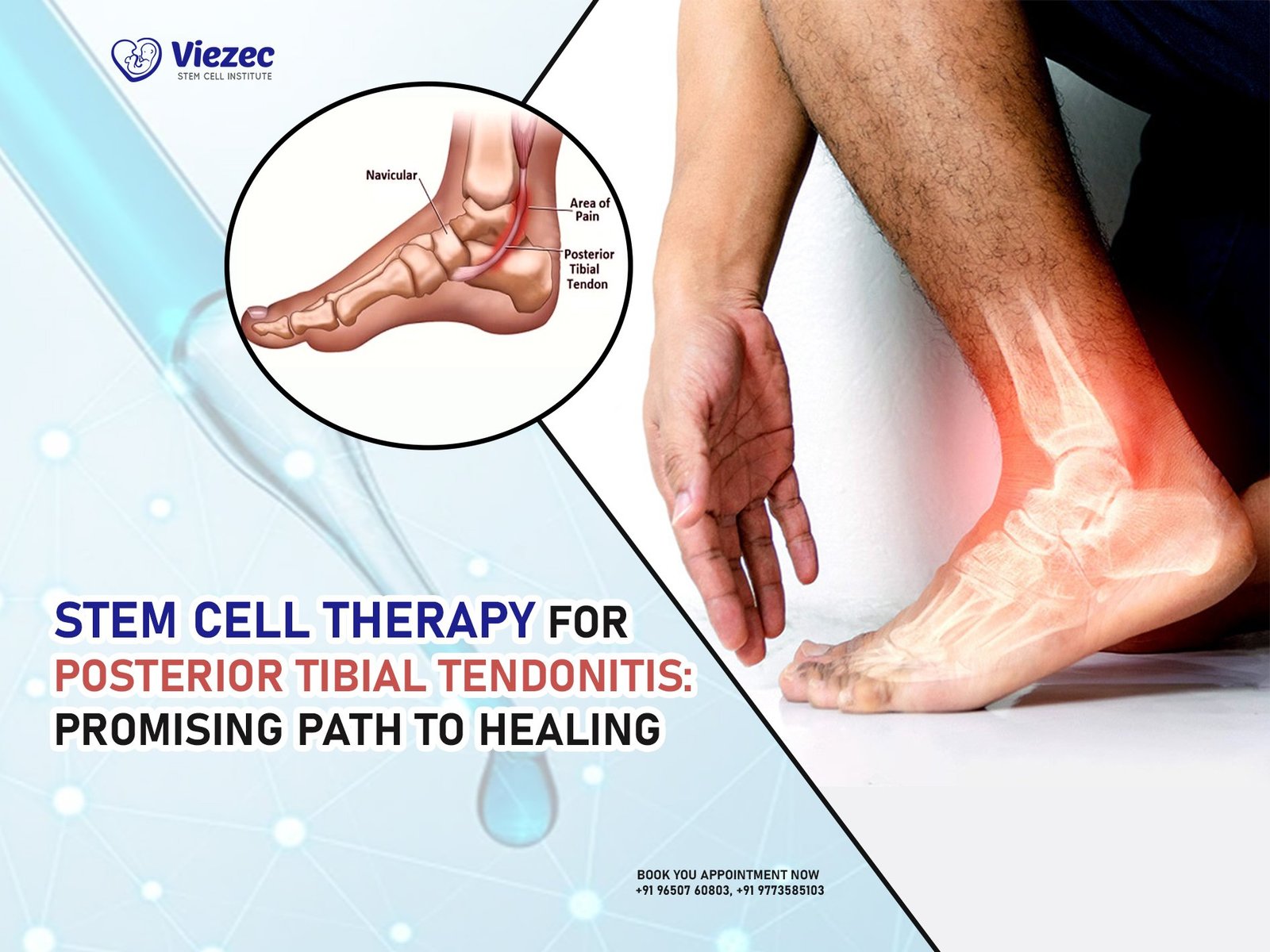
Stem cell transplantation has emerged as a promising therapy for various immune disorders, offering new hope to patients with conditions that were once considered untreatable. Immune disorders encompass a broad range of conditions where the immune system malfunctions, leading to autoimmune diseases, immunodeficiencies, and other related disorders. Traditional treatments often focus on managing symptoms rather than addressing the root cause of the condition. However, stem cell transplantation presents a revolutionary approach by targeting the immune system itself, aiming to restore its balance and functionality. In recent years, significant advancements have been made in this field, paving the way for more effective and safer treatment options.
Understanding Stem Cell Transplantation
Stem cell transplantation involves the infusion of healthy stem cells into a patient’s body to replace damaged or dysfunctional cells. These stem cells possess the unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, including those of the immune system. Depending on the type of immune disorder being treated, different sources of stem cells may be used. Hematopoietic stem cells, found primarily in bone marrow, peripheral blood, and umbilical cord blood, are commonly utilized in immune disorder therapies.
Types of Stem Cell Transplantation
- Autologous Transplantation: In this approach, a patient’s own stem cells are collected and then reinfused after intensive treatment to eradicate abnormal cells. Autologous transplantation is often used in conditions where the immune system needs to be “reset” without the risk of graft rejection.
- Allogeneic Transplantation: Allogeneic transplantation involves using stem cells from a donor, typically a family member or unrelated matched donor. This method is more commonly employed for immune disorders with a genetic basis or those requiring a complete overhaul of the immune system.
- Syngeneic Transplantation: This rare form of transplantation involves using stem cells from an identical twin, minimizing the risk of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), a potentially severe complication where the donor cells attack the recipient’s tissues.
Advancements in Stem Cell Transplantation Techniques
Reduced-Intensity Conditioning Regimens
Traditionally, stem cell transplantation required high-dose chemotherapy or radiation therapy to eliminate the recipient’s existing immune cells, making room for the donor cells to engraft successfully. However, these intensive conditioning regimens often resulted in significant toxicity and adverse effects. Recent advancements have focused on developing reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) regimens, which employ lower doses of chemotherapy and radiation while still allowing for successful engraftment. RIC not only reduces the risk of treatment-related complications but also extends the eligibility of transplantation to older patients and those with comorbidities.
Tolerance Induction Strategies
One of the challenges in stem cell transplantation is the risk of graft rejection or GVHD, where the donor immune cells attack the recipient’s tissues. To mitigate these risks, researchers have been exploring tolerance induction strategies aimed at promoting immune tolerance between the donor and recipient. This includes the use of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and other immune-modulating agents to suppress harmful immune responses while preserving the graft-versus-tumor effect.
Gene Editing Technologies
Advancements in gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR-Cas9, hold immense potential for improving the safety and efficacy of stem cell transplantation. Researchers are exploring the possibility of genetically modifying donor stem cells to enhance their compatibility with the recipient’s immune system, reduce the risk of GVHD, and improve long-term engraftment. Additionally, gene editing techniques can be used to correct genetic mutations underlying certain immune disorders before transplantation, offering a curative approach for these conditions.
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs) as Adjunctive Therapy
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) have emerged as promising adjunctive therapy in stem cell transplantation for immune disorders. MSCs possess immunomodulatory properties and can regulate the activity of various immune cells, thereby promoting tolerance and reducing inflammation. Clinical studies have shown that co-infusion of MSCs with hematopoietic stem cells can improve engraftment rates, reduce GVHD incidence, and enhance overall treatment outcomes.
Clinical Applications and Future Perspectives
Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases
Stem cell transplantation has shown considerable promise in treating autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues. Conditions such as multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and rheumatoid arthritis have been targeted using stem cell transplantation to reset the immune system and halt disease progression. While the outcomes of these treatments vary depending on factors such as disease severity and patient characteristics, many individuals experience long-term remission and improved quality of life following transplantation.
Management of Primary Immunodeficiencies
For patients with primary immunodeficiencies, stem cell transplantation offers a potential cure by providing them with a healthy immune system. Conditions such as severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, and chronic granulomatous disease have been successfully treated with allogeneic stem cell transplantation, allowing patients to lead normal, healthy lives free from recurrent infections and immune dysfunction.
Emerging Therapeutic Targets
As our understanding of immune disorders continues to evolve, researchers are uncovering novel therapeutic targets and treatment approaches for stem cell transplantation. This includes exploring the use of engineered stem cells with enhanced therapeutic properties, developing personalized treatment strategies based on genetic profiling, and investigating the potential of combination therapies involving stem cells and immune-modulating agents. Furthermore, ongoing research into the mechanisms of immune tolerance and immune reconstitution post-transplantation will inform the development of more targeted and effective therapies for a wide range of immune disorders.
Make an informed Decision
Stem cell transplantation represents a groundbreaking approach for treating immune disorders, offering the potential for long-term remission and even cure in many cases. Recent advancements in transplantation techniques, tolerance induction strategies, gene editing technologies, and adjunctive therapies have significantly improved treatment outcomes and expanded the scope of conditions that can be effectively targeted. While challenges such as graft rejection, GVHD, and treatment-related toxicities remain, ongoing research and clinical trials hold promise for further optimizing stem cell transplantation as a safe, curative therapy for immune disorders. As we continue to unravel the complexities of the immune system and refine our therapeutic approaches, stem cell transplantation is poised to revolutionize the field of immunology and transform the lives of patients affected by these debilitating conditions.