Sleep apnea is a prevalent sleep disorder characterized by interruptions in breathing during sleep, leading to fragmented sleep and diminished oxygenation. It affects millions of people worldwide, with significant implications for health and quality of life. While current treatments such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines and oral appliances offer relief for many, they are not always effective or well-tolerated. As such, there is a pressing need for alternative therapies that can address the underlying causes of sleep apnea and provide long-lasting solutions. In recent years, stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising approach that holds the potential to revolutionize the treatment of sleep apnea.
Understanding Sleep Apnea
Before delving into the potential of stem cell therapy, it is essential to grasp the mechanisms underlying sleep apnea. The disorder is broadly classified into two main types: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA). OSA, the more common form, occurs when the muscles in the throat relax excessively during sleep, leading to a partial or complete blockage of the airway. CSA, on the other hand, results from a malfunction in the brain’s respiratory control center, causing the cessation of breathing during sleep.
Both forms of sleep apnea can have serious consequences if left untreated. Chronic sleep deprivation and oxygen deprivation associated with sleep apnea have been linked to a range of health problems, including hypertension, cardiovascular disease, stroke, diabetes, and cognitive impairment. Additionally, the disrupted sleep patterns experienced by individuals with sleep apnea can lead to daytime fatigue, irritability, and impaired concentration, significantly impacting their quality of life.
Challenges with Current Treatments
While CPAP therapy is considered the gold standard for treating sleep apnea, it is not without its drawbacks. Many patients find CPAP masks uncomfortable and claustrophobic, leading to poor compliance and treatment abandonment. Oral appliances, which reposition the jaw to keep the airway open during sleep, are another option for those who cannot tolerate CPAP. However, they may not be effective for all patients, particularly those with severe OSA.
Surgical interventions such as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) and maxillomandibular advancement (MMA) aim to widen the airway by removing excess tissue or repositioning the jaw. While these procedures can be effective for some individuals, they are invasive and carry risks such as pain, bleeding, infection, and changes in facial structure.
Given the limitations of current treatments, researchers have been exploring alternative approaches to address the root causes of sleep apnea and provide more effective and patient-friendly solutions.
Promise of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy has emerged as a cutting-edge approach with the potential to revolutionize the treatment of sleep apnea. Stem cells are unique cells with the ability to differentiate into various cell types and repair damaged tissues. By harnessing the regenerative capabilities of stem cells, researchers aim to target the underlying structural and functional abnormalities associated with sleep apnea, offering the promise of long-lasting relief and improved quality of life for patients.
How Stem Cell Therapy Works
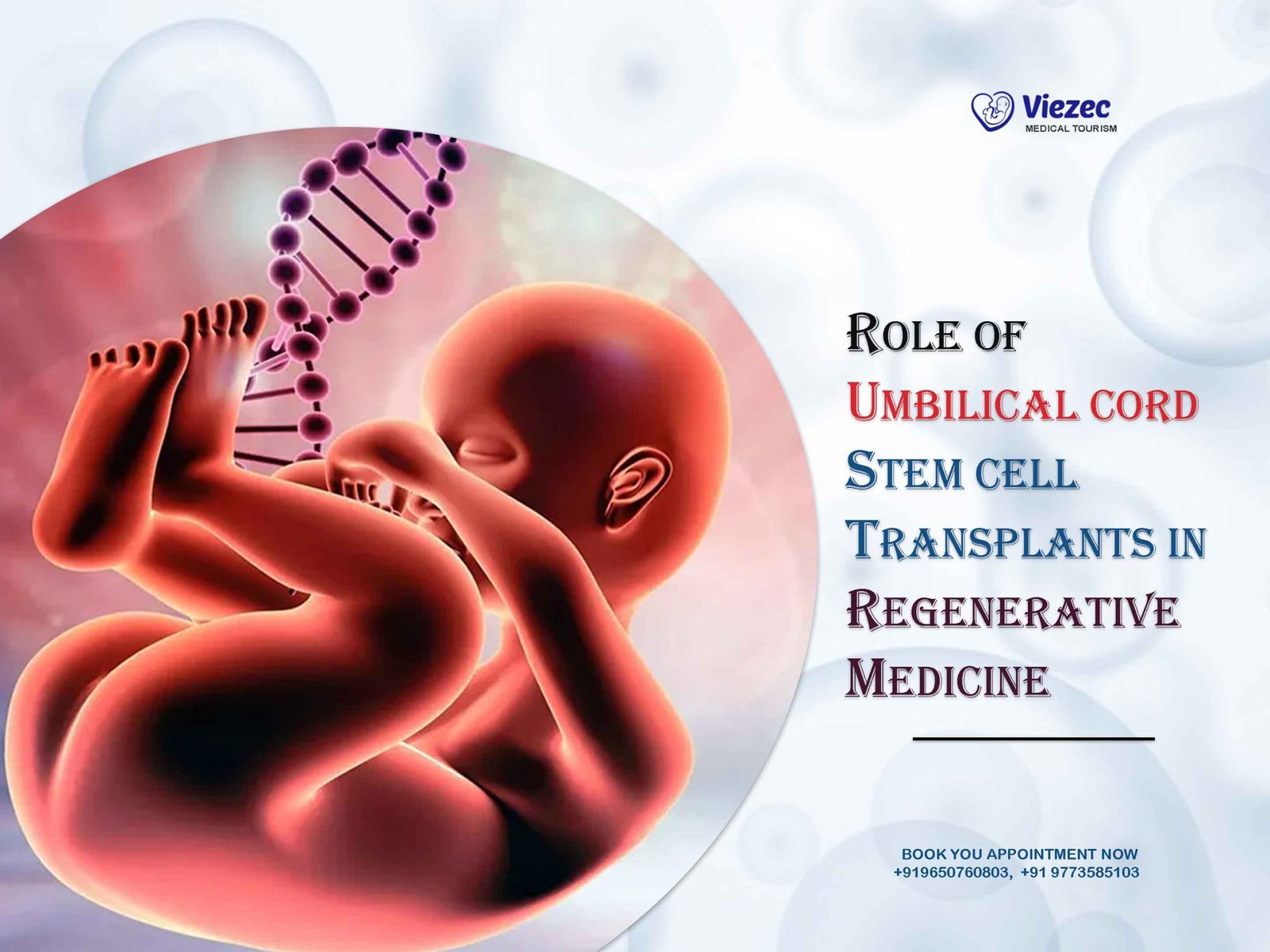
The concept behind stem cell therapy for sleep apnea is relatively straightforward. Stem cells can be derived from various sources, including bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood. Once harvested, these stem cells can be processed and prepared for therapeutic use.
In the context of sleep apnea, researchers are exploring two main approaches to stem cell therapy:
- Tissue Regeneration: Stem cells are injected directly into the tissues of the upper airway, where they differentiate into specialized cell types and promote tissue repair and regeneration. This approach aims to address structural abnormalities such as airway narrowing and tissue collapse that contribute to OSA.
- Neuromodulation: Stem cells are delivered to the brainstem or peripheral nerves involved in respiratory control, where they exert neuroprotective and neuroregenerative effects. By enhancing neural signaling and function, this approach aims to restore normal breathing patterns and mitigate the central components of sleep apnea.
Advantages of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy offers several advantages over traditional treatments for sleep apnea:
- Regenerative Potential: Unlike symptomatic treatments such as CPAP therapy, which merely alleviate symptoms, stem cell therapy has the potential to address the underlying structural and functional abnormalities associated with sleep apnea, offering the possibility of long-term cure or remission.
- Minimally Invasive: Stem cell therapy can be performed using minimally invasive techniques, such as transnasal or transoral delivery, reducing the risk of complications and speeding up recovery compared to traditional surgical interventions.
- Personalized Treatment: Stem cell therapy can be tailored to individual patients based on factors such as disease severity, anatomical characteristics, and underlying health conditions, maximizing the likelihood of therapeutic success.
Preclinical and Clinical Studies
Early preclinical studies investigating the use of stem cells for sleep apnea have shown promising results. In animal models of OSA, stem cell transplantation has been shown to improve airway patency, reduce inflammation, and enhance respiratory function. These findings have paved the way for clinical trials aimed at evaluating the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapy in humans with sleep apnea.
Make an informed Decision
Sleep apnea is a prevalent sleep disorder with significant implications for health and quality of life. While current treatments offer relief for many patients, they are not always effective or well-tolerated. Stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising approach that holds the potential to address the underlying causes of sleep apnea and provide long-lasting solutions. Through tissue regeneration and neuromodulation, stem cells offer the promise of repairing damaged tissues and restoring normal breathing patterns, offering hope for millions of individuals affected by sleep apnea. While challenges remain, ongoing research efforts are paving the way for the development of safe, effective, and personalized stem cell therapies for sleep apnea, bringing us one step closer to a future where sleep apnea is no longer a chronic condition but a treatable disorder.