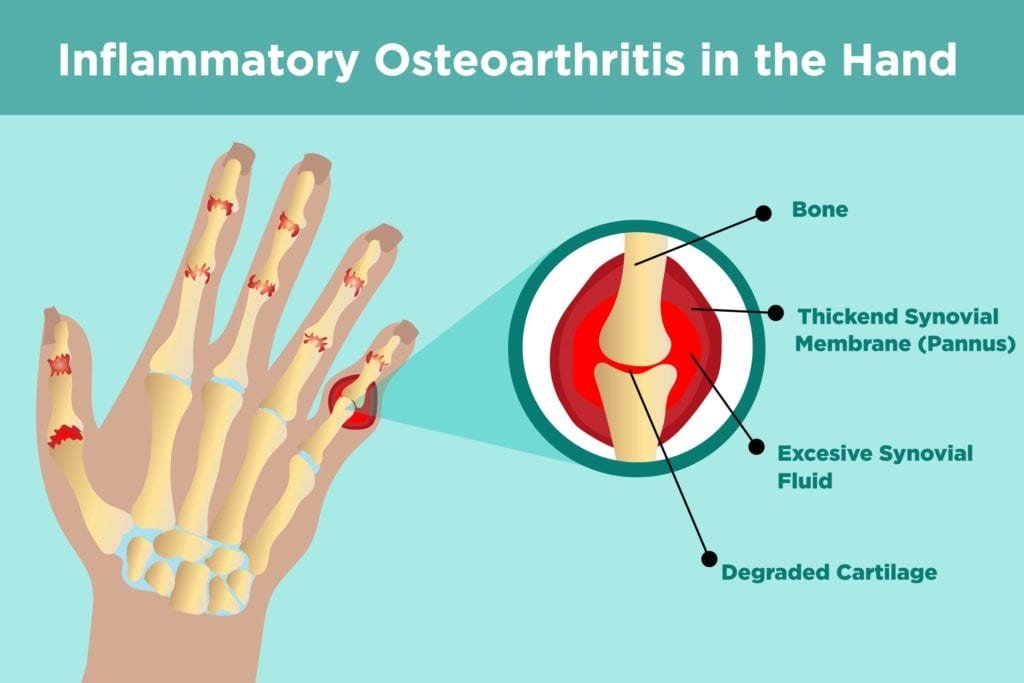
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. It primarily affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and spine, but can impact any joint in the body. The causes of osteoarthritis include age-related wear and tear, genetic predisposition, joint injuries, and repetitive stress on the joints. Inflammation is typically not a significant factor, distinguishing it from other forms of arthritis. Managing osteoarthritis involves a combination of lifestyle changes, physical therapy, medications, and sometimes surgical interventions to alleviate symptoms and improve joint function.
Common symptoms of osteoarthritis include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion. These symptoms tend to worsen with activity and improve with rest. Over time, the joint may lose its normal shape, and bone spurs may develop, contributing to discomfort and limited movement. The progression of osteoarthritis can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, making daily activities more challenging and painful. Early detection and intervention are crucial in managing symptoms effectively and slowing the progression of the disease.
Connection Between Cerebral Palsy and Osteoarthritis
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of disorders affecting movement and muscle tone, often resulting from damage to the developing brain. Individuals with CP frequently experience joint abnormalities and muscle imbalances, which can contribute to the development of osteoarthritis. The abnormal muscle tone and spasticity associated with CP place additional stress on the joints, leading to wear and tear over time. This increased stress can accelerate the degeneration of cartilage, making individuals with CP more susceptible to osteoarthritis at a younger age compared to the general population.
People with CP often exhibit altered gait patterns, joint deformities, and muscle contractures, all of which can exacerbate joint degeneration. The uneven distribution of forces across the joints can lead to increased friction and damage to the cartilage, further contributing to the development of osteoarthritis. Additionally, limited mobility and physical activity in individuals with CP can result in weakened muscles, reducing the joint’s ability to absorb shock and protect against degeneration. Understanding these risk factors is essential for early intervention and effective management of osteoarthritis in individuals with CP.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of osteoarthritis in individuals with cerebral palsy is vital for implementing effective management strategies and preventing further joint damage. Recognizing the symptoms of osteoarthritis early can help individuals seek appropriate medical attention and begin treatment before the condition progresses. Symptoms to watch for include persistent joint pain, especially after activity, joint stiffness in the morning or after periods of inactivity, and swelling around the joints. Decreased range of motion and difficulty performing everyday tasks can also indicate the onset of osteoarthritis.
Diagnostic techniques for osteoarthritis include physical examinations, imaging tests, and laboratory tests. During a physical examination, a healthcare provider will assess the affected joints for tenderness, swelling, and range of motion. Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, and CT scans can provide detailed images of the joint structure, revealing cartilage loss, bone spurs, and joint space narrowing. Laboratory tests may be used to rule out other types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, by analyzing blood samples for specific markers. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing a personalized treatment plan and preventing further joint damage.
The Role of Physical Therapy
Benefits of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing osteoarthritis in individuals with cerebral palsy by improving mobility and alleviating pain. Through targeted exercises and manual therapies, physical therapy can enhance joint function, increase muscle strength, and reduce stiffness. Improved mobility allows individuals to perform daily activities more easily and maintain their independence. Physical therapy also focuses on improving balance and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and further joint injury.
Pain management is another significant benefit of physical therapy. Techniques such as manual therapy, heat and cold therapy, and ultrasound can help alleviate pain and inflammation in the affected joints. Additionally, physical therapists can teach individuals pain-relief techniques and strategies to manage symptoms during daily activities. Regular physical therapy sessions can lead to long-term improvements in joint function and quality of life, making it an essential component of osteoarthritis management for individuals with cerebral palsy.
Types of Physical Therapy
There are various types of physical therapy exercises that can benefit individuals with osteoarthritis and cerebral palsy. Range-of-motion exercises are designed to improve joint flexibility and prevent stiffness. These exercises involve gently moving the joint through its full range of motion, which can help maintain joint function and reduce pain. Strengthening exercises focus on building muscle strength around the affected joints, providing better support and stability. Stronger muscles can absorb more shock and reduce the stress on the joints, slowing the progression of osteoarthritis.
Other types of physical therapy may include aquatic therapy, where exercises are performed in a pool to reduce the impact on the joints, and functional training, which focuses on improving the ability to perform everyday tasks. Physical therapists may also use modalities such as electrical stimulation, ultrasound, and laser therapy to reduce pain and inflammation. A comprehensive physical therapy program tailored to the individual’s needs and abilities can significantly improve joint health and overall well-being.
Creating a Physical Therapy Plan
Creating an effective physical therapy plan involves setting realistic goals and monitoring progress over time. Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For example, a goal might be to increase the range of motion in the knee joint by 10 degrees within three months. Setting achievable goals helps individuals stay motivated and focused on their rehabilitation journey. Regular assessments and adjustments to the plan ensure that the therapy remains effective and aligned with the individual’s progress and needs.
Monitoring progress involves tracking improvements in joint function, pain levels, and overall mobility. Physical therapists use various tools and techniques to assess progress, such as range-of-motion measurements, strength tests, and patient-reported outcome measures. Regular feedback sessions allow individuals to discuss their experiences, challenges, and achievements with their therapist, ensuring that the therapy plan remains personalized and effective. Consistent monitoring and goal setting are essential for achieving long-term success in managing osteoarthritis through physical therapy.
Exercise and Movement
Low-Impact Exercises
Low-impact exercises are particularly beneficial for individuals with osteoarthritis and cerebral palsy, as they minimize stress on the joints while promoting physical activity and overall health. Swimming is an excellent low-impact exercise that provides a full-body workout without putting excessive pressure on the joints. The buoyancy of water supports the body, reducing the impact on the joints and allowing for a greater range of motion. Swimming can improve cardiovascular fitness, muscle strength, and joint flexibility, making it an ideal exercise for managing osteoarthritis.
Cycling is another low-impact exercise that can help improve joint function and overall fitness. Stationary cycling or using a recumbent bike can provide a cardiovascular workout while reducing stress on the knees and hips. Cycling strengthens the muscles around the joints, improves balance and coordination, and enhances overall mobility. Incorporating low-impact exercises into a regular fitness routine can help individuals with osteoarthritis maintain joint health and reduce pain and stiffness.
Stretching Routines
Stretching is a vital component of managing osteoarthritis and maintaining joint flexibility. Daily stretching practices can help reduce stiffness, improve range of motion, and prevent muscle imbalances. Gentle stretches targeting the affected joints should be performed regularly, holding each stretch for 15-30 seconds without bouncing. Stretching should be done after a warm-up or physical activity when the muscles are more pliable. Incorporating stretching into a daily routine can help individuals with osteoarthritis maintain joint function and reduce pain.
Stretching aids, such as resistance bands and foam rollers, can enhance stretching routines by providing additional support and resistance. Resistance bands can be used to perform gentle stretching exercises, improving flexibility and muscle strength. Foam rollers can be used for self-myofascial release, a technique that targets tight muscles and fascia to reduce tension and improve mobility. Using stretching aids can make stretching routines more effective and enjoyable, helping individuals with osteoarthritis achieve better joint health and overall well-being.
Importance of Consistency
Consistency is key to achieving long-term benefits from exercise and movement in managing osteoarthritis. Developing a regular exercise routine helps individuals build habits and maintain joint health. Consistent exercise can improve muscle strength, joint flexibility, and overall fitness, reducing pain and enhancing quality of life. It is essential to find a balance between staying active and avoiding overexertion, as excessive exercise can exacerbate joint pain and damage. A well-planned exercise routine tailored to individual needs and abilities can provide significant benefits in managing osteoarthritis.
Tracking improvements is an essential aspect of maintaining consistency and motivation. Keeping a journal or using a fitness app to record exercise routines, progress, and symptoms can help individuals stay on track and monitor their achievements. Regularly reviewing progress with a healthcare provider or physical therapist can provide valuable feedback and encouragement. Celebrating milestones and setting new goals can help individuals stay motivated and committed to their exercise routine, leading to better long-term outcomes in managing osteoarthritis.
Nutrition and Weight Management
Nutritional Needs
Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in managing osteoarthritis and overall health. Anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce inflammation and alleviate joint pain. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, have anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit individuals with osteoarthritis. Incorporating a variety of fruits and vegetables, particularly those high in antioxidants like berries, leafy greens, and tomatoes, can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation. Whole grains, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins are also essential components of a balanced diet that supports joint health.
Vitamins and minerals are vital for maintaining healthy joints and cartilage. Vitamin D and calcium are essential for bone health, while vitamin C plays a role in collagen formation, a key component of cartilage. Other important nutrients include vitamin E, which has antioxidant properties, and magnesium, which helps maintain muscle and nerve function. A well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods can support joint health and overall well-being
, helping individuals manage osteoarthritis more effectively.
Weight Management Strategies
Maintaining a healthy weight is critical for individuals with osteoarthritis, as excess weight can put additional stress on the joints, exacerbating pain and damage. Healthy eating habits, such as portion control, eating balanced meals, and avoiding processed foods, can help individuals achieve and maintain a healthy weight. Incorporating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into the diet can provide essential nutrients without excessive calories. Staying hydrated and limiting sugary beverages and snacks can also support weight management and overall health.
Regular physical activity is another key component of weight management. Engaging in low-impact exercises, strength training, and cardiovascular activities can help burn calories, build muscle, and improve overall fitness. Combining physical activity with healthy eating habits can lead to sustainable weight loss and better joint health. It is essential to find enjoyable and accessible activities to stay motivated and maintain a regular exercise routine. Consulting with a healthcare provider or dietitian can provide personalized guidance and support for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
Consulting a Dietitian
Consulting a dietitian can provide valuable insights and personalized recommendations for managing osteoarthritis through nutrition. A dietitian can help individuals develop personalized diet plans that address their specific needs and preferences. These plans may include anti-inflammatory foods, appropriate portion sizes, and strategies for maintaining a healthy weight. A dietitian can also provide guidance on managing dietary restrictions and ensuring that individuals receive all the necessary nutrients for optimal joint health and overall well-being.
Monitoring nutritional intake is essential for maintaining a balanced diet and achieving health goals. A dietitian can help individuals track their food intake, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments to their diet plans. Regular check-ins with a dietitian can provide ongoing support and motivation, ensuring that individuals stay on track with their nutrition goals. Collaborating with a dietitian can enhance the effectiveness of dietary strategies in managing osteoarthritis and improving overall health.
Pain Management Techniques
Medications and Supplements
Medications and supplements can play a crucial role in managing pain associated with osteoarthritis in individuals with cerebral palsy. Over-the-counter options, such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help alleviate mild to moderate pain and reduce inflammation. These medications are widely accessible and can provide effective relief for many individuals. However, it is important to use them as directed and consult a healthcare provider to avoid potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
Prescription medications may be necessary for individuals with more severe pain or those who do not respond to over-the-counter options. These may include stronger pain relievers, corticosteroids, or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications that target specific symptoms, such as muscle relaxants or antidepressants. Supplements, such as glucosamine and chondroitin, may also provide joint support and reduce pain for some individuals. It is essential to discuss the use of supplements with a healthcare provider to ensure their safety and efficacy.
Non-Medication Approaches
Non-medication approaches can be effective in managing osteoarthritis pain and improving overall quality of life. Heat and cold therapy are simple yet effective methods for reducing pain and inflammation. Applying a warm compress or heating pad can relax muscles and improve blood flow to the affected area, while cold packs can reduce swelling and numb sharp pain. Alternating between heat and cold therapy can provide comprehensive relief for joint pain and stiffness.
Acupuncture is another non-medication approach that can help manage osteoarthritis pain. This traditional Chinese medicine technique involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate the nervous system and promote natural pain relief. Some individuals find significant relief from acupuncture, although its effectiveness can vary from person to person. Other complementary therapies, such as massage, yoga, and tai chi, can also provide pain relief and improve joint function. Exploring various non-medication approaches can help individuals find the most effective strategies for managing their pain.
Developing a Pain Management Plan
Developing a comprehensive pain management plan involves identifying pain triggers and tailoring strategies to address them. Keeping a pain diary can help individuals track their symptoms, identify patterns, and pinpoint activities or conditions that exacerbate pain. This information can be invaluable for developing a personalized pain management plan that addresses specific needs and challenges. Collaborating with healthcare providers, physical therapists, and other professionals can provide additional insights and support in creating an effective plan.
Tailoring strategies to individual needs may include a combination of medications, physical therapy, non-medication approaches, and lifestyle changes. Regularly reviewing and adjusting the pain management plan ensures that it remains effective and responsive to changes in symptoms and needs. Open communication with healthcare providers and a willingness to try different approaches can lead to better pain management and improved quality of life. A well-rounded pain management plan can empower individuals with osteoarthritis to take control of their symptoms and maintain an active and fulfilling life.
Assistive Devices and Modifications
Types of Assistive Devices
Assistive devices can significantly enhance mobility and reduce pain for individuals with osteoarthritis and cerebral palsy. Braces and orthotics are commonly used to support and stabilize affected joints, reducing stress and preventing further damage. Custom-made braces can provide optimal support and comfort, while off-the-shelf options are more accessible and can still offer substantial benefits. Orthotic inserts for shoes can also improve alignment and reduce pain in the lower extremities.
Mobility aids, such as canes, walkers, and wheelchairs, can help individuals with osteoarthritis maintain independence and move around more easily. These devices provide support and stability, reducing the risk of falls and joint strain. Choosing the right mobility aid depends on the individual’s specific needs and level of mobility. Consulting with a healthcare provider or physical therapist can help determine the most appropriate devices for improving mobility and managing osteoarthritis symptoms.
Home Modifications
Making home modifications can create a safer and more accessible living environment for individuals with osteoarthritis. Accessible living spaces can reduce the risk of falls and make daily activities easier to perform. Installing grab bars in the bathroom, using non-slip mats, and ensuring adequate lighting can enhance safety. Rearranging furniture to create clear pathways and reducing clutter can also improve mobility and reduce the risk of accidents.
Ergonomic adjustments, such as using chairs with proper support, adjustable desks, and ergonomic kitchen tools, can reduce joint strain and improve comfort. Simple changes, like using lever handles instead of doorknobs and placing frequently used items within easy reach, can make a significant difference in daily life. Home modifications tailored to the individual’s needs can enhance their ability to perform daily tasks independently and reduce pain and discomfort associated with osteoarthritis.
Utilizing Technology
Technology can provide valuable support for managing osteoarthritis in individuals with cerebral palsy. Various apps for pain management can help individuals track their symptoms, medication use, and physical activity. These apps often include features such as reminders, pain diaries, and educational resources, making it easier to manage osteoarthritis effectively. Using technology to monitor progress and stay organized can enhance the overall management plan.
Wearable devices, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, can provide real-time feedback on physical activity, heart rate, and sleep patterns. These devices can help individuals stay active, set fitness goals, and monitor their progress. Some wearables also offer features like guided breathing exercises and mindfulness practices, which can be beneficial for managing pain and stress. Integrating technology into the daily routine can provide valuable insights and support for individuals managing osteoarthritis.
Psychological and Emotional Support
Coping with Chronic Pain
Coping with chronic pain requires a holistic approach that addresses both physical and emotional well-being. Mindfulness and meditation are effective techniques for managing chronic pain by promoting relaxation and reducing stress. Practicing mindfulness involves focusing on the present moment and accepting one’s experiences without judgment. Meditation techniques, such as deep breathing and guided imagery, can help individuals manage pain and improve their overall sense of well-being.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is another valuable tool for coping with chronic pain. CBT focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to pain and distress. Through CBT, individuals can develop healthier coping strategies and improve their emotional resilience. Working with a trained therapist can provide personalized support and guidance in managing the psychological aspects of chronic pain.
Building a Support Network
Building a strong support network is essential for managing osteoarthritis and maintaining emotional well-being. Family and friends can provide emotional support, practical assistance, and encouragement. Open communication with loved ones about one’s needs and challenges can strengthen relationships and foster a supportive environment. Involving family and friends in the management plan can also enhance their understanding and ability to provide meaningful support.
Support groups offer a valuable opportunity to connect with others who are experiencing similar challenges. Sharing experiences, tips, and encouragement with peers can provide a sense of community and reduce feelings of isolation. Support groups can be found in person or online, providing flexible options for individuals seeking connection and support. Participating in a support group can provide valuable insights and emotional strength for managing osteoarthritis.
Professional Psychological Support
Professional psychological support, such as counseling and therapy, can be instrumental in managing the emotional impact of chronic pain and osteoarthritis. Counseling options, such as individual therapy, group therapy, and family therapy, can provide a safe space to explore emotions, develop coping strategies, and receive support. Working with a mental health professional can help individuals address the emotional challenges associated with chronic pain and improve their overall quality of life.
Knowing when to seek help is crucial for managing mental health effectively. Signs that professional support may be needed include persistent feelings of sadness, anxiety, or hopelessness, difficulty coping with daily activities, and changes in sleep or appetite. Seeking help early can prevent these issues from becoming more severe and improve overall well-being. Accessing professional psychological support can provide the tools and resources needed to navigate the emotional challenges of managing osteoarthritis.
Regular Medical Check-Ups
Importance of Regular Visits
Regular medical check-ups are essential for monitoring the progression of osteoarthritis and adjusting treatment plans as needed. These visits allow healthcare providers to assess joint health, evaluate the effectiveness of current treatments, and make necessary adjustments. Regular check-ups also provide an opportunity to discuss any new symptoms or concerns and receive personalized advice and support. Consistent medical care can help individuals manage their osteoarthritis more effectively and prevent complications.
Monitoring progression involves tracking changes in joint function, pain levels, and overall health. Healthcare providers may use various diagnostic tools, such as X-rays, MRI, and physical examinations, to assess the condition of the joints. Regular monitoring can help identify any changes in the disease’s progression and inform treatment decisions. Staying proactive about medical care can lead to better long-term outcomes and improved quality of life.
Role of the Healthcare Team
The healthcare team plays a vital role in managing osteoarthritis and providing comprehensive care. Collaboration among specialists, such as rheumatologists, physical therapists, and dietitians, ensures that individuals receive well-rounded and personalized treatment. Each member of the healthcare team brings unique expertise and perspectives, contributing to a holistic approach to managing osteoarthritis. Regular communication and coordination among healthcare providers can enhance the effectiveness of the treatment plan.
Regular follow-ups with the healthcare team allow for ongoing assessment and adjustments to the management plan. These visits provide an opportunity to review progress, discuss any challenges or concerns, and receive guidance on managing symptoms. Building a strong relationship with the healthcare team can foster trust and improve communication, leading to more effective and personalized care. Working closely with the healthcare team is essential for achieving optimal outcomes in managing osteoarthritis.
Preventive Measures
Preventive measures play a crucial role in managing osteoarthritis and maintaining joint health. Early intervention and lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of further joint damage and improve overall well-being. Preventive strategies may include regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and practicing good posture. Avoiding activities that put excessive stress on the joints and taking breaks during repetitive tasks can also help protect joint health.
Education on joint health is essential for understanding the importance of preventive measures and making informed decisions. Healthcare providers can offer valuable information and resources on managing osteoarthritis and preventing further damage. Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options can empower individuals to take control of their joint health and make proactive choices. Preventive measures, combined with regular medical care, can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with osteoarthritis.
Make an informed Decision
Managing osteoarthritis in individuals with cerebral palsy requires a comprehensive and personalized approach that addresses physical, nutritional, psychological, and medical needs. Early detection and intervention, physical therapy, exercise, nutrition, pain management, assistive devices, psychological support, and regular medical check-ups all play crucial roles in managing the condition effectively. By implementing these daily practices and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with osteoarthritis can improve their joint health, reduce pain, and enhance their overall quality of life.
FAQs
What are the early signs of osteoarthritis in individuals with cerebral palsy?
Early signs include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion. It is important to consult a healthcare provider if these symptoms persist.
Can physical therapy help manage osteoarthritis pain?
Yes, physical therapy can improve joint function, reduce pain, and enhance mobility through targeted exercises and manual therapies.
What are some low-impact exercises suitable for individuals with osteoarthritis?
Swimming, cycling, and stretching exercises are beneficial as they minimize stress on the joints while promoting physical activity and overall health.
How can diet and weight management affect osteoarthritis?
A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on the joints, alleviate pain, and improve overall health. For more information or to learn more, visit us online.