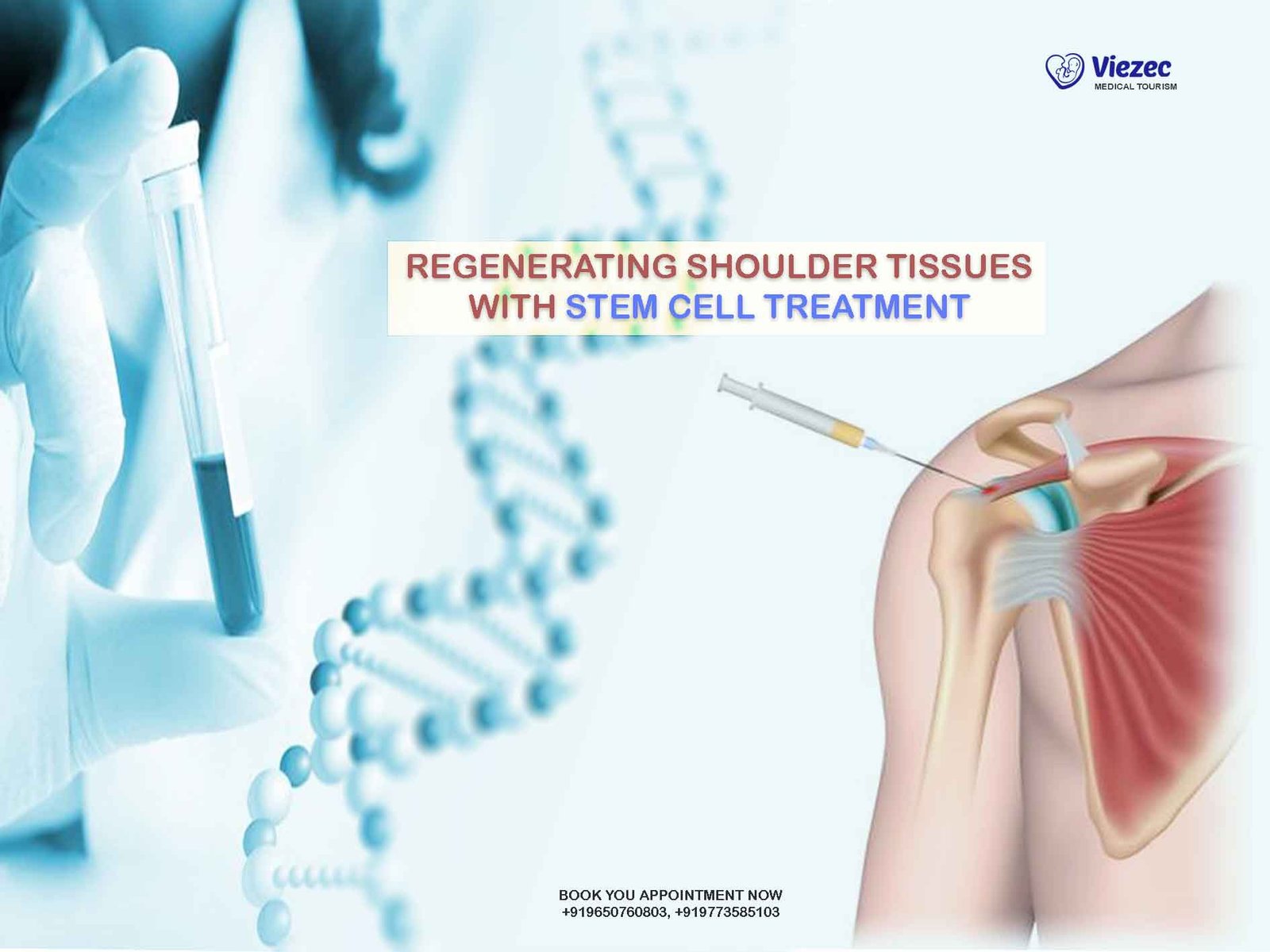
Shoulder injuries are prevalent in both athletes and the general population, often resulting from repetitive motion, trauma, or degenerative conditions. The shoulder is a complex joint, allowing a wide range of motion, but this flexibility makes it susceptible to injuries such as rotator cuff tears, tendonitis, and bursitis. These injuries can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, limiting daily activities and causing chronic pain. Traditional treatments for shoulder injuries include physical therapy, medications, and surgical interventions. However, these methods often come with limitations, such as long recovery times, incomplete healing, and the potential for further complications.
Importance of Shoulder Mobility
The shoulder joint is integral to various daily activities, from simple tasks like reaching and lifting to more complex actions involved in sports and occupational tasks. Maintaining shoulder mobility is crucial for overall functionality and independence. Impaired shoulder function can lead to a cascade of issues, including decreased physical activity, which in turn affects overall health and well-being. Understanding the importance of shoulder mobility underscores the need for effective treatments that not only address pain and dysfunction but also restore the joint’s full range of motion and strength.
Conventional Treatments and Their Limitations
Conventional treatments for shoulder injuries typically include rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and corticosteroid injections. In more severe cases, surgical interventions such as rotator cuff repair or shoulder arthroscopy may be necessary. While these treatments can be effective, they often have significant limitations. Medications and injections may provide temporary relief but do not address the underlying cause of the injury. Surgery, although sometimes necessary, comes with risks such as infection, prolonged recovery periods, and the possibility of incomplete healing or recurrent injuries. These limitations have led to the exploration of alternative treatments, such as stem cell therapy, which offers the potential for more effective and lasting solutions.
Introduction to Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising treatment for a variety of medical conditions, including shoulder injuries. This innovative approach utilizes the body’s own regenerative capabilities to promote healing and tissue repair. Stem cells have the unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, making them ideal for regenerating damaged tissues. In the context of shoulder injuries, stem cell therapy aims to restore the function and integrity of the shoulder joint by repairing damaged tendons, cartilage, and other structures. This treatment offers a potential alternative to conventional methods, with the promise of faster recovery times, reduced pain, and improved outcomes.
Understanding Stem Cells
Definition and Types of Stem Cells
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells with the remarkable ability to develop into various specialized cell types. They play a crucial role in growth, development, and tissue repair. There are several types of stem cells used in medical treatments:
Embryonic Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are derived from early-stage embryos and have the ability to differentiate into any cell type in the body. Their pluripotency makes them highly versatile for research and potential therapeutic applications. However, ethical concerns and the risk of immune rejection limit their clinical use.
Adult Stem Cells
Adult stem cells, also known as somatic stem cells, are found in various tissues throughout the body. They are multipotent, meaning they can develop into a limited range of cell types related to their tissue of origin. Common sources include bone marrow and adipose tissue. These cells are commonly used in regenerative therapies due to their availability and lower risk of ethical issues.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
Induced pluripotent stem cells are generated by reprogramming adult cells to a pluripotent state, similar to embryonic stem cells. iPSCs offer the potential for personalized medicine, as they can be derived from a patient’s own cells, reducing the risk of immune rejection. They hold promise for various therapeutic applications, including tissue regeneration.
Properties of Stem Cells
Stem cells possess several key properties that make them suitable for regenerative medicine. They have the ability to self-renew, meaning they can divide and produce more stem cells indefinitely. Additionally, they can differentiate into various specialized cell types, a process guided by specific signals in their environment. This plasticity allows stem cells to contribute to tissue repair and regeneration. Stem cells also secrete bioactive molecules, such as growth factors and cytokines, which play a critical role in modulating the healing process and promoting tissue repair.
Sources of Stem Cells for Treatment
There are multiple sources of stem cells used for therapeutic purposes. Bone marrow and adipose tissue are common sources of adult stem cells, with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) being widely studied for their regenerative potential. Adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) are obtained from fat tissue and have shown promise in various regenerative applications due to their abundance and ease of harvest. Amniotic fluid and placental tissues are also rich in stem cells and are increasingly explored for their regenerative capabilities. The choice of stem cell source depends on factors such as the specific condition being treated, availability, and patient-specific considerations.
Mechanism of Stem Cell Therapy in Shoulder Regeneration
How Stem Cells Promote Tissue Repair
Stem cell therapy promotes tissue repair through several mechanisms. When introduced into the injured area, stem cells can differentiate into the specific cell types needed for repair, such as tenocytes for tendon repair or chondrocytes for cartilage regeneration. Additionally, stem cells secrete bioactive molecules, including growth factors and cytokines, that modulate the local immune response, reduce inflammation, and promote the recruitment of endogenous repair cells. These combined actions facilitate the healing process and contribute to the restoration of normal tissue structure and function.
Differentiation into Specific Cell Types
A critical aspect of stem cell therapy is the ability of stem cells to differentiate into specific cell types required for tissue repair. This process is influenced by the local microenvironment and signaling cues within the injured tissue. For shoulder injuries, stem cells can differentiate into tenocytes to repair torn tendons, chondrocytes to regenerate damaged cartilage, or even osteoblasts to support bone healing. The differentiation process ensures that the new cells integrate seamlessly with the existing tissue, restoring both structural integrity and functionality.
Role of Growth Factors and Cytokines
Growth factors and cytokines play a vital role in the regenerative process facilitated by stem cells. These bioactive molecules are secreted by stem cells and modulate various aspects of tissue repair. For instance, growth factors such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) promote cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and extracellular matrix remodeling. Cytokines, on the other hand, help regulate the inflammatory response, reducing chronic inflammation and creating a conducive environment for healing. The combined action of growth factors and cytokines enhances the regenerative potential of stem cells, contributing to more effective and efficient tissue repair.
Case Studies and Preclinical Research
Numerous case studies and preclinical research have demonstrated the potential of stem cell therapy in shoulder regeneration. For example, studies on animal models with rotator cuff injuries have shown that stem cell injections can significantly improve tendon healing and biomechanical strength. Clinical case studies involving patients with severe shoulder injuries have reported positive outcomes, including reduced pain, improved range of motion, and faster recovery times. These findings underscore the promise of stem cell therapy as a viable alternative to traditional treatments, providing hope for patients with challenging shoulder conditions.
Types of Shoulder Injuries Treatable with Stem Cells
Rotator Cuff Tears
Rotator cuff tears are among the most common shoulder injuries, often resulting from repetitive stress, trauma, or age-related degeneration. These injuries can cause significant pain, weakness, and limited range of motion. Stem cell therapy offers a promising treatment option by promoting the regeneration of torn tendons and enhancing the healing process. Studies have shown that stem cell injections can improve tendon quality, reduce pain, and restore function, making it a viable alternative to surgical repair.
Tendonitis and Bursitis
Tendonitis and bursitis are inflammatory conditions affecting the tendons and bursae in the shoulder joint. These conditions often result from overuse or repetitive motion and can lead to chronic pain and impaired function. Stem cell therapy can help alleviate these conditions by reducing inflammation and promoting the repair of damaged tissues. The anti-inflammatory properties of stem cells, combined with their ability to regenerate damaged tendons, offer a potential solution for patients suffering from chronic tendonitis or bursitis.
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Damage
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. In the shoulder, osteoarthritis can significantly impair daily activities and quality of life. Stem cell therapy aims to address cartilage damage by promoting the regeneration of cartilage tissue and reducing inflammation. Clinical studies have shown that stem cell injections can improve cartilage quality, reduce pain, and enhance joint function in patients with osteoarthritis, offering a potential alternative to joint replacement surgery.
Labral Tears and Instability
Labral tears and shoulder instability often result from trauma or repetitive overhead activities, such as throwing or lifting. These injuries can lead to pain, limited range of motion, and recurrent dislocations. Stem cell therapy can help repair labral tears and stabilize the shoulder joint by promoting the regeneration of damaged tissues and enhancing the healing process. The ability of stem cells to differentiate into various cell types and secrete bioactive molecules makes them a promising treatment option for labral injuries and shoulder instability.
Stem Cell Sources for Shoulder Treatment
Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells
Bone marrow-derived stem cells (BMSCs) are one of the most widely studied sources of stem cells for regenerative therapies. These cells are harvested from the patient’s bone marrow, typically from the iliac crest, and are rich in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). BMSCs have demonstrated significant potential in promoting tissue repair and regeneration, making them a popular choice for treating shoulder injuries. Their ability to differentiate into various cell types, including tenocytes and chondrocytes, and their secretion of bioactive molecules contribute to their effectiveness in shoulder regeneration.
Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
Adipose tissue-derived stem cells (ASCs) are obtained from the patient’s fat tissue, usually through a minimally invasive liposuction procedure. ASCs are abundant and easily accessible, making them an attractive source of stem cells for regenerative therapies. These cells have shown promise in promoting tissue repair and reducing inflammation, particularly in musculoskeletal conditions. In the context of shoulder injuries, ASCs can differentiate into the necessary cell types for tendon and cartilage repair, providing a potential alternative to bone marrow-derived cells.
Amniotic Fluid and Placental Stem Cells
Amniotic fluid and placental tissues are rich sources of stem cells with significant regenerative potential. These cells are typically harvested from donated placental tissues or amniotic fluid collected during childbirth, making them a non-invasive and ethically acceptable source. Amniotic fluid and placental stem cells have shown promise in promoting tissue repair, reducing inflammation, and enhancing the healing process. Their use in shoulder regeneration is being increasingly explored, with studies demonstrating positive outcomes in preclinical models and early clinical trials.
Allogenic vs. Autologous Stem Cells
Stem cell therapies can utilize either autologous or allogenic cells. Autologous stem cells are derived from the patient’s own tissues, such as bone marrow or adipose tissue, minimizing the risk of immune rejection and ethical concerns. Allogenic stem cells, on the other hand, are obtained from donor tissues, offering the advantage of being readily available and eliminating the need for a harvesting procedure. The choice between autologous and allogenic cells depends on various factors, including the patient’s condition, the availability of donor cells, and the specific treatment protocol.
Clinical Application of Stem Cell Therapy
Patient Selection Criteria
Patient selection is critical for the success of stem cell therapy in shoulder regeneration. Ideal candidates for this treatment typically include individuals with chronic shoulder injuries, such as rotator cuff tears, tendonitis, or osteoarthritis, who have not responded adequately to conventional treatments. Other considerations include the patient’s overall health, age, and the extent of tissue damage. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is essential to determine whether stem cell therapy is a suitable option for a particular patient.
Pre-Treatment Evaluation
Before undergoing stem cell therapy, patients undergo a comprehensive pre-treatment evaluation. This assessment includes a detailed medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies, such as X-rays or MRI scans, to assess the extent of the injury. The evaluation helps determine the appropriate source and type of stem cells, as well as the specific injection site and protocol. Additionally, patients are educated about the potential benefits, risks, and expected outcomes of the treatment to ensure informed decision-making.
Injection Techniques and Protocols
The success of stem cell therapy for shoulder injuries depends on precise injection techniques and protocols. The procedure typically involves the extraction of stem cells from the chosen source, followed by their concentration and preparation for injection. The stem cells are then injected into the injured area using imaging guidance, such as ultrasound or fluoroscopy, to ensure accurate placement. The injection protocol may vary depending on the specific injury and the source of stem cells used. Some protocols may involve a single injection, while others may require multiple injections over a period of time to achieve optimal results.
Post-Treatment Rehabilitation
Post-treatment rehabilitation is a crucial component of the overall success of stem cell therapy. Following the injection, patients are typically advised to rest the affected shoulder and avoid strenuous activities for a specified period. Physical therapy may be initiated to gradually restore range of motion, strength, and function. The rehabilitation program is tailored to the individual patient’s needs and the specific nature of the injury. Adherence to the rehabilitation protocol helps optimize the healing process and ensures the best possible outcomes from stem cell therapy.
Efficacy and Safety of Stem Cell Therapy
Clinical Trials and Outcomes
Clinical trials have provided valuable insights into the efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy for shoulder injuries. Numerous studies have reported positive outcomes, including significant improvements in pain relief, range of motion, and overall shoulder function. For example, a clinical trial involving patients with rotator cuff tears demonstrated that stem cell injections led to better tendon healing and reduced pain compared to conventional treatments. These findings highlight the potential of stem cell therapy as an effective treatment option for various shoulder conditions.
Success Rates and Patient Satisfaction
Success rates and patient satisfaction are important indicators of the effectiveness of stem cell therapy. Many patients report high levels of satisfaction with the treatment, citing improvements in pain, function, and quality of life. Success rates can vary depending on factors such as the severity of the injury, the type of stem cells used, and the patient’s adherence to post-treatment rehabilitation. Overall, the positive outcomes reported in clinical studies and patient testimonials support the growing use of stem cell therapy for shoulder injuries.
Potential Risks and Complications
While stem cell therapy offers promising benefits, it is not without potential risks and complications. Common risks include infection, bleeding, and pain at the injection site. There is also the possibility of an adverse immune response, particularly with allogenic stem cells. However, these risks are generally low, and serious complications are rare. Thorough patient evaluation, careful selection of stem cell sources, and adherence to standardized protocols help minimize the potential risks associated with the treatment.
Long-Term Follow-Up Studies
Long-term follow-up studies are essential to evaluate the sustained benefits and safety of stem cell therapy. These studies track patients over extended periods to assess the durability of the treatment outcomes and monitor for any late-onset complications. Long-term data provide valuable insights into the longevity of the regenerative effects of stem cell therapy and its impact on the patient’s quality of life. The continued collection of long-term data is crucial for advancing the field and optimizing treatment protocols.
Comparative Analysis with Other Regenerative Therapies
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy involves the use of concentrated platelets from the patient’s blood to promote healing and tissue regeneration. PRP contains growth factors that stimulate cell proliferation and tissue repair. While PRP therapy has shown positive results in treating various musculoskeletal conditions, it may not be as effective as stem cell therapy for certain shoulder injuries. The combination of PRP and stem cells is also being explored to enhance the regenerative potential of both treatments.
Prolotherapy
Prolotherapy is a regenerative treatment that involves injecting a solution, typically dextrose, into the injured area to stimulate the body’s natural healing response. This treatment aims to strengthen and repair damaged tissues by promoting inflammation and subsequent tissue repair. While prolotherapy has shown promise in treating certain shoulder conditions, its effectiveness may be limited compared to the regenerative capabilities of stem cells. Combining prolotherapy with stem cell therapy is being investigated as a potential approach to enhance treatment outcomes.
Hyaluronic Acid Injections
Hyaluronic acid injections are commonly used to treat osteoarthritis and joint pain by providing lubrication and cushioning to the affected joint. While these injections can provide symptomatic relief, they do not promote tissue regeneration or address the underlying cause of the injury. Stem cell therapy, on the other hand, offers the potential for long-term healing and regeneration, making it a more comprehensive treatment option for shoulder injuries.
Combined Approaches
The combination of different regenerative therapies, such as stem cells, PRP, and hyaluronic acid injections, is being explored to enhance treatment outcomes. These combined approaches aim to leverage the unique benefits of each therapy, providing a synergistic effect for more effective tissue repair and regeneration. For example, combining stem cell therapy with PRP may enhance the regenerative potential and accelerate the healing process. The development of optimized combined approaches represents an exciting frontier in regenerative medicine.
Case Studies and Patient Testimonials
Success Stories from Around the World
Numerous success stories from around the world highlight the potential of stem cell therapy in treating shoulder injuries. Patients who have undergone the treatment report significant improvements in pain, function, and overall quality of life. For example, a professional athlete with a severe rotator cuff tear experienced a full recovery and returned to competitive sports following stem cell therapy. These success stories underscore the transformative potential of this innovative treatment.
Experiences of Patients in India
In India, stem cell therapy has gained popularity as a treatment for shoulder injuries, with many patients experiencing positive outcomes. Indian patients report reduced pain, improved range of motion, and enhanced shoulder function following the treatment. The availability of advanced medical facilities and skilled healthcare professionals has made stem cell therapy an accessible and effective option for patients in India, contributing to the growing adoption of this treatment.
Long-Term Recovery and Quality of Life
Long-term recovery and improved quality of life are key goals of stem cell therapy for shoulder injuries. Patients who have undergone the treatment report sustained benefits, including reduced pain, improved mobility, and enhanced overall well-being. Long-term follow-up studies support these findings, demonstrating the durability of the regenerative effects of stem cell therapy. The ability to restore normal shoulder function and improve quality of life makes this treatment a valuable option for patients with chronic shoulder conditions.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
The experiences of patients and healthcare professionals provide valuable insights and lessons learned in the application of stem cell therapy for shoulder injuries. Best practices include thorough patient evaluation, careful selection of stem cell sources, precise injection techniques, and adherence to post-treatment rehabilitation protocols. Ongoing research and clinical studies continue to refine and optimize treatment protocols, contributing to the advancement of stem cell therapy as a reliable and effective treatment option.
FAQs
Q1: Is stem cell therapy safe for shoulder injuries? A1: Stem cell therapy is generally considered safe, with a low risk of complications. Common side effects include mild pain or swelling at the injection site. Serious complications are rare, especially when the treatment is performed by experienced healthcare professionals following standardized protocols.
Q2: How long does it take to see results from stem cell therapy? A2: The timeline for seeing results can vary depending on the severity of the injury and the individual patient. Some patients report improvements within a few weeks, while others may take several months to experience significant benefits. Follow-up evaluations and adherence to rehabilitation protocols can influence the outcome.
Q3: Can stem cell therapy be combined with other treatments? A3: Yes, stem cell therapy can be combined with other regenerative treatments, such as PRP or hyaluronic acid injections, to enhance the healing process. Combined approaches are being explored to optimize treatment outcomes and provide more comprehensive care for shoulder injuries.
Q4: Is stem cell therapy suitable for all types of shoulder injuries? A4: Stem cell therapy is suitable for various shoulder injuries, including rotator cuff tears, tendonitis, bursitis, osteoarthritis, and labral tears. However, patient selection is crucial, and a thorough evaluation is necessary to determine if stem cell therapy is the most appropriate treatment option for a specific injury.