Financial Implications for Patients
Stem cell therapy costs vary based on factors such as the source of stem cells, treatment protocols, and additional medical services. Patients should consider potential out-of-pocket expenses and financing options when planning for treatment.
Insurance Coverage and Reimbursement Policies
Insurance coverage for stem cell therapy may vary depending on the specific procedure, medical necessity, and individual insurance policies. Patients are advised to consult with their insurance providers to understand coverage limitations and reimbursement options.
Strategies for Affordability and Access
To improve affordability and accessibility, healthcare providers may offer payment plans, financing options, or assistance programs to help patients manage the costs associated with stem cell therapy.
FAQs
What types of back injuries can stem cell therapy treat?
Stem cell therapy can potentially treat various back injuries, including degenerative disc disease, herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and vertebral fractures, among others.
How safe is stem cell therapy for treating back injuries?
Stem cell therapy for back injuries is generally considered safe when performed by trained healthcare professionals in accredited facilities, with minimal risk of complications compared to invasive surgical procedures.
What are the expected outcomes of stem cell treatment for back injuries?
Patients may experience reduced pain, improved mobility, and enhanced quality of life following stem cell therapy, with outcomes varying based on individual health factors and the specific injury being treated.
Is stem cell therapy covered by insurance for back injuries?
Insurance coverage for stem cell therapy varies widely and may depend on specific policy terms, medical necessity, and documentation supporting the therapeutic benefit for treating back injuries.
For more information on stem cell treatment options for back injuries and to explore how regenerative medicine can benefit you, visit our website or contact us to schedule a consultation with our experienced medical team.