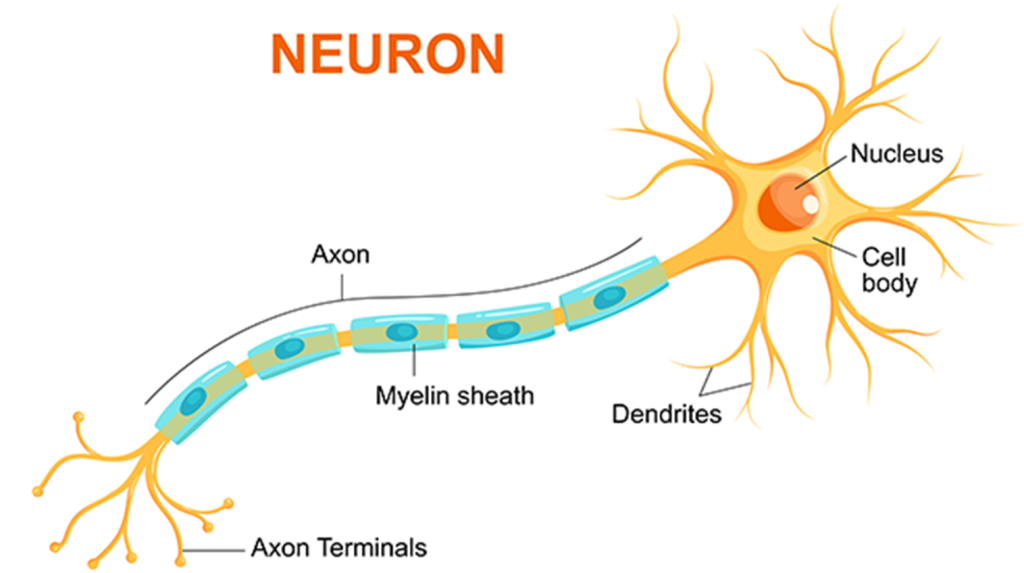
Nerve growth factor (NGF) is a crucial protein that belongs to the neurotrophic factor family, also known as neurotrophins (NTFs). These molecules are essential for the growth, development, and survival of nerve cells. NGF plays a pivotal role in maintaining the health of the nervous system by promoting the growth, differentiation, and survival of neurons.
The Vital Role of NGF in Nerve Cell Health
Supporting Nerve Cell Survival
NGF’s primary function is to prevent the death of nerve cells. By inhibiting cell apoptosis (programmed cell death), it helps to maintain the integrity of neurons. This vital role is crucial for the ongoing health and function of the nervous system, especially during periods of stress or injury.
Encouraging Nerve Cell Growth and Differentiation
In addition to preventing cell death, NGF stimulates the growth and differentiation of nerve cells. It supports the development of new neurons from stem cells, a process known as neurogenesis. This is particularly important for the growth of the central nervous system (CNS) and for maintaining its functionality.
NGF Synthesis and Secretion: Where Does It Come From?
Sources of NGF Production
NGF is synthesized and secreted by a variety of tissues, including corneal epithelial cells, endothelial cells, and corneal stromal cells. These tissues release NGF into the surrounding environment, where it can interact with nerve cells and exert its beneficial effects.
Transport and Storage Mechanism of NGF
Once NGF is produced and released, it is taken up by nerve endings, such as those of sympathetic or sensory neurons. The protein is then transported to the neuronal cell bodies, where it is stored and ready to facilitate the growth and differentiation of nerve cells as needed.
How NGF Promotes Neurogenesis
Neurogenesis and Its Importance in Nerve Regeneration
NGF plays an essential role in neurogenesis, which is the process of creating new neurons from stem cells. This regenerative process is crucial for the repair and maintenance of the nervous system, especially after injury or degeneration. NGF helps stimulate the development of new neurons, supporting the healing and functional recovery of damaged nerves.
NGF’s Contribution to Central Nervous System Recovery
In the central nervous system (CNS), NGF aids in the development of neurons, contributing to tissue repair and regeneration. The ability of NGF to support neurogenesis plays a significant role in maintaining cognitive function and aiding recovery following damage to the CNS.
NGF and Its Regenerative Role in the Peripheral Nervous System
NGF in Peripheral Nerve Repair
Beyond its effects on the CNS, NGF also plays a vital role in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). It promotes the regeneration of injured neurons in the PNS, facilitating nerve repair after trauma. By stimulating neuronal growth and differentiation, NGF helps to restore function in damaged peripheral nerves.
Enhancing Healing in Peripheral Nerve Injuries
NGF supports the healing process by reducing the pathology of injured neurons. It encourages the repair and growth of axons (nerve fibers), which are crucial for restoring normal function in the PNS after nerve damage.
Protecting Neurons from Damage
NGF’s Defense Against Hypoxia and Ischemia
NGF plays a protective role in safeguarding neurons from environmental stresses such as hypoxia (lack of oxygen) and ischemia (reduced blood supply). These conditions can lead to neuronal death and irreversible damage. NGF’s ability to promote cellular survival helps to counteract these harmful effects, allowing neurons to endure and function under these stressful conditions.
NGF’s Impact on Neurological Disorders
Potential Therapeutic Applications for Neurodegenerative Diseases
NGF’s neuroprotective and regenerative properties make it a promising candidate for the treatment of various neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis. By stimulating the growth of new neurons and preventing cell death, NGF could help slow the progression of these debilitating conditions.
NGF in Treating Nerve Injuries
NGF is also being explored for its potential in treating nerve injuries, particularly in cases where peripheral nerve damage has occurred. By supporting the regeneration of damaged neurons, NGF could provide a therapeutic approach for individuals with nerve injuries, promoting faster recovery and functional restoration.
The Future of NGF in Nerve Treatment
Nerve growth factor is a vital protein with immense potential for treating neurological conditions and nerve injuries. Its role in promoting nerve cell survival, growth, differentiation, and regeneration makes it a key player in maintaining a healthy nervous system. As research advances, NGF could become an essential therapeutic agent in the treatment of various nerve-related disorders, offering hope for patients suffering from nerve damage and neurodegenerative diseases.