Stem cells are remarkable biological entities with the potential to develop into various cell types in the body. They possess self-renewal capabilities, enabling them to proliferate and differentiate into specialized cells, such as muscle, nerve, or blood cells, among others. This inherent plasticity makes them promising candidates for regenerative medicine applications.
Types of Stem Cells Used in Therapy
In stem cell therapy for lymphedema, various types of stem cells are utilized, including embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and adult stem cells. Each type offers distinct advantages and challenges concerning proliferation, differentiation potential, and immunogenicity, influencing their suitability for therapeutic use.
Mechanisms of Stem Cell Therapy
The therapeutic efficacy of stem cells in treating lymphedema is attributed to their multifaceted mechanisms of action. These include paracrine signaling, immunomodulation, and differentiation into lymphatic endothelial cells, which collectively promote tissue regeneration and lymphatic network repair.
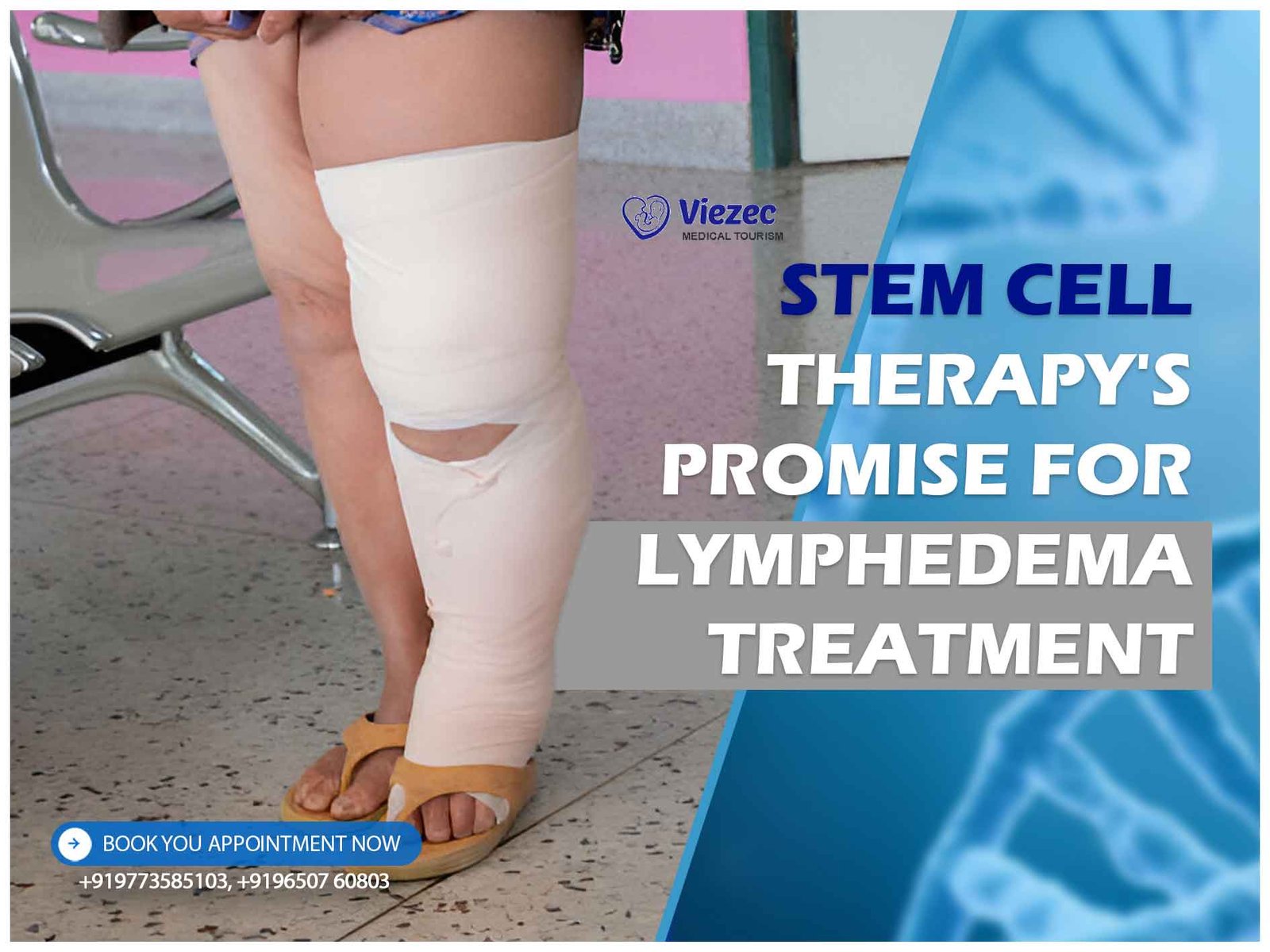
Lymphedema: Causes and Symptoms
Definition and Classification of Lymphedema
Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by the accumulation of lymph fluid in interstitial spaces, resulting in tissue swelling and dysfunction of the lymphatic system. It can be categorized as primary, arising from congenital abnormalities, or secondary, triggered by injury, infection, or cancer treatment.
Primary and Secondary Causes
Primary lymphedema often stems from genetic mutations affecting lymphatic development or function, whereas secondary lymphedema commonly arises following surgical interventions, radiation therapy, or infection that disrupt lymphatic drainage pathways.
Clinical Manifestations of Lymphedema
The clinical presentation of lymphedema varies in severity and may include swelling, discomfort, impaired limb mobility, recurrent infections, and fibrotic changes in affected tissues. These symptoms can significantly impact patients’ quality of life and necessitate comprehensive management strategies.
Current Treatment Challenges
Limitations of Traditional Approaches
Conventional treatment modalities for lymphedema, such as compression therapy, physical rehabilitation, and lymphatic drainage massage, aim to alleviate symptoms and prevent disease progression. However, they often provide only symptomatic relief and fail to address underlying lymphatic dysfunction effectively.
Persistent Symptoms and Recurrence Rates
Despite ongoing advancements in lymphedema management, many patients continue to experience persistent symptoms and face the risk of disease recurrence, especially following cancer-related surgeries or lymph node dissection. This highlights the need for more efficacious and durable therapeutic interventions.
Need for Alternative Therapeutic Strategies
The complex pathophysiology of lymphedema underscores the importance of exploring alternative therapeutic approaches that target fundamental mechanisms of disease progression, such as impaired lymphangiogenesis, chronic inflammation, and fibrotic tissue remodeling.
Stem Cell Therapy: Rationale and Potential
Regenerative Properties of Stem Cells
Stem cells possess unique regenerative capabilities, enabling them to repair damaged tissues and promote neovascularization and lymphangiogenesis. By secreting growth factors, cytokines, and extracellular matrix components, they create a conducive microenvironment for tissue regeneration.
Targeting Lymphatic Regeneration
In the context of lymphedema, stem cell therapy offers a promising strategy for stimulating lymphatic vessel formation and restoring functional lymphatic drainage. By enhancing lymphangiogenesis and modulating immune responses, stem cells can mitigate tissue fibrosis and improve lymphedema-associated symptoms.
Potential Advantages Over Conventional Treatments
Compared to traditional therapeutic modalities, stem cell-based approaches hold several potential advantages, including their ability to address underlying pathophysiological processes, promote tissue regeneration, and offer long-lasting therapeutic effects. Moreover, they can be tailored to individual patient needs, optimizing treatment outcomes.
Preclinical Studies and Experimental Models
Animal Models of Lymphedema
Preclinical studies utilizing animal models have provided valuable insights into the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapies for lymphedema. These models, including rodent and large animal models, allow researchers to evaluate treatment outcomes, mechanisms of action, and long-term effects in a controlled laboratory setting.
Efficacy and Safety Assessments
Experimental investigations have demonstrated the therapeutic potential of stem cell-based interventions in ameliorating lymphedema-related symptoms and promoting tissue regeneration. Moreover, rigorous safety assessments ensure the translatability of preclinical findings to clinical applications, minimizing potential risks to patients.
Insights into Stem Cell Behavior in Lymphatic Tissues
Understanding the behavior and fate of transplanted stem cells within lymphatic tissues is crucial for optimizing treatment protocols and enhancing therapeutic efficacy. Advances in imaging techniques and molecular tracking methods enable researchers to monitor cell survival, migration, and integration into host tissues with high precision.
Clinical Trials and Evidence
Overview of Clinical Trials
Clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapy for lymphedema have shown promising results, with improvements in limb volume reduction, symptom relief, and functional outcomes observed in treated patients. These trials encompass diverse patient populations and utilize various stem cell sources and delivery methods.
Patient Selection Criteria
Effective patient selection criteria are essential for identifying individuals who are most likely to benefit from stem cell therapy while minimizing potential risks and complications. Factors such as disease severity, treatment history, comorbidities, and patient preferences are carefully considered to optimize treatment outcomes.
Reported Outcomes and Long-Term Effects
Long-term follow-up data from clinical trials provide valuable insights into the durability and safety of stem cell-based interventions for lymphedema. While short-term improvements in symptoms and quality of life are commonly reported, sustained therapeutic effects and the prevention of disease progression remain areas of active investigation.
Mechanistic Insights into Stem Cell Therapy
Immunomodulatory Effects
Stem cells exert potent immunomodulatory effects by modulating inflammatory responses, suppressing immune cell activation, and promoting tissue repair and regeneration. These immunomodulatory properties play a crucial role in attenuating chronic inflammation and fibrosis associated with lymphedema pathology.
Angiogenic and Lymphangiogenic Pathways
Stem cells facilitate neovascularization and lymphangiogenesis through the secretion of pro-angiogenic and lymphangiogenic factors, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF), and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). By enhancing vascular and lymphatic network remodeling, they restore tissue homeostasis and improve lymphatic function.
Interactions with Host Tissue Microenvironment
The interaction between transplanted stem cells and the host tissue microenvironment influences treatment outcomes and therapeutic efficacy. Factors such as hypoxia, inflammation, and extracellular matrix remodeling modulate stem cell behavior, engraftment, and differentiation, highlighting the importance of optimizing tissue-specific niche conditions for successful regeneration.
Engineering Approaches and Biomaterials
Scaffold-Based Delivery Systems
Scaffold-based delivery systems provide a supportive framework for stem cell transplantation, facilitating cell retention, localization, and integration within target tissues. These biomaterial scaffolds can be engineered to mimic the native extracellular matrix, promoting cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation in vivo.
Bioengineered Stem Cell Constructs
Bioengineered stem cell constructs combine stem cells with biomaterial scaffolds and bioactive factors to enhance therapeutic efficacy and tissue regeneration. By creating controlled microenvironments that mimic physiological conditions, these constructs optimize cell viability, functionality, and engraftment, improving treatment outcomes in preclinical and clinical settings.
Enhancing Cell Survival and Engraftment
Strategies to enhance stem cell survival and engraftment in vivo include genetic modifications, preconditioning techniques, and the use of pro-survival factors and cytokines. By increasing cell viability and retention at the transplantation site, these approaches maximize the therapeutic potential of stem cell-based therapies for lymphedema and other regenerative medicine applications.
Regulatory Considerations and Future Directions
Regulatory Landscape for Stem Cell Therapies
The regulatory oversight of stem cell therapies for lymphedema involves ensuring patient safety, treatment efficacy, and adherence to ethical standards. Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA and EMA, evaluate preclinical data, clinical trial protocols, and manufacturing processes to assess the quality, safety, and effectiveness of investigational treatments.
Translational Challenges and Opportunities
Translating promising preclinical findings into clinically viable therapies poses significant challenges, including standardizing cell manufacturing processes, optimizing delivery methods, and demonstrating long-term safety and efficacy in human trials. Collaborative efforts between academia, industry, and regulatory bodies are essential for overcoming these hurdles and advancing stem cell-based interventions to clinical practice.
Future Prospects and Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies, such as genome editing, tissue engineering, and cell reprogramming, hold promise for enhancing the therapeutic potential of stem cell-based therapies for lymphedema and other lymphatic disorders. By harnessing the power of interdisciplinary research and innovation, researchers aim to develop personalized and precision medicine approaches that address the diverse needs of patients with lymphatic diseases.
Patient Perspectives and Ethical Issues
Patient Expectations and Decision-Making
Patients with lymphedema often face complex treatment decisions, balancing potential benefits, risks, and uncertainties associated with stem cell therapy. Informed consent processes play a crucial role in ensuring patient autonomy, understanding, and participation in clinical trials, fostering transparent communication and shared decision-making between healthcare providers and patients.
Informed Consent and Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations surrounding stem cell therapy for lymphedema encompass issues of patient safety, privacy, equity, and access to investigational treatments. Transparent communication, comprehensive risk-benefit assessments, and adherence to ethical guidelines are paramount to safeguarding patient welfare and upholding ethical principles in research and clinical practice.
Balancing Risks and Benefits in Clinical Practice
Clinicians must weigh the potential risks and benefits of stem cell therapy against alternative treatment options and patients’ individual circumstances. Ethical dilemmas may arise concerning treatment prioritization, resource allocation, and equitable access to innovative therapies, necessitating thoughtful deliberation and ethical decision-making within healthcare systems.
Summary of Key Findings
Stem cell therapy holds significant promise for the treatment of lymphedema, offering regenerative and immunomodulatory benefits that address underlying pathophysiological mechanisms. Preclinical studies and clinical trials have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of stem cell-based interventions in improving lymphatic function, reducing limb swelling, and enhancing patient quality of life.
Implications for Lymphedema Management
The integration of stem cell therapy into multimodal treatment approaches has the potential to revolutionize lymphedema management, providing more effective and durable solutions for patients with refractory symptoms or recurrent disease. By targeting lymphatic regeneration and tissue repair, stem cell-based interventions offer hope for alleviating the burden of this debilitating condition.
Further Research and Collaboration
Future research endeavors should focus on elucidating the optimal cell sources, delivery methods, and treatment protocols for maximizing the therapeutic potential of stem cell therapy in lymphedema. Collaborative efforts across disciplines, including stem cell biology, tissue engineering, and clinical medicine, are essential for advancing translational research and bringing innovative therapies from bench to bedside.