Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic, often disabling disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS). The progression, severity, and specific symptoms of MS are unpredictable and vary from one person to another. Given the complexity and variability of the disease, understanding life expectancy for those diagnosed with MS can be challenging. Life expectancy in MS patients can be influenced by various factors, including the type of MS, the age at diagnosis, the effectiveness of treatments, and lifestyle choices. Understanding these factors can help patients and their families make informed decisions about managing the disease.
Understanding Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the myelin sheath, the protective covering of nerve fibers in the CNS. This damage disrupts the flow of information within the brain and between the brain and body, leading to a wide range of symptoms. These can include physical issues like muscle weakness and spasticity, cognitive problems such as memory loss, and emotional challenges like depression. The cause of MS is still unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. MS is typically diagnosed between the ages of 20 and 50, though it can occur at any age.
Overview of Life Expectancy in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
On average, the life expectancy for people with MS is slightly shorter than that of the general population. Historically, the prognosis for MS was quite grim, but with advancements in treatment and a better understanding of the disease, the outlook has improved significantly. Today, many people with MS live close to a normal lifespan, especially if the disease is diagnosed early and managed effectively. While the disease itself is rarely fatal, complications arising from severe symptoms or co-existing conditions can impact life expectancy.
Importance of Knowing Life Expectancy in Multiple Sclerosis
Knowing the potential impact of MS on life expectancy is crucial for patients and their families. It helps in planning for the future, making informed decisions about treatment options, and adopting lifestyle changes that can improve quality of life. Understanding life expectancy can also provide a sense of hope and motivate patients to adhere to their treatment regimens and make positive lifestyle adjustments. Moreover, it can guide healthcare providers in tailoring their approach to each patient’s unique needs.
Factors Influencing Life Expectancy in Multiple Sclerosis
Genetic Factors and Life Expectancy in Multiple Sclerosis
Genetic predisposition plays a role in the development of MS, but its influence on life expectancy is less clear. While certain genetic markers can indicate a higher risk of developing the disease, they do not necessarily predict the progression or severity of MS. Researchers continue to investigate the genetic components of MS to understand how they might impact the course of the disease and its implications for life expectancy. Early detection of genetic markers might lead to more personalized treatment plans that could improve outcomes and potentially extend life expectancy.
Lifestyle Choices and Their Impact on Multiple Sclerosis Life Expectancy
Lifestyle choices significantly affect the life expectancy of individuals with MS. Healthy habits such as maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help manage symptoms and prevent complications. Regular exercise, in particular, has been shown to improve strength, mobility, and overall well-being, which can positively influence life expectancy. Additionally, stress management techniques, including mindfulness and meditation, can reduce the impact of stress on the body, potentially mitigating some of the disease’s adverse effects.
Role of Early Diagnosis in Improving Multiple Sclerosis Life Expectancy
Early diagnosis and intervention are critical in managing MS and improving life expectancy. The sooner MS is diagnosed, the earlier treatment can begin, which can help slow the progression of the disease and manage symptoms more effectively. Advances in imaging techniques and diagnostic criteria have made it possible to identify MS in its early stages. Early treatment with disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) can reduce the frequency and severity of relapses, delay disability progression, and improve the overall quality of life, thereby potentially extending life expectancy.
Types of Multiple Sclerosis and Their Impact on Life Expectancy
Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis and Life Expectancy
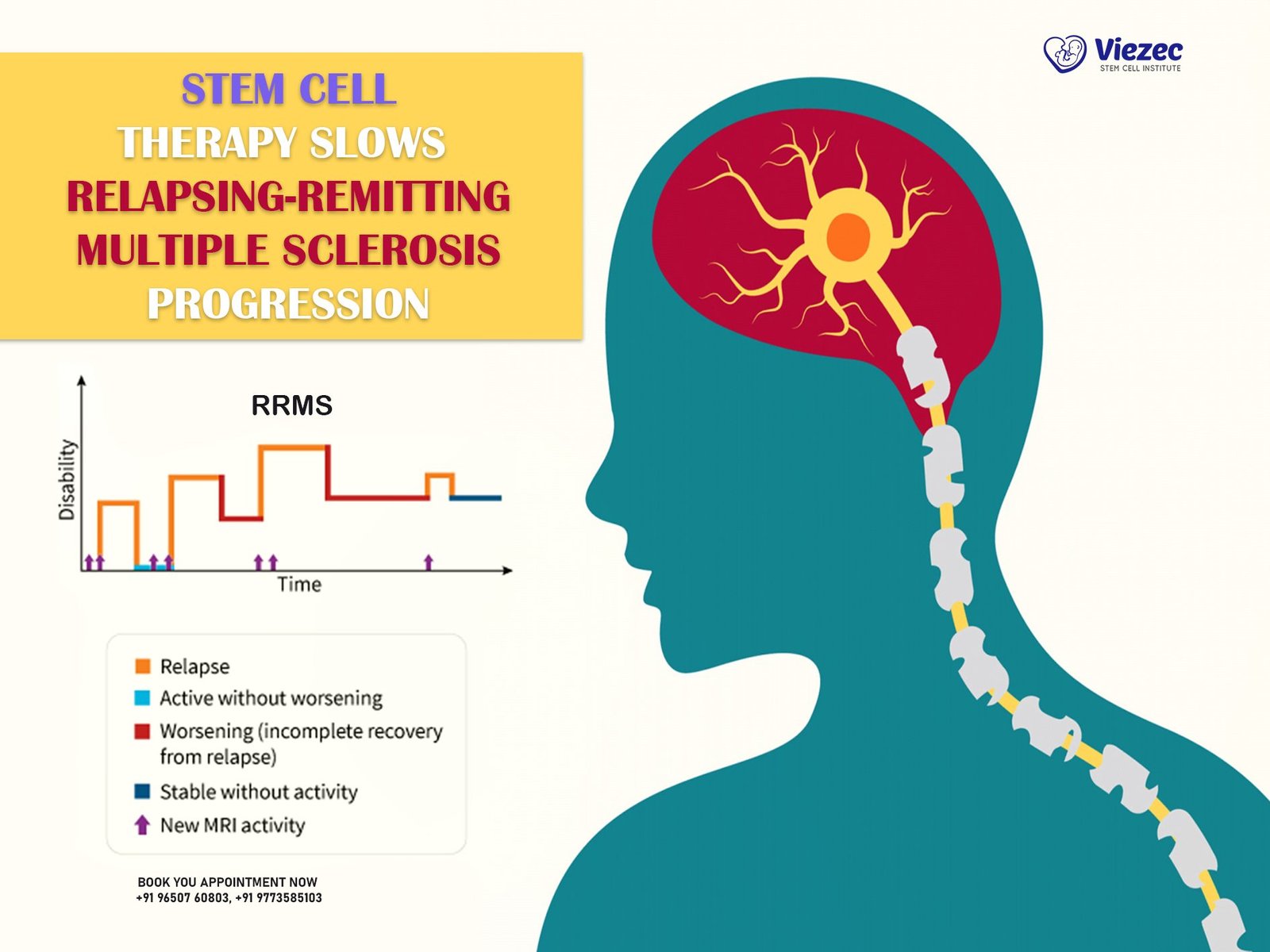
Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis (RRMS) is the most common form of MS, characterized by periods of new or increasing symptoms (relapses) followed by periods of partial or complete recovery (remissions). The prognosis for RRMS is generally more favorable compared to other forms of MS. Many patients with RRMS live relatively normal lives with periods of stability. However, without effective treatment, RRMS can progress to Secondary-Progressive MS (SPMS), which can have a more significant impact on life expectancy. Early and aggressive treatment can help manage relapses and reduce long-term disability.
Secondary-Progressive Multiple Sclerosis: Prognosis and Life Expectancy
Secondary-Progressive Multiple Sclerosis (SPMS) follows an initial relapsing-remitting course. Over time, the disease transitions into a phase of steady progression of disability, with or without relapses. SPMS is associated with a more severe progression of symptoms and a greater impact on daily functioning. As the disease advances, complications such as mobility issues, respiratory problems, and infections can arise, which can affect life expectancy. However, new treatments targeting SPMS specifically have shown promise in slowing disease progression and improving outcomes.
Primary-Progressive Multiple Sclerosis and Its Effect on Life Expectancy
Primary-Progressive Multiple Sclerosis (PPMS) is characterized by a steady progression of symptoms from the onset without relapses or remissions. PPMS affects a smaller proportion of MS patients and is often diagnosed later in life. This form of MS tends to lead to more significant disability over time and can have a greater impact on life expectancy compared to RRMS. Despite the challenges, recent advances in treatment options for PPMS, such as specific DMTs, have provided new hope for patients, offering the potential to slow disease progression and improve quality of life.
Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis Affecting Life Expectancy
Physical Symptoms and Their Impact on Multiple Sclerosis Life Expectancy
The physical symptoms of MS, such as muscle weakness, spasticity, and difficulty with coordination and balance, can significantly impact a patient’s life expectancy. These symptoms can lead to decreased mobility and an increased risk of falls and injuries, which can result in complications such as fractures and infections. In severe cases, MS can affect respiratory function, leading to breathing difficulties and an increased risk of respiratory infections. Effective management of physical symptoms through medication, physical therapy, and assistive devices is crucial in maintaining mobility and reducing the risk of complications.
Cognitive Symptoms in Multiple Sclerosis: Life Expectancy Considerations
Cognitive symptoms, including memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and impaired executive function, can also affect the life expectancy of individuals with MS. Cognitive decline can lead to difficulties in managing daily activities, adhering to treatment regimens, and maintaining independence. This can increase the risk of accidents, decrease overall quality of life, and contribute to mental health issues such as depression and anxiety. Early intervention with cognitive rehabilitation, mental exercises, and support from healthcare professionals can help manage these symptoms and improve outcomes.
Emotional and Psychological Symptoms Influencing Life Expectancy
The emotional and psychological impact of MS cannot be overlooked when considering life expectancy. Many patients with MS experience depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders, which can negatively affect their overall health and well-being. Untreated psychological symptoms can lead to a decline in physical health, reduced adherence to treatment, and an overall decrease in quality of life. Psychological support through counseling, support groups, and medications can play a crucial role in managing these symptoms and improving life expectancy.
Role of Treatment in Enhancing Multiple Sclerosis Life Expectancy
Disease-Modifying Therapies and Life Expectancy in Multiple Sclerosis
Disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) are a cornerstone in the treatment of MS. These medications work by altering the course of the disease, reducing the frequency and severity of relapses, and slowing the progression of disability. Early and consistent use of DMTs has been shown to significantly improve the prognosis for individuals with MS. By preventing new lesions and reducing the overall burden of the disease, DMTs can enhance the quality of life and potentially extend life expectancy. Regular monitoring and adjustments to treatment plans are essential to maximize the benefits of DMTs.
Symptomatic Treatments and Their Effect on Life Expectancy
In addition to DMTs, symptomatic treatments play a vital role in managing the wide range of symptoms associated with MS. Medications to control pain, muscle spasms, fatigue, and other symptoms can significantly improve daily functioning and quality of life. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy can also help patients maintain independence and reduce the risk of complications. By effectively managing symptoms, these treatments can help prevent secondary issues that might impact life expectancy, such as injuries from falls or severe infections.
Rehabilitation and Supportive Therapies for Improving Life Expectancy
Rehabilitation and supportive therapies are essential components of a comprehensive MS treatment plan. These therapies focus on maintaining and improving physical abilities, cognitive function, and emotional well-being. Regular physical therapy can help manage mobility issues, improve strength, and reduce spasticity. Cognitive rehabilitation can address memory and attention problems, while psychological support can help manage depression and anxiety. Supportive therapies, including occupational therapy and social services, can assist patients in adapting to changes and maintaining a high quality of life, thereby potentially extending life expectancy.
Advances in Stem Cell Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis Life Expectancy
Overview of Stem Cell Therapy in Multiple Sclerosis
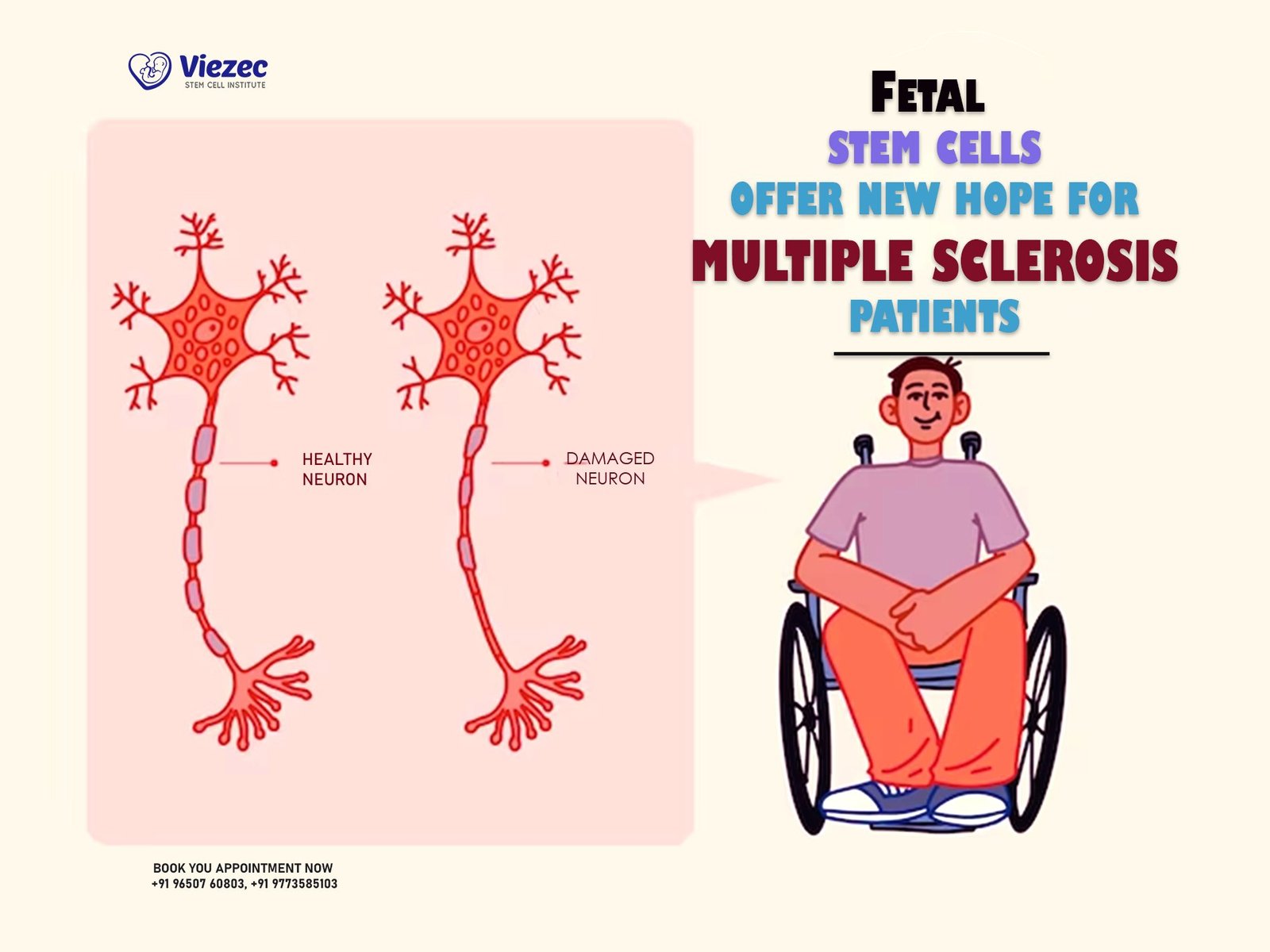
Stem cell therapy represents a promising area of research in the treatment of MS. This innovative approach aims to repair damaged tissues in the CNS and modulate the immune system to reduce autoimmune attacks. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) and mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy are two main types of stem cell treatments being explored. HSCT involves the use of stem cells to reset the immune system, while MSC therapy focuses on repairing damaged tissues and promoting neuroprotection.
Potential Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy on Life Expectancy
The potential benefits of stem cell therapy for MS patients are significant. By repairing myelin damage and promoting the regeneration of nerve cells, stem cell therapy could reduce the progression of disability and improve neurological function. This could lead to better management of symptoms, fewer relapses, and a higher quality of life. Although still in experimental stages, early clinical trials have shown promising results in terms of safety and efficacy, suggesting that stem cell therapy could one day become a viable option for extending life expectancy in MS patients.
Current Research and Future Prospects in Stem Cell Therapy
Current research in stem cell therapy for MS is focused on refining treatment protocols, improving safety, and understanding the long-term effects. Ongoing clinical trials aim to determine the optimal sources of stem cells, the best methods for administration, and the most effective ways to enhance their regenerative capabilities. The future prospects of stem cell therapy are hopeful, with researchers striving to develop treatments that not only halt disease progression but also restore lost function. If successful, these advancements could revolutionize MS treatment and significantly improve life expectancy for patients.
Lifestyle Modifications to Improve Multiple Sclerosis Life Expectancy
Dietary Adjustments and Multiple Sclerosis Life Expectancy
Diet plays a crucial role in the overall health and well-being of individuals with MS. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help manage symptoms and improve energy levels. Certain dietary approaches, such as the Mediterranean diet, have been suggested to have anti-inflammatory properties that could benefit MS patients. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the strain on muscles and joints, improve mobility, and decrease the risk of comorbid conditions such as cardiovascular disease, which can negatively impact life expectancy.
Exercise and Physical Activity for Prolonging Life Expectancy
Regular physical activity is essential for individuals with MS to maintain strength, flexibility, and overall health. Exercise can help manage symptoms such as fatigue, improve cardiovascular health, and enhance mood and cognitive function. Activities such as swimming, yoga, and low-impact aerobics are particularly beneficial as they can be adapted to varying levels of mobility and fitness. Engaging in regular exercise can also help prevent secondary health issues, such as obesity and diabetes, which can negatively affect life expectancy. It’s important for MS patients to work with healthcare providers to develop a safe and effective exercise plan tailored to their needs.
Stress Management and Its Role in Enhancing Life Expectancy
Chronic stress can exacerbate MS symptoms and negatively impact overall health. Effective stress management techniques are vital for improving quality of life and potentially extending life expectancy in MS patients. Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help reduce stress and promote relaxation. Engaging in hobbies, maintaining social connections, and seeking support from mental health professionals can also help manage stress levels. By reducing the impact of stress on the body, MS patients can improve their overall well-being and potentially reduce the progression of the disease.
Comorbid Conditions and Their Impact on Multiple Sclerosis Life Expectancy
Cardiovascular Diseases and Multiple Sclerosis Life Expectancy
Cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension, heart disease, and stroke, can significantly impact the life expectancy of individuals with MS. MS patients are at a higher risk of developing cardiovascular conditions due to factors such as reduced physical activity, inflammation, and the side effects of certain medications. Managing cardiovascular health through regular check-ups, a healthy diet, exercise, and medication when necessary is crucial for improving life expectancy. Healthcare providers should closely monitor MS patients for signs of cardiovascular issues and provide appropriate interventions to mitigate risks.
Diabetes and Its Effect on Life Expectancy in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
Diabetes is another comorbid condition that can affect the life expectancy of MS patients. The presence of diabetes can complicate the management of MS symptoms and increase the risk of complications such as infections and cardiovascular disease. Maintaining good glycemic control through diet, exercise, and medication is essential for preventing the adverse effects of diabetes on MS. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and working closely with healthcare providers can help manage both conditions effectively, improving overall health and potentially extending life expectancy.
Respiratory Issues and Their Influence on Life Expectancy
Respiratory issues, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and respiratory infections, can significantly impact the life expectancy of individuals with MS. MS can weaken respiratory muscles, making it difficult to breathe and increasing the risk of infections. Effective management of respiratory health, including pulmonary rehabilitation, breathing exercises, and timely treatment of infections, is crucial for maintaining respiratory function and preventing complications. Vaccinations, such as the flu and pneumonia vaccines, can also help reduce the risk of respiratory infections and improve life expectancy.
Psychological Support and Multiple Sclerosis Life Expectancy
Importance of Mental Health in Multiple Sclerosis Life Expectancy
Mental health is a critical component of overall well-being for individuals with MS. Depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders are common among MS patients and can negatively impact physical health and life expectancy. Poor mental health can lead to reduced adherence to treatment, unhealthy lifestyle choices, and increased risk of comorbid conditions. Addressing mental health issues through counseling, medication, and support groups is essential for improving quality of life and potentially extending life expectancy. A holistic approach that includes mental health care can help MS patients manage the emotional challenges of the disease more effectively.
Counseling and Support Groups for Enhancing Life Expectancy
Counseling and support groups provide invaluable support for individuals with MS and their families. Professional counseling can help patients cope with the emotional and psychological challenges of living with MS, including managing stress, anxiety, and depression. Support groups offer a sense of community and understanding, allowing patients to share experiences, gain insights, and feel less isolated. These resources can improve mental health, enhance resilience, and encourage adherence to treatment plans, all of which can contribute to a better quality of life and potentially extend life expectancy.
Family Support and Its Impact on Life Expectancy
Family support plays a crucial role in the well-being and life expectancy of MS patients. A supportive family environment can provide emotional comfort, practical assistance, and motivation to adhere to treatment plans. Family members can help with daily activities, accompany patients to medical appointments, and provide encouragement during challenging times. Educating family members about MS and involving them in care plans can enhance their ability to provide effective support. A strong support system can significantly improve the overall health and quality of life for MS patients, contributing to longer life expectancy.
Gender Differences in Multiple Sclerosis Life Expectancy
Life Expectancy in Women with Multiple Sclerosis
Women are more frequently diagnosed with MS than men, with a ratio of approximately 3:1. However, studies suggest that life expectancy in women with MS is generally similar to that of men with the disease. The progression and severity of MS can vary widely among individuals, and while some studies indicate that women may experience a slower progression of disability, others show no significant difference between genders. Women with MS may face unique challenges, such as managing the disease during pregnancy and menopause, but with appropriate care and management, they can lead fulfilling lives with a near-normal life expectancy.
Life Expectancy in Men with Multiple Sclerosis
Men with MS often face a different set of challenges compared to women. While the overall incidence of MS is lower in men, studies suggest that they may experience a more aggressive form of the disease and faster progression of disability. This can impact life expectancy, as men with MS may have a higher risk of severe complications and comorbid conditions. Early diagnosis, aggressive treatment, and proactive management of symptoms and comorbidities are crucial for improving outcomes and extending life expectancy in men with MS.
Gender-Specific Factors Affecting Life Expectancy
Several gender-specific factors can influence life expectancy in MS patients. Hormonal differences, genetic factors, and variations in immune system responses can all play a role in the progression and severity of MS. For women, hormonal changes during pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause can affect disease activity and symptom management. Men, on the other hand, may experience different patterns of disease progression and response to treatment. Understanding these gender-specific factors can help healthcare providers develop tailored treatment plans that address the unique needs of each patient, potentially improving outcomes and life expectancy.
Age-Related Considerations in Multiple Sclerosis Life Expectancy
Life Expectancy in Early-Onset Multiple Sclerosis
Early-onset MS, diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, presents unique challenges and considerations for life expectancy. Young patients may experience different patterns of disease progression and response to treatment compared to adults. Early intervention with appropriate therapies can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression, improving long-term outcomes. However, the psychosocial impact of growing up with a chronic illness can affect mental health and overall well-being. Comprehensive care that includes physical, cognitive, and emotional support is essential for improving the quality of life and life expectancy for young MS patients.
Life Expectancy in Late-Onset Multiple Sclerosis
Late-onset MS, diagnosed after the age of 50, tends to have a more progressive course and may be associated with greater disability. Older adults with MS are more likely to have comorbid conditions, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes, which can complicate disease management and impact life expectancy. However, with advancements in treatment and a better understanding of the disease, many older adults with MS can still achieve a good quality of life. Early diagnosis and proactive management of both MS and comorbid conditions are crucial for improving outcomes and extending life expectancy in this population.
Aging with Multiple Sclerosis: Challenges and Life Expectancy
Aging with MS presents its own set of challenges. As individuals with MS age, they may experience an accumulation of disability, increased risk of comorbid conditions, and greater difficulty in managing symptoms. Mobility issues, cognitive decline, and mental health challenges can become more pronounced, affecting quality of life and life expectancy. Access to comprehensive healthcare, including regular monitoring, physical and cognitive rehabilitation, and mental health support, is essential for addressing these challenges. By managing symptoms effectively and maintaining overall health, older adults with MS can improve their quality of life and potentially extend their life expectancy.
Multiple factors influence the life expectancy of individuals with MS, including the type of MS, the timing and effectiveness of treatment, lifestyle choices, and the presence of comorbid conditions. Advances in medical research, particularly in the areas of disease-modifying therapies and stem cell therapy, offer hope for improving outcomes and extending life expectancy. Comprehensive care that addresses physical, cognitive, and emotional health is essential for enhancing the quality of life for MS patients. With appropriate management and support, many individuals with MS can lead fulfilling lives with a life expectancy close to that of the general population.