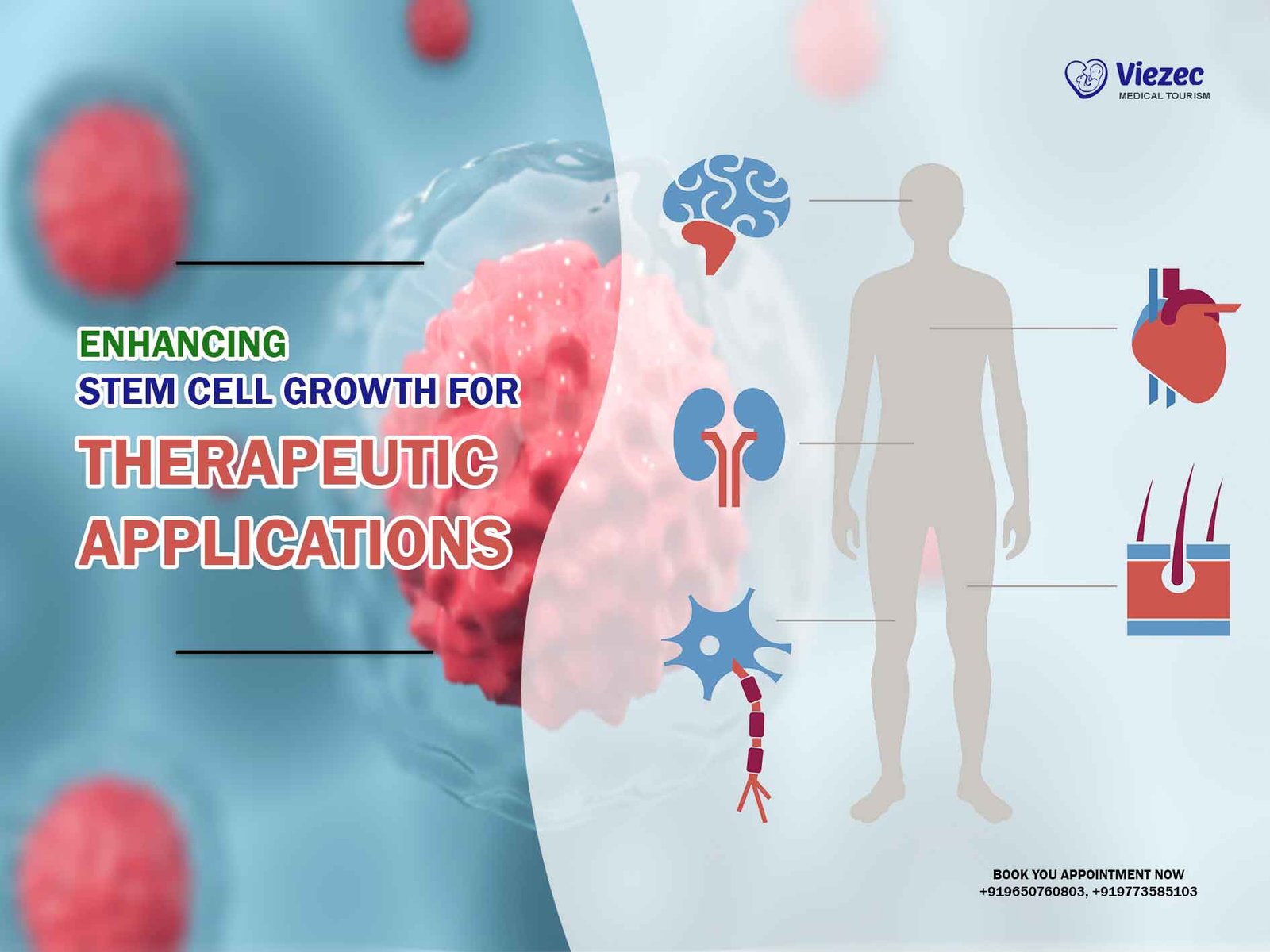
Stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising field in regenerative medicine, offering potential solutions for a wide range of medical conditions. The ability of stem cells to differentiate into various cell types and repair damaged tissues has sparked significant interest in their therapeutic applications. However, the success of stem cell therapy depends largely on selecting the right type of stem cells for a particular condition. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the key considerations that should be taken into account when choosing the right stem cells for therapeutic purposes.
Understanding Stem Cell Types
Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs)
Embryonic stem cells are derived from embryos and have the capacity to differentiate into any cell type in the human body. Their pluripotency makes them highly versatile for regenerative applications. However, ethical concerns surrounding their extraction from embryos have limited their widespread use.
Adult or Somatic Stem Cells
Adult stem cells, also known as somatic or tissue-specific stem cells, exist throughout the body and play a crucial role in tissue repair and regeneration. They are multipotent, meaning they can differentiate into a limited number of cell types. These cells can be isolated from various tissues, including bone marrow, adipose tissue, and the umbilical cord.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
Induced pluripotent stem cells are generated by reprogramming adult cells to revert to a pluripotent state. iPSCs share many characteristics with embryonic stem cells, offering the advantage of pluripotency without the ethical concerns associated with embryonic stem cells. However, challenges such as tumorigenicity and genetic instability must be addressed.
Considerations for Therapeutic Use
Matching the Cell Type to the Condition
Different medical conditions may require different types of stem cells. For instance, disorders affecting the blood may benefit from hematopoietic stem cells derived from bone marrow, while conditions involving the nervous system may require neural stem cells.
Immunogenicity and Compatibility
The immune response triggered by transplanted cells is a critical consideration. Autologous stem cells, derived from the patient’s own body, are less likely to elicit an immune response compared to allogeneic cells from a donor. However, obtaining a sufficient quantity of autologous cells may not always be feasible.
Purity and Potency of Stem Cells
The purity and potency of stem cells are crucial for their effectiveness. Contaminants or improper differentiation can compromise therapeutic outcomes. Rigorous quality control measures must be in place to ensure that the stem cell population is homogeneous and possesses the desired therapeutic potential.
Safety Concerns and Risk of Tumorigenesis
One of the major challenges in stem cell therapy is the risk of tumor formation. Pluripotent stem cells, in particular, have the potential to form teratomas—tumors containing tissues from all three germ layers. Researchers must implement strategies to minimize the risk of tumorigenesis, such as pre-differentiation of cells before transplantation.
Delivery Methods and Engraftment
The method of delivering stem cells to the target tissue or organ is a critical consideration. Factors such as cell viability during transplantation, migration to the target site, and successful engraftment into the host tissue influence the therapeutic efficacy of stem cell treatments.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations
Gene Editing for Precision Medicine
Advancements in gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR-Cas9, have opened new avenues for enhancing the therapeutic potential of stem cells. Precise genetic modifications can be introduced to optimize the functionality and safety of stem cells for specific applications.
Biomaterials and Scaffold Design
Incorporating biomaterials and scaffold design into stem cell therapy can improve cell delivery and support tissue regeneration. Engineered scaffolds provide a physical framework for cells to adhere, proliferate, and differentiate, enhancing the overall success of stem cell treatments.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Regulatory Approval and Compliance
Stem cell therapies are subject to strict regulatory scrutiny to ensure safety and efficacy. Researchers and clinicians must navigate regulatory pathways, including obtaining approvals from regulatory agencies, conducting rigorous clinical trials, and adhering to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for cell production.
Stem Cell Research and Therapy in India
India has emerged as a significant player in the field of stem cell research and therapy. Here’s an overview of the current state of stem cell research in India:
Research and Clinical Trials
- Research Institutions: India is home to several leading research institutions, such as the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), which are actively involved in stem cell research.
- Clinical Trials: India is conducting numerous clinical trials on stem cell-based therapies for conditions such as osteoarthritis, diabetes, and spinal cord injuries.
Ethical Guidelines and Informed Consent
Respecting ethical guidelines is paramount in stem cell research and therapy. Clear and transparent communication with patients regarding the nature of stem cell treatments, potential risks, and alternative options is essential. Informed consent is a cornerstone in ensuring ethical standards are met in stem cell therapies.
Choosing the right stem cells for therapeutic applications involves a nuanced consideration of various factors, from the type of stem cells and their source to the delivery methods and ethical considerations. As research in stem cell biology and regenerative medicine continues to advance, the potential for innovative and effective treatments grows. Researchers, clinicians, and regulatory bodies must work collaboratively to harness the full therapeutic potential of stem cells while ensuring the highest standards of safety, efficacy, and ethical conduct. In navigating the complex landscape of stem cell therapy, a holistic approach that embraces scientific innovation, ethical principles, and regulatory compliance is paramount.