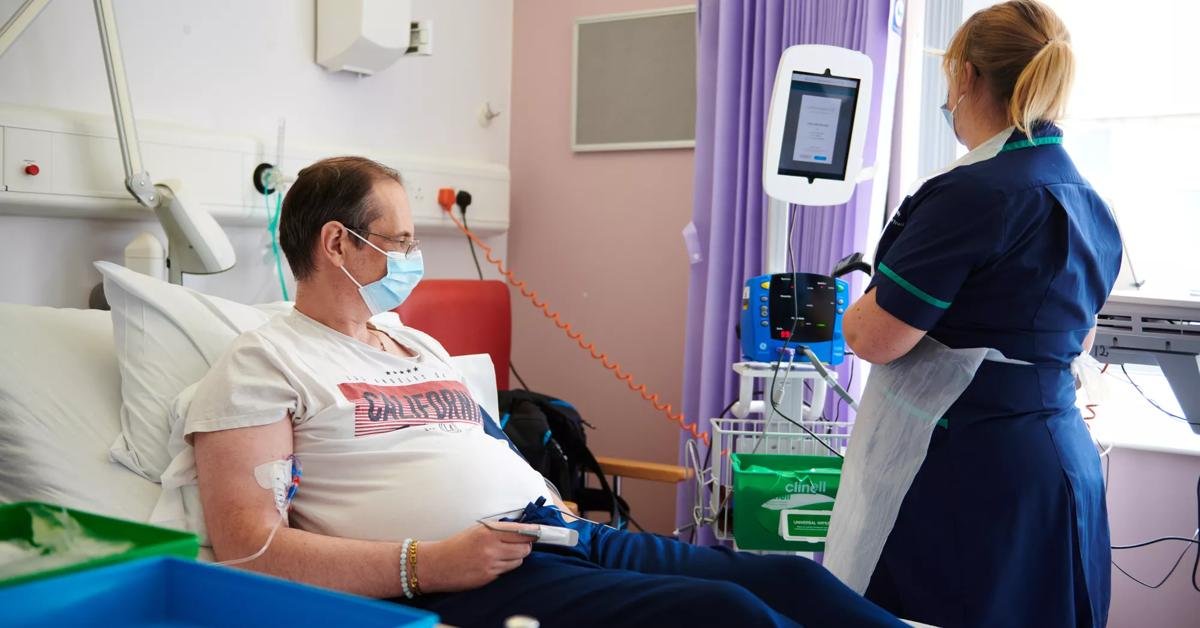
Procedure of Stem Cell Therapy
A clear, step-by-step guide to our treatment pathway — from initial assessment and cell harvesting to targeted delivery and post-treatment care. Learn how we personalise protocols to maximise safety and outcomes for each patient.
Performed by experienced physicians in a certified clinical environment — patient safety and personalised protocols are our priority.
Step-by-Step Stem Cell Therapy Procedure
At Viezec, our procedure follows internationally accepted standards, ensuring every step — from initial evaluation to follow-up care — is handled with precision, transparency and a patient-first approach.
1. Initial Consultation & Medical Evaluation
Our specialists review medical records, perform diagnostic assessments and determine eligibility for stem cell therapy, ensuring a personalized approach.
2. Stem Cell Source Selection
Depending on the patient’s condition, stem cells are derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, or cord blood to ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
3. Stem Cell Harvesting
A safe, minimally invasive process is carried out by experienced doctors to collect stem cells from the selected source.
4. Laboratory Processing & Quality Testing
Collected cells are isolated, purified and tested in advanced labs to ensure their safety, purity and effectiveness before transplantation.
5. Stem Cell Transplantation / Delivery
Processed stem cells are reintroduced into the body via intravenous infusion or site-specific injection, based on the treatment plan.
6. Post-Treatment Care & Monitoring
After the procedure, our medical team provides continuous monitoring, rehabilitation guidance and follow-up care for safe and sustained recovery.
Preparation Before Stem Cell Therapy
Proper preparation is essential for safe and effective stem cell treatment. Our team guides patients through medical assessments, lifestyle adjustments and pre-procedure care to ensure the best possible outcomes.
1. Comprehensive Medical Evaluation
Patients undergo detailed medical history review, physical examination and diagnostic assessments to confirm their eligibility for stem cell therapy.
2. Laboratory Investigations
Blood work, imaging scans and other necessary tests are performed to assess health status and ensure readiness for treatment.
3. Medication Review & Adjustment
Our doctors review current medications and may recommend adjustments or discontinuation of certain drugs before the therapy.
4. Lifestyle & Dietary Guidelines
Patients are encouraged to maintain a balanced diet, avoid smoking, alcohol and follow specific lifestyle recommendations for better outcomes.
5. Informed Consent & Counseling
Our team provides counseling sessions, explains treatment protocols, risks and expected results, ensuring patients make informed decisions.
6. Travel & Accommodation Assistance
For international patients, our support team arranges travel, accommodation and local assistance to ensure a smooth treatment journey.
Start Your Stem Cell Journey Today
Schedule a consultation with our expert team and take the first step towards better health.
Contact Us
During the Stem Cell Therapy Procedure
On the day of the procedure, our medical team ensures patient comfort, safety and precision. From admission to the actual transplantation, every step is carried out in a controlled and sterile environment.
1. Patient Admission & Comfort
Upon arrival, patients are admitted into a sterile clinical facility and provided with all necessary comfort measures before the procedure begins.
2. Vital Signs Monitoring
Medical staff record vital signs including blood pressure, oxygen saturation and heart rate to ensure the patient’s stability before transplantation.
3. Anesthesia / Sedation (if required)
Depending on the patient’s condition and procedure type, local anesthesia or mild sedation may be administered for comfort.
4. Stem Cell Infusion / Injection
The processed stem cells are introduced into the patient’s body either through intravenous infusion or targeted local injection.
5. Continuous Monitoring
Throughout the infusion, our team closely observes the patient’s vital signs and comfort to ensure maximum safety and efficacy.
6. Recovery & Observation
After infusion, patients are shifted to a recovery area where they are monitored until stable before being discharged or moved to inpatient care.
Post-Treatment Care & Recovery
After stem cell transplantation, careful post-treatment care is critical for optimal recovery. Our team provides personalised monitoring, rehabilitation guidance and follow-up consultations to ensure safety and long-term results.
1. Immediate Observation & Monitoring
Patients are closely observed immediately after therapy to monitor vital signs, ensure comfort and check for any reactions or side effects.
2. Medications & Supportive Therapy
Prescribed medications such as pain relievers or anti-inflammatories are given to manage discomfort and support the healing process.
3. Lifestyle & Activity Guidelines
Patients receive guidance on diet, hydration, light exercise and rest to promote smooth and effective recovery.
4. Regular Follow-Up Assessments
Follow-up appointments, lab tests and imaging are conducted to track progress, ensure therapy effectiveness and adjust care plans if needed.
5. Patient Education & Counseling
Our team educates patients on expected outcomes, potential side effects and long-term care practices to support sustained recovery.
Have Questions? Get in Touch
Our team is ready to guide you through the stem cell therapy process and answer any queries.
Contact Us
Expected Outcomes & Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy aims to restore function, reduce pain and promote natural healing. Benefits vary depending on patient condition, but many experience significant improvements in mobility, tissue regeneration and overall quality of life.
1. Pain Reduction & Improved Mobility
Patients often report reduced pain and enhanced joint or tissue mobility, enabling easier daily activities and movement.
2. Enhanced Healing & Tissue Regeneration
Stem cells stimulate natural repair mechanisms, aiding regeneration of damaged
tissues and supporting long-term recovery.
3. Reduced Inflammation & Swelling
Anti-inflammatory effects of stem cells help reduce swelling and discomfort, promoting faster and more comfortable recovery.
4. Improved Quality of Life
Patients experience enhanced physical health, better mobility and increased ability to perform everyday activities comfortably.
5. Long-Term Benefits
Stem cell therapy offers the potential for sustained improvements with minimal
long-term side effects, supporting ongoing health and wellness.
Safety & Quality Assurance
At Viezec, patient safety and treatment quality are our top priorities. From laboratory processing to clinical delivery, every step follows strict protocols to ensure effective, safe and trustworthy stem cell therapy.
1. Certified Clinical Environment
All procedures are conducted in state-of-the-art, certified clinical facilities equipped with advanced medical technology to ensure maximum safety.
2. Experienced Medical Team
Our team of specialists are highly trained and follow internationally accepted medical protocols to deliver safe and effective therapy.
3. Strict Quality Control
Stem cells are processed in certified laboratories under strict quality control
protocols to ensure purity, viability and safety.
4. Patient Safety Protocols
Safety measures include sterile operating environments, continuous monitoring,
and emergency preparedness during and after the procedure.
5. Regulatory Compliance & Accreditation
Viezec adheres to both local and international medical regulations, ensuring ethical, transparent and safe treatment practices at every stage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some of the most common questions about stem cell therapy at Viezec.
What is stem cell therapy?
Stem cell therapy uses regenerative cells to repair damaged tissues and improve function.
Is the procedure painful?
Most procedures are minimally invasive and local anesthesia or sedation ensures comfort.
How long does it take to recover?
Recovery varies per patient and treatment area, but most can resume daily activities within days to weeks.
Are there any side effects?
Side effects are usually mild, such as temporary soreness, swelling, or fatigue. Serious complications are rare.
When will I see results?
Some patients notice improvement within weeks, while full regenerative effects may take several months.
Is stem cell therapy safe?
At Viezec, all procedures follow strict clinical protocols, quality standards and regulatory guidelines to ensure safety.
Ready to Begin Your Stem Cell Therapy Journey?
Our expert medical team at Viezec is here to guide you every step of the way. Get personalized guidance, schedule your consultation and take the first step towards better health today.
Schedule Your Consultation
Trusted by 500+ patients from 20+ countries
This website uses cookies to improve your experience. If you continue to use this site, you agree with it.
Ok