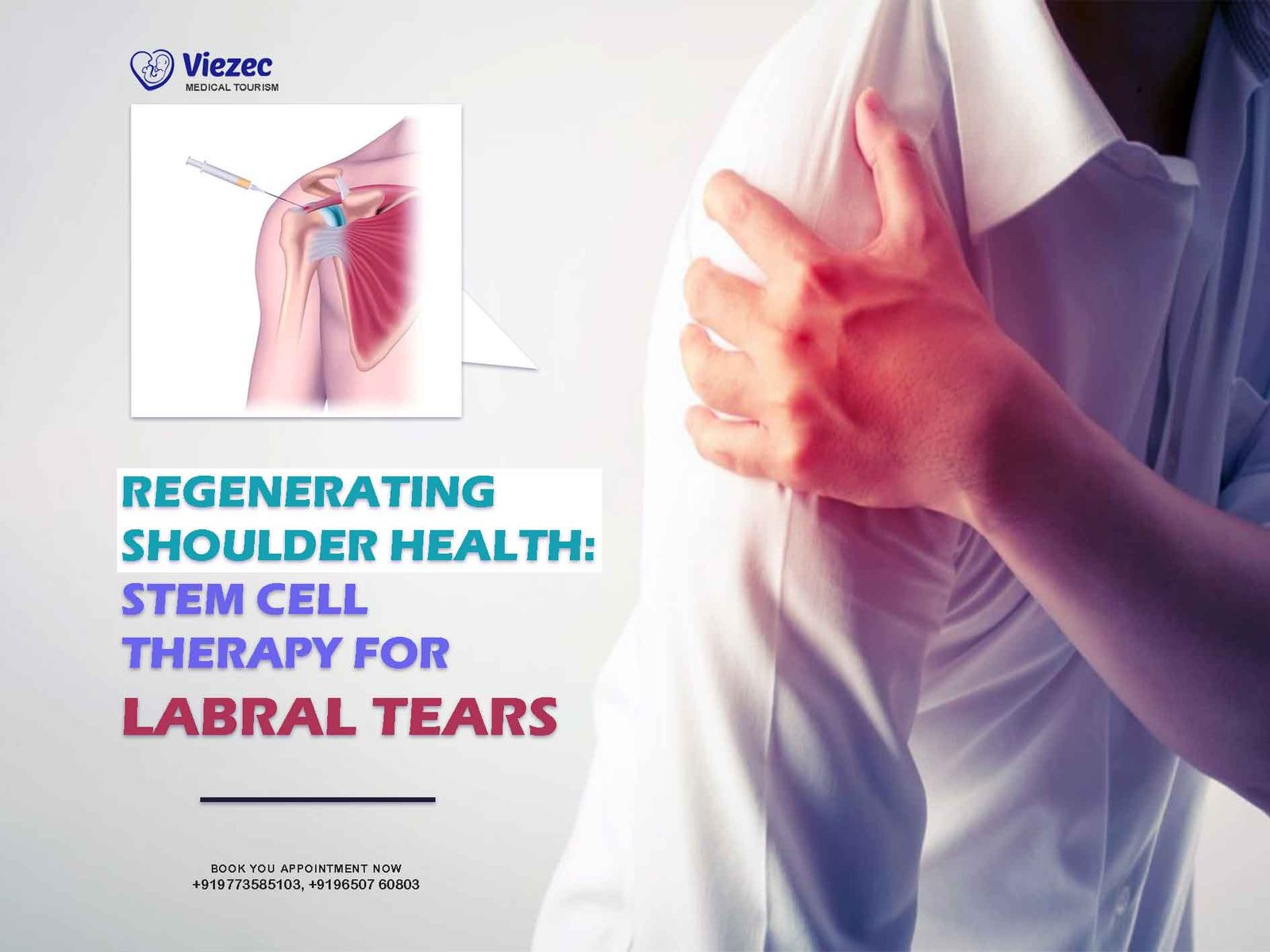
Shoulder injuries, particularly labral tears, can be debilitating and severely impact one’s quality of life. The labrum is a crucial structure in the shoulder joint, providing stability and support to the ball and socket joint. When the labrum is torn, whether due to trauma, overuse, or degeneration, it can lead to pain, limited range of motion, and instability.
Traditional treatments for labral tears often involve physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, corticosteroid injections, and in severe cases, surgery. However, these approaches may not always provide satisfactory results and can come with risks and long recovery periods.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in regenerative medicine approaches for treating shoulder injuries, including stem cell therapy. Stem cells have the remarkable ability to differentiate into various cell types and promote tissue repair and regeneration. This article explores the potential of stem cell therapy in regenerating shoulder health, particularly focusing on labral tears.
Understanding Labral Tears
Anatomy of the Shoulder Labrum
The shoulder is a complex joint composed of the humerus (upper arm bone), scapula (shoulder blade), and clavicle (collarbone). The head of the humerus fits into the shallow socket of the scapula, forming a ball-and-socket joint known as the glenohumeral joint. The labrum is a ring of fibrous cartilage that surrounds the glenoid (the shallow socket of the scapula) and deepens its surface, providing stability to the joint.
Causes and Symptoms of Labral Tears
Labral tears can occur due to acute trauma, such as a fall or direct blow to the shoulder, or from repetitive stress and overuse, common in athletes who engage in overhead activities like throwing or swimming. Degenerative changes in the shoulder joint, as seen in conditions like osteoarthritis, can also predispose individuals to labral tears.
Symptoms of a labral tear may include:
- Shoulder pain: Often described as a deep ache in the shoulder joint.
- Catching or locking sensation: Especially during certain movements of the arm.
- Decreased range of motion: Difficulty reaching overhead or behind the back.
- Shoulder instability: Feeling as if the shoulder may pop out of joint.
Conventional Treatments for Labral Tears
Conservative Management
Initial treatment for labral tears typically involves conservative measures aimed at reducing pain and inflammation and improving shoulder function. This may include rest, activity modification, physical therapy exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding the shoulder joint, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to alleviate pain and swelling.
Corticosteroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections into the shoulder joint can provide temporary relief by reducing inflammation and pain. However, repeated corticosteroid injections may weaken the surrounding tissues and increase the risk of further injury.
Surgical Intervention
For severe or persistent labral tears that do not respond to conservative treatments, surgical intervention may be necessary. Arthroscopic surgery, a minimally invasive procedure, is commonly performed to repair or remove the torn portion of the labrum. In some cases, the surgeon may also address other issues contributing to shoulder instability, such as repairing ligaments or tightening the joint capsule.
Limitations of Traditional Treatments
While traditional treatments like physical therapy and surgery can be effective for many patients with labral tears, they are not without limitations.
Limited Success Rates
Surgical outcomes for labral repair can vary, and some patients may continue to experience pain and limited function despite undergoing surgery. Additionally, the recovery period following surgery can be lengthy, requiring weeks to months of rehabilitation.
Risk of Complications
As with any surgical procedure, there are inherent risks associated with arthroscopic shoulder surgery, including infection, nerve injury, and stiffness. Moreover, the success of surgery relies on the ability of the repaired tissue to heal properly, which may not always occur, particularly in cases of extensive damage or poor tissue quality.
Degenerative Changes
In some cases, labral tears are accompanied by degenerative changes in the shoulder joint, such as osteoarthritis. Traditional treatments may not address these underlying degenerative processes, leading to continued joint deterioration and symptoms over time.
The Promise of Stem Cell Therapy
What Are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells capable of self-renewal and differentiation into various cell types. They can be found in various tissues throughout the body, including bone marrow, adipose tissue (fat), and umbilical cord blood.
Mechanisms of Action
Stem cell therapy for labral tears harnesses the regenerative potential of stem cells to promote tissue repair and regeneration within the injured shoulder joint. The mechanisms by which stem cells exert their therapeutic effects include:
- Differentiation: Stem cells can differentiate into chondrocytes, the cells responsible for producing cartilage, thereby aiding in the repair of damaged labral tissue.
- Paracrine Signaling: Stem cells secrete bioactive molecules such as growth factors, cytokines, and extracellular vesicles, which modulate inflammation, promote angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), and stimulate the proliferation and migration of endogenous repair cells.
- Immunomodulation: Stem cells have immunomodulatory properties, helping to dampen excessive inflammation and promote a favorable environment for tissue healing.
Sources of Stem Cells
Stem cells used for shoulder regeneration can be obtained from various sources, including:
- Bone Marrow: Bone marrow aspirate contains mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) capable of differentiating into bone, cartilage, and fat cells.
- Adipose Tissue: Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) can be isolated from fat tissue obtained through liposuction.
- Umbilical Cord Blood: Umbilical cord blood contains hematopoietic stem cells as well as MSCs with regenerative potential.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Stem Cell Therapy for Labral Tears
Preclinical Studies
Animal studies investigating the efficacy of stem cell therapy for labral tears have shown promising results. For example, research using animal models of shoulder injury has demonstrated that intra-articular injection of MSCs can improve tissue healing, reduce inflammation, and enhance joint function.
Clinical Trials
While clinical research on stem cell therapy for labral tears is still in its early stages, several small-scale clinical trials have provided preliminary evidence of its safety and potential efficacy. These studies have reported improvements in pain, function, and radiographic findings following stem cell treatment for various shoulder conditions, including labral tears.
Case Studies
Numerous case studies and anecdotal reports have described favorable outcomes in patients treated with stem cell therapy for labral tears. These cases often involve individuals who have failed to respond to conventional treatments or are seeking alternatives to surgery. While individual cases do not provide conclusive evidence, they contribute to the growing body of clinical experience supporting the use of stem cells in shoulder regeneration.
Considerations and Challenges
Patient Selection
Not all patients with labral tears may be suitable candidates for stem cell therapy. Factors such as the extent of the tear, the presence of underlying joint pathology, and the patient’s overall health and lifestyle factors must be carefully considered when determining candidacy for treatment.
Treatment Protocol
The optimal treatment protocol for stem cell therapy in shoulder regeneration has yet to be standardized. Variables such as the source of stem cells, the method of delivery (e.g., intra-articular injection, surgical implantation), and the adjunctive use of growth factors or scaffolds may influence treatment outcomes.
Regulatory Considerations
Stem cell therapy falls within the realm of regenerative medicine, which is subject to regulatory oversight aimed at ensuring patient safety and treatment efficacy. Clinicians and researchers must adhere to applicable regulatory guidelines and obtain appropriate approvals when using stem cell-based interventions in clinical practice or research studies.
Cost and Accessibility
Stem cell therapy for labral tears may not be covered by health insurance plans and can be costly, potentially limiting access for some patients. Moreover, access to specialized clinics or providers offering stem cell treatments may be limited in certain geographic regions.
Make informed Decision
Labral tears pose significant challenges in terms of diagnosis and management, often requiring a multifaceted approach to treatment. While traditional treatments such as physical therapy and surgery have their place in managing these injuries, there is growing interest in the potential of stem cell therapy to regenerate damaged shoulder tissue and improve patient outcomes.
Despite the need for further research and standardization of treatment protocols, stem cell therapy holds promise as a promising avenue for enhancing shoulder health and function in individuals with labral tears. By harnessing the regenerative properties of stem cells, clinicians and researchers aim to revolutionize the management of shoulder injuries and provide patients with safer, more effective treatment options.