Key Takeaways
- 01. Treatment overview:
The article explains the use of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to support kidney repair in patients with Diabetic Nephropathy by reducing inflammation, improving micro-circulation, and protecting renal cells. - 02. Early results reported:
Some patients reportedly showed stabilization or improvement in creatinine and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) following the therapy at the clinic described. - 03. Experimental status:
The therapy remains experimental and has not yet achieved routine standard-of-care status, according to the article. - 04. Patient factors influence outcome:
Success depends on disease stage, baseline kidney damage, blood sugar and blood pressure control, and the type and delivery protocol of stem cells used.
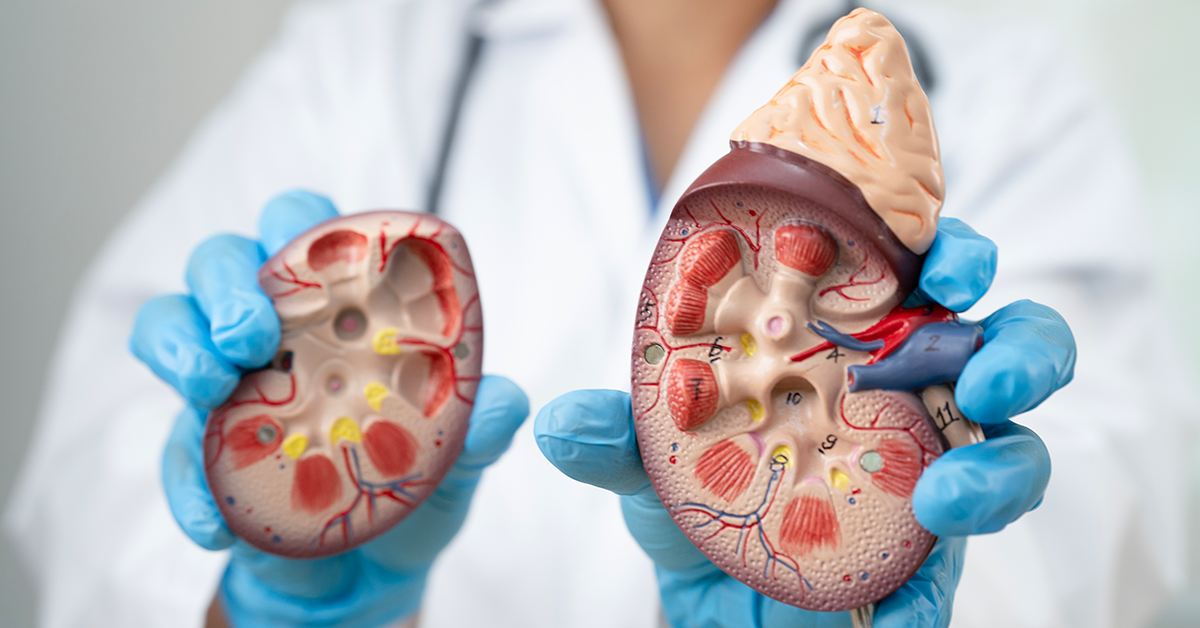
Diabetic nephropathy is a progressive kidney disease that affects individuals with diabetes. It occurs due to damage to the kidneys’ filtering units, known as nephrons, which become less effective over time. The condition is linked to long-term high blood sugar levels, which can cause structural and functional changes in the kidneys. This leads to increased leakage of proteins, especially albumin, into the urine.
The disease progresses through distinct stages. In early stages, there might be subtle changes to the kidney’s function that can only be detected through specific tests. As diabetic nephropathy advances, kidney function continues to decline, leading to more significant complications. The final stage may result in end-stage renal disease, requiring kidney replacement therapies such as dialysis or transplantation.
Preventive strategies focus on managing blood glucose levels and maintaining blood pressure within a healthy range to reduce the risk of further kidney damage. Regular monitoring of kidney health and urine protein levels is crucial in assessing the progression of the disease. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and weight management play a critical role in managing the impact of diabetic nephropathy.
Diabetic nephropathy remains a leading cause of chronic kidney disease and kidney failure worldwide. Its impact on overall health is significant, as reduced kidney function can lead to complications affecting the heart and other vital organs. Furthermore, the financial burden associated with kidney-related complications is considerable, emphasizing the importance of proactive care and lifestyle adjustments.
The interplay between diabetes and kidney health is complex, as multiple mechanisms contribute to the gradual decline in kidney function. This highlights the importance of continuous medical advancements and research to better understand and mitigate the effects of diabetic nephropathy. Engaging in educational programs and support groups can also help individuals make informed choices to manage the progression of the disease.
Diabetic nephropathy, a serious complication of diabetes, gradually damages the kidneys and can lead to chronic kidney disease. It occurs due to long-term, poorly controlled blood sugar levels, which harm the kidneys’ filtering system. Here are key causes and contributing factors:
- High Blood Sugar: Uncontrolled diabetes causes excess sugar in the blood, which damages the blood vessels in the kidneys over time. The filtering units, known as nephrons, become scarred and lose their ability to function properly.
- High Blood Pressure: People with diabetes often develop high blood pressure. This increases pressure in the delicate capillaries within the kidneys, accelerating damage.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals are genetically more likely to develop diabetic nephropathy. Specific genes can influence susceptibility to kidney damage.
- Duration of Diabetes: The longer a person has diabetes, the higher their risk of kidney complications. Those who have had diabetes for many years, especially without strict blood sugar control, face an increased risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: Unhealthy diets, obesity, and lack of physical activity can worsen both blood sugar levels and blood pressure, further contributing to kidney damage.
- Smoking: Smoking constricts blood vessels, decreases kidney blood flow, and accelerates kidney damage. It also raises blood pressure and worsens diabetes complications.
- Chronic Inflammation: Diabetes may trigger low-grade, chronic inflammation in the body. This inflammation can harm kidney tissues and contribute to nephropathy.
Addressing these risk factors through effective diabetes management, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups can significantly reduce the risk of developing diabetic nephropathy.
Diabetic nephropathy, a type of kidney damage that occurs as a complication of diabetes, often develops gradually. This condition primarily affects individuals with long-standing, poorly controlled diabetes and is characterized by progressive damage to the small blood vessels (glomeruli) in the kidneys, which are responsible for filtering waste products from the blood. Recognizing early signs and symptoms is crucial for managing and preventing further complications. Here’s a detailed look at the symptoms associated with diabetic nephropathy:
1. Early Stage Symptoms
In the initial stages, diabetic nephropathy may present no noticeable symptoms. During this time, kidney function can still be preserved, and the damage may only be detectable through specific tests, like microalbuminuria, which reveals small amounts of protein in the urine. Routine medical screenings for diabetics often help catch this early stage, underscoring the importance of regular check-ups.
2. Proteinuria
As kidney damage progresses, larger amounts of protein, particularly albumin, leak into the urine. This symptom, known as proteinuria, may cause the urine to appear frothy or foamy. It indicates that the kidneys are losing their filtering efficiency. People with diabetes should monitor for any changes in the appearance of their urine and report these findings to their healthcare provider.
3. Swelling (Edema)
When the kidneys become unable to properly filter waste and excess fluids, these fluids may accumulate in the body. This leads to swelling, especially in the legs, ankles, feet, hands, and sometimes around the eyes. This symptom, known as edema, may vary in severity and is usually more pronounced in the later stages of the disease. Managing fluid retention is vital to alleviate discomfort and prevent complications.
4. Increased Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is both a symptom and a contributing factor to diabetic nephropathy. As the kidneys fail to regulate fluid and sodium levels properly, blood pressure may rise. In turn, elevated blood pressure worsens kidney damage, creating a harmful cycle. Effective blood pressure management is critical for slowing the progression of kidney disease and protecting heart health.
5. Fatigue and Weakness
The buildup of waste products and toxins in the blood due to reduced kidney function can cause fatigue, weakness, and a general feeling of being unwell. Anemia, or low levels of red blood cells, can also develop, leading to increased tiredness. This is because damaged kidneys may not produce enough erythropoietin, a hormone responsible for stimulating red blood cell production.
6. Loss of Appetite and Weight Changes
As kidney function declines, individuals may experience a loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting. These symptoms can lead to unintentional weight loss. The accumulation of waste products in the bloodstream may also cause a metallic taste in the mouth, contributing to a decreased desire to eat. In advanced stages, malnutrition can become a serious concern.
7. Urinary Changes
Besides proteinuria, diabetic nephropathy can cause other noticeable urinary changes. These may include increased frequency of urination, particularly at night (nocturia), or difficulty urinating. Some individuals may also experience a decrease in urine output as kidney function worsens. Tracking these changes can provide insight into kidney health.
8. Persistent Itching
When the kidneys are unable to eliminate waste effectively, these toxins can accumulate in the bloodstream and lead to persistent itching. The itching, often described as intense and widespread, may be caused by an imbalance of minerals and electrolytes, particularly calcium and phosphorus. This symptom can affect quality of life and may require medical intervention.
9. Shortness of Breath
Fluid overload in the body, particularly in the lungs, can lead to shortness of breath. This symptom often occurs in the advanced stages of diabetic nephropathy. Anemia, a common issue in kidney disease, may also contribute to feelings of breathlessness. Individuals should report any difficulties with breathing to their healthcare provider, as this can indicate worsening kidney function or heart problems.
10. Muscle Cramps
Imbalances in electrolytes such as potassium, calcium, and phosphorus, due to impaired kidney function, may result in muscle cramps. These cramps can be uncomfortable and affect daily activities. Proper management of electrolyte levels through diet and medication can help alleviate this symptom.
11. Advanced Stage Symptoms
In the final stages of diabetic nephropathy, known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD), the kidneys lose most of their function. At this point, symptoms may include severe fatigue, difficulty concentrating, persistent nausea, vomiting, and swelling in the legs and face. Dialysis or a kidney transplant may be necessary to sustain life.
Note: Early detection and management of diabetic nephropathy are crucial for slowing its progression. Regular check-ups, blood pressure control, blood sugar management, and lifestyle changes can help protect kidney function and improve outcomes. If you experience any of these symptoms, consult your healthcare provider for appropriate tests and treatment options.
Diabetic nephropathy, a severe kidney complication of diabetes, affects many individuals globally. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management and prevention of further kidney damage. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the diagnosis process.
1. Initial Screening and Medical History
Diagnosis starts with a comprehensive medical history review, particularly focusing on diabetes duration, control, and presence of other complications. The doctor assesses family history of kidney disease and checks for signs of diabetes-related damage in other organs, such as the eyes. Risk factors, including high blood pressure and lifestyle habits, are also discussed.
2. Urine Tests for Albuminuria
A primary method to detect diabetic nephropathy is checking for albumin in the urine. The test measures microalbuminuria (30–300 mg of albumin per day) and macroalbuminuria (over 300 mg per day). Even small amounts of albumin in urine may indicate early kidney damage. A first-morning urine sample or a 24-hour urine collection provides reliable results. Repeated testing ensures accuracy.
3. Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) Calculation
The Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) estimates how well the kidneys filter blood. Doctors calculate GFR using blood creatinine levels, age, gender, and body size. A GFR below 60 mL/min/1.73 m² suggests reduced kidney function. Monitoring GFR over time helps assess kidney disease progression. A significant decline warrants immediate medical intervention.
4. Blood Tests for Kidney Function
Blood tests measure levels of waste products like creatinine and urea nitrogen, which build up if the kidneys are not working efficiently. Elevated levels may point to impaired kidney function. Additionally, tests for blood sugar control, like HbA1c, indicate diabetes management and its impact on kidney health.
5. Blood Pressure Monitoring
High blood pressure accelerates kidney damage in diabetic nephropathy. Regular monitoring helps detect abnormalities early. Consistently high readings may confirm the progression of kidney complications. Controlling blood pressure is vital to slow kidney damage.
6. Kidney Imaging Studies
Doctors may recommend imaging studies like ultrasounds to assess the structure and size of the kidneys. These tests help rule out other causes of kidney dysfunction. In diabetic nephropathy, kidneys may initially appear enlarged but gradually shrink with disease progression. Imaging also detects cysts, obstructions, or structural anomalies.
7. Kidney Biopsy for Confirmation
In some cases, a kidney biopsy may be necessary to confirm diabetic nephropathy. This procedure involves extracting a small tissue sample from the kidney using a needle. The tissue is examined under a microscope to check for characteristic damage, such as thickening of the glomerular basement membrane and mesangial expansion. A biopsy also helps rule out other conditions.
8. Monitoring Urine Protein-Creatinine Ratio
The urine protein-to-creatinine ratio (UPCR) provides another measure of kidney function. A high ratio indicates significant protein loss in urine, confirming kidney damage. This test complements albumin measurements, offering more comprehensive insights into kidney health.
9. Testing for Other Diabetes-Related Complications
Since diabetic nephropathy often accompanies other complications, doctors check for diabetic retinopathy, neuropathy, and cardiovascular issues. The presence of these conditions further supports the diagnosis. Eye exams and nerve function tests provide additional diagnostic information.
10. Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up
Continuous monitoring is crucial for individuals with diabetes, even without initial signs of kidney disease. Routine screening for kidney function helps detect early damage and allows timely interventions. Follow-up appointments track the effectiveness of treatment plans, ensuring kidney health preservation.
Diagnosing diabetic nephropathy involves multiple steps, including urine and blood tests, GFR calculations, and sometimes a kidney biopsy. Early diagnosis helps manage the disease and slow progression, significantly impacting patient outcomes. People with diabetes should undergo regular kidney function tests and maintain optimal blood sugar and blood pressure levels to protect their kidneys.
If you are concerned about diabetic nephropathy, consult your healthcare provider for proper assessment and guidance.
Diabetic nephropathy, a serious complication of diabetes, affects the kidneys, often leading to kidney failure if untreated. Current treatments aim to manage symptoms and slow disease progression, but stem cell therapy is emerging as a promising intervention. This guide explores how stem cells can be utilized in treating diabetic nephropathy.
1. Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy is caused by high blood sugar levels damaging the kidneys’ delicate filtering system. The glomeruli, which are crucial for filtering waste, become scarred and less effective. Patients experience reduced kidney function, proteinuria (protein leakage in the urine), and eventually, kidney failure. Effective treatments are urgently needed to restore or improve kidney health.
2. How Stem Cells Work in Kidney Repair
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells capable of becoming various types of specialized cells. For kidney repair, they can transform into renal cells, aiding in the regeneration of damaged kidney tissue. Their anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties also contribute to healing, making stem cells effective for conditions involving chronic inflammation, like diabetic nephropathy.
3. Types of Stem Cells Used
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): Derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, or umbilical cord tissue, MSCs are known for their regenerative potential. They release growth factors that help repair kidney tissues and reduce inflammation.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): These are adult cells reprogrammed to an embryonic-like state, allowing them to differentiate into any cell type. They offer a personalized approach but are still under research for safety and effectiveness.
- Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs): These cells are versatile but carry ethical concerns. Their potential to differentiate into any cell type makes them ideal for kidney tissue regeneration.
4. The Procedure: Step-by-Step Process
1. Patient Assessment and Preparation
Doctors first evaluate the patient’s medical history, disease stage, and overall health to determine suitability for stem cell therapy. Blood and imaging tests are conducted to understand the extent of kidney damage.
2. Stem Cell Collection and Processing
Stem cells are harvested from the patient or a donor. In autologous therapy (using the patient’s cells), stem cells are extracted from the bone marrow or fat tissue. In allogeneic therapy (using donor cells), umbilical cord or donor-derived stem cells are used. The collected stem cells are processed in a lab to increase their therapeutic potential.
3. Stem Cell Administration
Stem cells are administered through intravenous (IV) infusion or directly into the renal arteries. The method depends on the severity of kidney damage. IV infusion allows stem cells to circulate throughout the body, while direct renal artery administration delivers cells precisely to the kidneys.
5. Mechanism of Action in Diabetic Nephropathy
Stem cells work through multiple mechanisms:
- Tissue Regeneration: Stem cells differentiate into renal cells, replacing damaged kidney tissues.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: They release anti-inflammatory cytokines, reducing chronic inflammation in the kidneys.
- Immunomodulation: Stem cells modulate the immune system, preventing further autoimmune damage.
- Angiogenesis Promotion: They stimulate the formation of new blood vessels, improving kidney oxygenation and function.
- Anti-Fibrotic Effects: Stem cells prevent or reverse fibrosis (scar tissue formation), a key issue in diabetic nephropathy.
6. Expected Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy
- Improved Kidney Function: Clinical studies have shown improved glomerular filtration rates (GFR) and reduced proteinuria.
- Reduction in Inflammation and Fibrosis: The anti-inflammatory properties of stem cells can significantly reduce kidney inflammation and fibrosis.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Patients experience better overall health and a reduced risk of progressing to end-stage renal disease.
If you or a loved one is struggling with diabetic nephropathy, consult a healthcare professional to discuss the latest advancements in stem cell therapy. Staying informed can open the door to innovative treatment options.
Diabetic nephropathy, a serious complication of diabetes, causes progressive kidney damage. It is one of the primary causes of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal failure. Traditional treatments aim to control blood sugar levels and manage symptoms but do not reverse kidney damage. Stem cell therapy, however, is emerging as a potential regenerative solution to treat diabetic nephropathy. India is becoming a popular destination for this advanced treatment, thanks to its rapidly growing medical infrastructure, skilled professionals, and affordable healthcare options. Let’s explore the landscape of stem cell treatment for diabetic nephropathy in India.
Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy occurs due to prolonged high blood sugar levels that damage the kidneys’ filtering units, the glomeruli. Over time, this damage results in kidney dysfunction, reduced filtration, proteinuria, and eventually kidney failure. Early symptoms include increased urinary protein levels, high blood pressure, and swelling. Controlling diabetes is crucial to slowing down the progression of the disease. However, when the kidneys sustain irreversible damage, conventional treatments may become insufficient, highlighting the need for innovative therapies such as stem cell treatment.
The Science Behind Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy uses the unique regenerative potential of stem cells to repair damaged tissues and organs. Stem cells, known for their ability to differentiate into various cell types, can regenerate damaged kidney tissues. In diabetic nephropathy, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are particularly effective. They possess anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties, promoting tissue repair and reducing fibrosis in the kidneys. Additionally, these cells help protect existing kidney cells and improve renal function by fostering a healing environment, making stem cell therapy a groundbreaking option for diabetic nephropathy patients.
Why India for Stem Cell Therapy?
India has become a global hub for medical tourism, particularly for stem cell therapy. The country offers world-class healthcare facilities, highly trained medical professionals, and cutting-edge research in regenerative medicine. Moreover, the cost of stem cell treatment in India is significantly lower compared to many Western countries, making it an attractive option for international patients. Hospitals and research centers in cities like Mumbai, Delhi, Chennai, and Bangalore are equipped with state-of-the-art technology, ensuring patients receive top-quality care. This combination of affordability and advanced medical care has placed India on the global map for stem cell treatments.
Types of Stem Cells Used for Treatment
Different types of stem cells are used in treating diabetic nephropathy, including:
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): These are derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, or umbilical cord tissue. MSCs have shown promising results in reducing kidney inflammation and promoting tissue repair.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): These cells are engineered from adult cells to have stem cell-like properties, capable of differentiating into kidney cells.
- Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs): Although potent, their use is controversial and regulated in India. Research focuses on ethical, safe applications for treating kidney disease.
The choice of stem cell type depends on the patient’s condition, research advancements, and regulatory approvals.
Procedure of Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetic Nephropathy
The stem cell therapy process generally involves several steps:
- Patient Evaluation: Doctors conduct a comprehensive evaluation, including medical history, lab tests, and kidney function assessment, to determine suitability for the treatment.
- Stem Cell Collection: Depending on the therapy type, stem cells are harvested from the patient’s bone marrow, fat tissue, or umbilical cord tissue (in case of donor cells).
- Stem Cell Preparation: Collected cells are processed and cultured in a laboratory to enhance their regenerative potential.
- Administration: The prepared stem cells are injected into the patient through intravenous infusion or directly into the kidney region.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: Patients are closely monitored for improvement in kidney function and any side effects. Follow-up visits are crucial to assess the treatment’s efficacy.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetic Nephropathy
Stem cell therapy offers several advantages over traditional treatments:
- Regenerative Potential: Unlike conventional therapies that only manage symptoms, stem cells have the ability to repair and regenerate damaged kidney tissues.
- Reduction of Inflammation: Stem cells reduce inflammation and fibrosis, preventing further kidney damage and improving renal function.
- Slowing Disease Progression: The therapy can slow or halt the progression of diabetic nephropathy, potentially reducing the need for dialysis or a kidney transplant.
- Personalized Treatment: Stem cell therapy can be tailored to individual patients based on their condition, maximizing treatment outcomes.
Cost of Stem Cell Therapy in India
The cost of stem cell therapy in India varies based on several factors, including the hospital, type of stem cells used, and treatment complexity. On average cost is significantly lower than in Western countries. This affordability, coupled with high-quality medical care, attracts many international patients. Additionally, some hospitals offer packages that include pre-treatment evaluation, stem cell therapy, and post-treatment care. Despite the costs, it is essential to consult with healthcare providers to understand the expenses involved and whether insurance covers any part of the treatment.
How to Choose the Right Treatment Center
Selecting the right treatment center is crucial for a successful outcome. Consider the following factors:
- Accreditation and Certification: Ensure the hospital is accredited by reputable health organizations and follows ethical practices.
- Expertise of Medical Team: Check the credentials and experience of doctors specializing in stem cell therapy for kidney diseases.
- Facilities and Technology: The center should have advanced facilities and technology for stem cell processing and administration.
- Patient Reviews and Success Rates: Research patient testimonials and inquire about the center’s success rates in treating diabetic nephropathy.
- Follow-Up Care: Choose a center that offers comprehensive follow-up care to monitor treatment progress and manage any complications.
Stem cell therapy holds immense potential for treating diabetic nephropathy, offering hope to millions of patients. India’s medical advancements and affordable healthcare options make it a leading destination for this innovative treatment. However, patients should conduct thorough research, consult with medical professionals, and consider all aspects of the treatment before proceeding. As research evolves, stem cell therapy may become a standard treatment for kidney diseases, transforming the future of nephrology. If you are considering this treatment, visit a reputable medical center and discuss your options with experts to make an informed decision.
Stem cell therapy holds significant promise for treating diabetic nephropathy, a common complication of diabetes that damages the kidneys. The primary goal of stem cell implantation is to regenerate damaged kidney tissue and improve overall kidney function. Here’s an in-depth look at how the process works:
1. Initial Patient Assessment and Diagnosis
Before stem cell therapy begins, patients undergo a thorough medical evaluation. Specialists review the patient’s medical history, kidney function tests, and diabetes management to ensure they are eligible for the procedure. Detailed imaging studies, like ultrasounds or MRIs, may also be performed to assess the extent of kidney damage.
This comprehensive assessment allows doctors to tailor the stem cell therapy to the patient’s unique needs, ensuring safety and maximizing effectiveness.
2. Stem Cell Source Selection
Stem cells can be sourced from several areas, primarily the patient’s bone marrow or adipose (fat) tissue. Sometimes, allogeneic (donor) stem cells may be considered, but autologous (patient’s own) stem cells are more commonly used to reduce the risk of rejection. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are frequently chosen for kidney regeneration due to their anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties.
The type of stem cell source and extraction method depends on patient factors, such as their health status and availability of suitable tissues.
3. Stem Cell Extraction
If bone marrow is the chosen source, a needle is inserted into the hip bone under local or general anesthesia to extract the marrow. The procedure is typically safe and quick, lasting about 30 to 60 minutes.
For adipose tissue extraction, liposuction is performed to harvest fat cells. This involves making a small incision and using a thin tube to remove the fat, often from the abdominal area. Both procedures are minimally invasive and have a relatively short recovery time.
4. Stem Cell Processing and Isolation
Once the stem cells are extracted, they are processed in a specialized lab. The cells are separated, purified, and prepared for implantation. Sophisticated techniques like centrifugation or filtration ensure a high concentration of viable stem cells.
The stem cell batch undergoes rigorous quality checks to confirm that the cells are active and free from contamination. In some cases, cells may be cultured to increase their numbers, but this depends on the therapeutic plan.
5. Stem Cell Administration
The processed stem cells are then administered to the patient. There are multiple methods for delivering the cells:
- Intravenous Infusion: This method involves injecting stem cells into a vein. The cells travel through the bloodstream and target the damaged kidney tissues.
- Intra-arterial Injection: Stem cells are delivered directly into the renal artery. This approach is more targeted and ensures a higher concentration of cells reaches the kidneys.
- Local Injection: In some advanced therapies, cells are directly injected into the kidney tissue.
The delivery method is chosen based on the severity of kidney damage and the therapy’s goals.
6. Monitoring and Follow-Up
After the procedure, patients are monitored closely for any immediate side effects or complications. Follow-up appointments are essential to evaluate kidney function, overall health, and the therapy’s effectiveness. Tests such as blood and urine analysis, along with imaging studies, help track progress and determine if additional treatments are necessary.
Long-term monitoring ensures that the stem cells are functioning as intended and that kidney health is improving or stabilizing.
How Stem Cells Help in Diabetic Nephropathy
Stem cells contribute to kidney regeneration through several mechanisms:
- Tissue Regeneration: They can differentiate into various cell types, helping to rebuild damaged kidney tissue.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Stem cells release factors that reduce inflammation, a key factor in diabetic nephropathy.
- Immunomodulation: They modulate the immune system to prevent further damage.
- Stimulation of Endogenous Repair: Stem cells can activate the body’s natural repair processes, promoting healing from within.
Overall, stem cell therapy represents a groundbreaking approach, though ongoing research is necessary to optimize treatment protocols and ensure long-term safety and efficacy.
Stem cell therapy is emerging as a potential treatment for diabetic nephropathy, a severe complication of diabetes affecting the kidneys. The therapy leverages the regenerative capabilities of stem cells, aiming to repair kidney damage and improve kidney function. Here’s how it works:
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Stem cells, particularly mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines, reducing inflammation in the kidneys. Chronic inflammation is a critical factor in the progression of diabetic nephropathy, so mitigating it can halt or slow damage.
- Anti-fibrotic Properties: Fibrosis, or scarring of kidney tissue, contributes to kidney dysfunction in diabetic nephropathy. Stem cells release factors that prevent or even reverse fibrosis. They modulate extracellular matrix production, reducing collagen deposition and preserving the structural integrity of kidney tissue.
- Angiogenesis and Blood Flow Improvement: Stem cells promote the formation of new blood vessels, or angiogenesis, improving blood flow and oxygen supply to the damaged kidney tissues. This enhanced microvascular environment supports tissue healing and sustains kidney function.
- Regeneration of Kidney Cells: Stem cells can differentiate into various cell types, including podocytes and renal tubular cells, which are crucial for kidney function. This regenerative potential allows for the replacement of damaged or lost cells, aiding in the recovery of the kidneys’ filtering capabilities.
- Immunomodulation: Stem cells can modulate the immune system’s response. By preventing immune attacks on kidney tissues, stem cells provide a protective environment that supports healing and slows disease progression.
- Microvesicles and Exosomes: Recent research highlights the role of exosomes and microvesicles released by stem cells. These small vesicles carry proteins, RNA, and other molecules that promote tissue repair and regulate gene expression in injured kidney cells.
Therapeutic Approaches: Various stem cell types are under investigation, including mesenchymal stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and hematopoietic stem cells. MSCs, derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, or umbilical cords, are particularly promising due to their immunomodulatory and regenerative properties.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stem cell treatment for diabetic nephropathy?
Stem cell treatment uses regenerative cells to repair damaged kidney tissue, improve kidney function, and reduce inflammation caused by diabetic nephropathy.
Who is eligible for stem cell therapy for diabetic nephropathy?
Patients with early to moderate stages of diabetic kidney disease, stable blood sugar levels, and no severe comorbidities are generally considered suitable candidates, as evaluated by specialists.
How is the therapy administered?
Stem cells are commonly administered intravenously or directly into the renal artery under controlled clinical conditions, ensuring targeted delivery to the kidneys.
Is stem cell therapy safe for patients with diabetes?
When performed in certified clinics with experienced teams, stem cell therapy is generally safe. Minor side effects may include temporary fever, fatigue, or localized swelling at the injection site.
How long does it take to see improvements in kidney function?
Improvements may be gradual, often observed over several weeks to months, depending on the stage of kidney disease, patient age, and overall health condition.
How many treatment sessions are required?
The number of sessions depends on individual response and disease severity. Most patients undergo 1–3 sessions, followed by regular monitoring of kidney function.
Can stem cell therapy replace dialysis or medication?
Stem cell therapy is usually used as a complementary treatment alongside medications and lifestyle management. It may delay disease progression but does not fully replace dialysis or standard therapies.
How can I schedule a consultation for stem cell therapy?
You can schedule a consultation by contacting our clinic via phone, email, or the appointment request form on our website. Our team will evaluate your condition and create a personalized treatment plan.
For more questions, visit our FAQs page or request an evaluation with our expert team.
How Much Does Stem Cell Therapy Cost for Diabetic Nephropathy?
The cost of stem cell therapy for diabetic nephropathy depends on factors such as the stage of kidney damage, patient’s age, type and source of stem cells used (autologous or allogeneic), number of sessions required, and the medical facility’s experience in regenerative nephrology. Costs vary between countries due to different healthcare regulations, laboratory technologies, and clinical expertise. Below is an approximate cost comparison across several countries.
Cost Comparison: Select Countries
The table below outlines the indicative price range for a comprehensive stem cell therapy program, including pre-assessment, stem cell preparation, infusion, medical supervision, and follow-up evaluation.
| Country | Average Cost (in USD) | Average Cost (in INR) |
|---|---|---|
| United States 🇺🇸 | $22,000 – $35,000 | ₹18,20,000 – ₹29,00,000 |
| United Kingdom 🇬🇧 | $17,000 – $26,000 | ₹14,10,000 – ₹21,60,000 |
| Germany 🇩🇪 | $19,000 – $28,000 | ₹15,80,000 – ₹23,30,000 |
| Singapore 🇸🇬 | $14,000 – $22,000 | ₹11,60,000 – ₹18,20,000 |
While the above countries are known for advanced healthcare infrastructure, the treatment expenses are significantly higher due to hospital overheads, medical insurance costs, and research expenditures. On the other hand, India provides equally effective and evidence-based regenerative treatments at a fraction of these costs, without compromising on clinical quality or safety standards.
The affordability in India stems from cost-efficient healthcare systems, lower operational expenses, and favorable exchange rates. Reputed hospitals and regenerative medicine centers in India maintain international-grade laboratories, certified stem cell processing units, and specialists trained abroad — ensuring reliable and outcome-driven treatments for patients worldwide.
Why Choose Viezec?
Viezec collaborates with accredited hospitals and stem cell experts to deliver personalized regenerative treatment plans. We ensure transparent pricing, ethical practices, and end-to-end patient support — from initial consultation to post-treatment follow-up — maintaining international care standards throughout your medical journey.
Get a Personalized Cost Estimate
Each case of diabetic nephropathy is unique. Connect with our medical team to receive a personalized treatment quotation and a detailed plan designed around your individual health requirements.
Testimonials
Arvind K. – Delhi, India – January 2020 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆
“My kidney function was worsening due to diabetes. After Viezec’s stem cell therapy, my creatinine levels stabilized, and I feel stronger.”
Emma L. – Manchester, UK – June 2020 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
“I was afraid of kidney failure. Post-treatment at Viezec, my sugar levels stabilized, and my kidney health improved significantly.”
Ahmed R. – Cairo, Egypt – November 2020 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆
“Diabetic nephropathy left me weak and tired. After Viezec’s therapy, my kidney function improved, and my energy returned.”
Isabella G. – Rome, Italy – March 2021 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
“Doctors warned me about dialysis. Thanks to Viezec’s stem cell therapy, my kidney performance stabilized, and I avoided dialysis.”
George T. – Athens, Greece – September 2021 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆
“I had swelling in my feet due to kidney damage. After Viezec’s treatment, the swelling reduced, and I feel healthier.”
Hannah P. – Toronto, Canada – February 2022 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
“Diabetic nephropathy was progressing fast. After therapy at Viezec, my kidney function markers improved, and I feel more confident.”
Omar S. – Amman, Jordan – August 2022 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆
“My blood pressure and kidney health were badly affected. Viezec’s stem cell therapy helped balance both and gave me relief.”
Maria R. – Madrid, Spain – April 2023 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
“I feared kidney failure due to diabetes. After Viezec’s therapy, my health stabilized, and I live more actively now.”
Daniel M. – Sydney, Australia – October 2023 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆
“My kidney damage was severe. Post stem cell treatment at Viezec, my function stabilized, and my need for medication reduced.”
Fatima H. – Istanbul, Turkey – May 2025 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
“Diabetic nephropathy had made life hard. Thanks to Viezec’s stem cell therapy, my kidney health improved, and I feel hopeful again.”
Stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising intervention for diabetic nephropathy, a severe kidney complication caused by diabetes. Research highlights significant improvements in kidney function and reduced inflammation following treatment. Here are some key benefits observed after undergoing stem cell therapy for diabetic nephropathy:
1. Improved Kidney Function
Stem cell treatment has shown potential to enhance kidney function in diabetic nephropathy patients. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), for instance, help in the regeneration of damaged kidney cells. After treatment, patients often report lower creatinine levels and improved glomerular filtration rates (GFR). This improvement indicates better waste filtration, which is crucial for overall health. The kidneys’ increased ability to remove toxins from the bloodstream can prevent further organ damage. Over time, enhanced kidney performance reduces the risk of end-stage renal disease, promoting a better quality of life for patients.
2. Reduction in Proteinuria
Proteinuria, the excessive loss of protein in urine, is a hallmark symptom of diabetic nephropathy. Stem cell therapy often leads to a significant decrease in proteinuria levels. This reduction suggests that the kidneys are regaining their ability to filter waste effectively without leaking vital proteins. By stabilizing the kidneys’ function, stem cells minimize complications associated with protein loss, such as muscle wasting and increased cardiovascular risk. For many patients, achieving lower proteinuria levels also reduces the need for aggressive interventions, like dialysis or kidney transplantation, which can be life-altering and expensive.
3. Decreased Inflammation and Fibrosis
Chronic inflammation and fibrosis are significant contributors to kidney damage in diabetic nephropathy. Stem cells, especially MSCs, exhibit anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties that combat these damaging processes. They secrete factors that suppress inflammatory responses and promote tissue healing. As a result, the progression of scarring (fibrosis) in the kidneys slows, preserving more functional tissue. Reduced inflammation also lowers oxidative stress, a major factor exacerbating kidney damage. Consequently, patients experience slower disease progression and greater kidney preservation, which enhances their overall prognosis and quality of life.
4. Regeneration of Damaged Kidney Tissue
One of the remarkable capabilities of stem cells is their ability to regenerate damaged tissues. In diabetic nephropathy, stem cells can differentiate into specialized kidney cells, replacing those lost due to the disease. They also stimulate the proliferation of resident kidney cells and support the formation of new blood vessels, improving kidney tissue oxygenation. This regeneration process is critical because it restores normal kidney architecture and function. Over time, patients report improved clinical outcomes, such as stabilized or improved kidney function metrics, and less reliance on traditional medications.
5. Improved Blood Sugar Control
Interestingly, stem cell therapy for diabetic nephropathy has also been associated with better blood sugar regulation. Stem cells help modulate immune responses, which can positively affect insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. In turn, improved blood sugar levels reduce the progression of diabetic complications, including nephropathy. For some patients, this improvement means a lower dependency on diabetes medications and a better ability to manage their condition. A stable blood sugar level also helps prevent further damage to the kidneys, creating a cycle of benefits that enhance long-term health.
6. Delay in Progression to End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
One of the most impactful outcomes of stem cell therapy for diabetic nephropathy is the delay or prevention of progression to ESRD. By improving kidney function and reducing complications, stem cells give patients more years without the need for dialysis or a kidney transplant. This is particularly beneficial because ESRD severely impacts the quality of life and comes with significant medical expenses. Studies have shown that stem cell therapy extends the window of manageable kidney function, offering hope to patients who previously faced grim prognoses.
7. Overall Quality of Life Improvement
Beyond clinical metrics, stem cell therapy often leads to an improved quality of life for diabetic nephropathy patients. They experience fewer complications, reduced medication dependence, and better overall well-being. Less proteinuria and stabilized kidney function mean less fatigue and fewer hospital visits. Patients can enjoy more active and fulfilling lives, engaging in daily activities with fewer health-related interruptions. The psychological benefit of seeing tangible improvements in their health also boosts their mental well-being, further enhancing their quality of life.
Stem cell therapy for diabetic nephropathy has shown substantial potential in clinical improvements, from better kidney function to reduced inflammation. While research continues to evolve, current evidence suggests that it can transform the management of this debilitating condition. Patients experiencing these positive outcomes often report a significant quality of life boost. However, it’s essential to consult with medical professionals to understand if this innovative treatment suits your specific case. Stay informed about the latest advancements in stem cell therapy and explore options that could make a lasting difference. Visit our website to learn more about cutting-edge medical treatments.
Stem cell treatment for diabetic nephropathy has shown promising results in various studies and clinical applications, including at Viezec, a renowned medical center that specializes in regenerative treatments. Diabetic nephropathy, a progressive kidney disease associated with diabetes, often leads to kidney failure if left untreated. Traditional treatments typically involve managing blood sugar and blood pressure, along with dialysis or kidney transplantation in advanced stages. However, stem cell therapy offers a potential breakthrough by targeting the root causes of kidney damage.
The Process of Stem Cell Treatment for Diabetic Nephropathy
At Viezec, stem cell therapy for diabetic nephropathy involves the use of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which are harvested from a patient’s own body (autologous) or from a healthy donor. These cells have the unique ability to regenerate damaged tissues and reduce inflammation, making them an ideal candidate for treating kidney diseases.
The procedure typically starts with a thorough consultation to evaluate the patient’s medical history, kidney function, and the severity of nephropathy. A personalized treatment plan is then designed. The stem cells are usually administered through intravenous injections or directly into the kidneys, depending on the specific needs of the patient.
Mechanism of Action
Stem cells work by promoting tissue repair and reducing inflammation in the kidneys. In diabetic nephropathy, high blood sugar levels cause damage to the glomeruli (the filtering units of the kidneys), leading to protein leakage into the urine and impaired kidney function. Stem cells help by:
- Regenerating Damaged Tissue: Stem cells have regenerative properties that help restore damaged kidney tissues, thereby improving their function.
- Reducing Inflammation: Stem cells secrete various growth factors and cytokines that reduce inflammation and fibrosis (scarring) in the kidney tissues.
- Promoting Angiogenesis: Stem cells can promote the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis), which improves blood flow to the kidneys and enhances kidney function.
- Balancing Immune Response: Stem cells can modulate the immune system to prevent further damage and control the autoimmune response that may exacerbate the disease.
Treatment Results at Viezec
Patients undergoing stem cell treatment for diabetic nephropathy at Viezec have reported a variety of positive outcomes, depending on the severity of the disease and the patient’s overall health. Some of the key results include:
- Improved Kidney Function: Many patients experience a noticeable improvement in kidney function after treatment, with a reduction in proteinuria (excessive protein in the urine), a common marker of kidney damage.
- Stabilization of Blood Glucose and Blood Pressure: Stem cell therapy has been shown to help stabilize blood sugar levels and blood pressure, which are critical in managing diabetic nephropathy.
- Reduced Dialysis Dependency: Some patients who were previously on dialysis have reported a reduction in their reliance on it, as their kidney function improves over time.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Patients often report improvements in energy levels, reduced fatigue, and better overall well-being. This can significantly enhance their quality of life and reduce the burden of managing chronic kidney disease.
- Slowing Disease Progression: In patients with early-stage diabetic nephropathy, stem cell therapy has been shown to slow the progression of kidney damage, potentially preventing the need for a kidney transplant in the future.
Stem cell treatment for diabetic nephropathy at Viezec is a revolutionary approach to managing a disease that typically leads to kidney failure. While more research is needed to fully understand its long-term effects, the early results show great promise. Patients experiencing diabetic nephropathy can benefit from this innovative therapy, which may offer a way to restore kidney function, reduce dependence on dialysis, and improve quality of life. If you or a loved one is suffering from diabetic nephropathy, consulting with a specialized clinic like Viezec could provide a potential path toward healing and long-term kidney health.
At Viezec, we are committed to offering cutting-edge solutions for individuals suffering from Diabetic Nephropathy. This condition, often a result of prolonged diabetes, can lead to kidney damage and, in severe cases, kidney failure. However, our promise at Viezec is to help transform the lives of our patients with advanced stem cell therapy tailored to reverse and manage the condition effectively.
Our stem cell therapy approach is based on the latest medical advancements, ensuring that patients receive the highest standard of care. The therapy involves using stem cells to repair and regenerate damaged kidney tissues, reducing inflammation and promoting healing. By targeting the root causes of Diabetic Nephropathy, our treatment offers a potential for long-term improvements, addressing both the symptoms and underlying damage that diabetes causes to the kidneys.
We recognize the challenges that come with this condition, which is why our expert team provides personalized care, assessing each patient’s unique medical history and needs. This ensures that the stem cell treatment is as effective as possible in managing and potentially reversing the kidney damage caused by diabetes. Furthermore, we provide continuous support throughout the treatment process, offering a comprehensive care plan that includes follow-up visits, lifestyle recommendations, and ongoing monitoring of kidney health.
At Viezec, we are dedicated to improving the quality of life for our patients. Our stem cell therapy offers hope to those struggling with the debilitating effects of Diabetic Nephropathy, providing an opportunity for kidney regeneration and enhanced well-being. Through innovative treatments and personalized care, we strive to deliver lasting results, ensuring that our patients can enjoy better health and a brighter future.
At Viezec, the quality control of stem cell therapy is of paramount importance to ensure the safety, efficacy, and ethical standards of treatments provided to patients. The clinic implements a rigorous and comprehensive quality management system that adheres to international standards and guidelines. This system is designed to oversee every aspect of stem cell therapy, from patient consultation to post-treatment monitoring. Below are the key aspects of Viezec’s quality control process for stem cell therapy:
Patient Screening and Evaluation
Before any stem cell therapy is administered, Viezec conducts an extensive screening process to evaluate the patient’s suitability for treatment. This involves reviewing the patient’s medical history, conducting necessary diagnostic tests, and assessing their overall health condition. Only those patients who meet specific eligibility criteria are considered for stem cell therapy. This personalized evaluation ensures that the treatment is appropriate for each individual, maximizing the potential for success while minimizing risks.
Stem Cell Sourcing and Quality Assurance
The stem cells used in Viezec’s therapies are sourced from reputable, ethical suppliers who adhere to the highest standards of cell collection and processing. Viezec follows strict protocols to ensure that all stem cells are harvested in sterile, controlled environments. The cells undergo thorough testing for viability, purity, and potency before being used in any treatment. This ensures that the stem cells are of the highest quality and suitable for therapeutic purposes.
Laboratory and Manufacturing Standards
Viezec’s state-of-the-art laboratories are equipped with advanced technology to handle stem cells safely and efficiently. The manufacturing process, including cell expansion, processing, and preparation for injection, is carried out under Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) conditions. GMP guidelines ensure that the entire stem cell processing workflow meets the highest standards for sterility, quality, and consistency. Additionally, regular internal audits and external inspections are conducted to maintain compliance with international quality standards.
Treatment Protocols and Medical Supervision
At Viezec, stem cell therapy is administered following well-established and scientifically validated protocols. Each therapy is customized based on the patient’s condition, ensuring that the right type and dosage of stem cells are delivered. Experienced and trained medical professionals supervise the treatment process to guarantee that it is carried out safely. Viezec ensures that all medical staff are well-trained in the latest techniques and have experience in stem cell therapy applications.
Monitoring and Follow-up Care
After stem cell therapy, Viezec closely monitors patients to assess their progress and detect any potential complications. This involves regular check-ups and follow-up tests to track the body’s response to the treatment. Viezec employs a structured system for post-treatment care, ensuring that any adverse effects or complications are promptly addressed. Long-term monitoring is also part of the clinic’s commitment to quality, allowing the medical team to evaluate the lasting effects of the therapy on the patient’s condition.
Regulatory Compliance and Ethical Standards
Viezec is committed to maintaining compliance with all relevant regulatory authorities, both locally and internationally. The clinic adheres to the ethical principles surrounding stem cell research and therapy. All procedures are conducted with patient safety and ethical treatment at the forefront. Viezec is dedicated to transparency and ethical practices, ensuring that all patients are fully informed about the treatment process, potential risks, and benefits.
Research and Continuous Improvement
To maintain the highest standards of care, Viezec invests in ongoing research and development. This includes staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in stem cell science and integrating new findings into their treatment protocols. Regular training and workshops for staff members ensure that they are well-versed in the latest developments in stem cell therapy. Viezec’s commitment to innovation and quality control ensures that patients receive the most effective and cutting-edge treatment options available.
Patient Feedback and Quality Assurance Audits
Viezec values patient feedback as an essential part of maintaining and improving the quality of care. Patients are encouraged to provide their input throughout the treatment process, helping the clinic understand their experience and satisfaction levels. In addition, regular quality assurance audits are conducted to review all aspects of stem cell therapy, from initial consultations to post-treatment care. This ensures that Viezec continuously meets its high standards of patient safety and therapeutic effectiveness.
Viezec maintains a robust quality control system for stem cell therapy, ensuring that patients receive safe, effective, and ethically delivered treatments. The clinic’s commitment to using the highest quality stem cells, adhering to rigorous standards, and constantly improving through research and patient feedback makes it a trusted choice for stem cell therapy.
Ahead of undergoing this process; a patient needs to understands that stem cell therapy is an experimental therapy that might not work at certain times. At the time of procedure, a patient might be refused the treatment or the proposed protocol might change depending on the patient’s health condition.
At Viezec Stem Cell Institute, our main motive is to give the best technology and safety available; of which has been proven across the globe.
As with any medical treatment, there are no guarantees or claims of cures are made as to the extent of the response to treatment. Every patient has different internal status of body; hence results vary from patient to patient, even with a similar diagnosis. This means that we cannot offer, infer or suggest that there is any certainty of a given outcome. For our any treatment we do not use embryonic or fetal cells.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy for diabetic nephropathy offers a promising regenerative approach to protect and restore kidney function by repairing damaged tissues and improving blood filtration capacity. At Viezec, we combine advanced stem cell research with internationally recognized medical standards to deliver safe, effective, and personalized care for every patient. Our multidisciplinary team ensures transparency, ethical treatment protocols, and ongoing medical support throughout your healing journey. With India emerging as a leading destination for regenerative medicine, Viezec empowers patients worldwide to explore innovative therapies that aim to slow disease progression and enhance quality of life. Contact our medical consultants today to learn how stem cell therapy in India could support your kidney health and overall well-being.
Other Disease Treatment
Our Testimonials
Related Videos
Recent Blog Posts
4.8 average based on 654 reviews.






