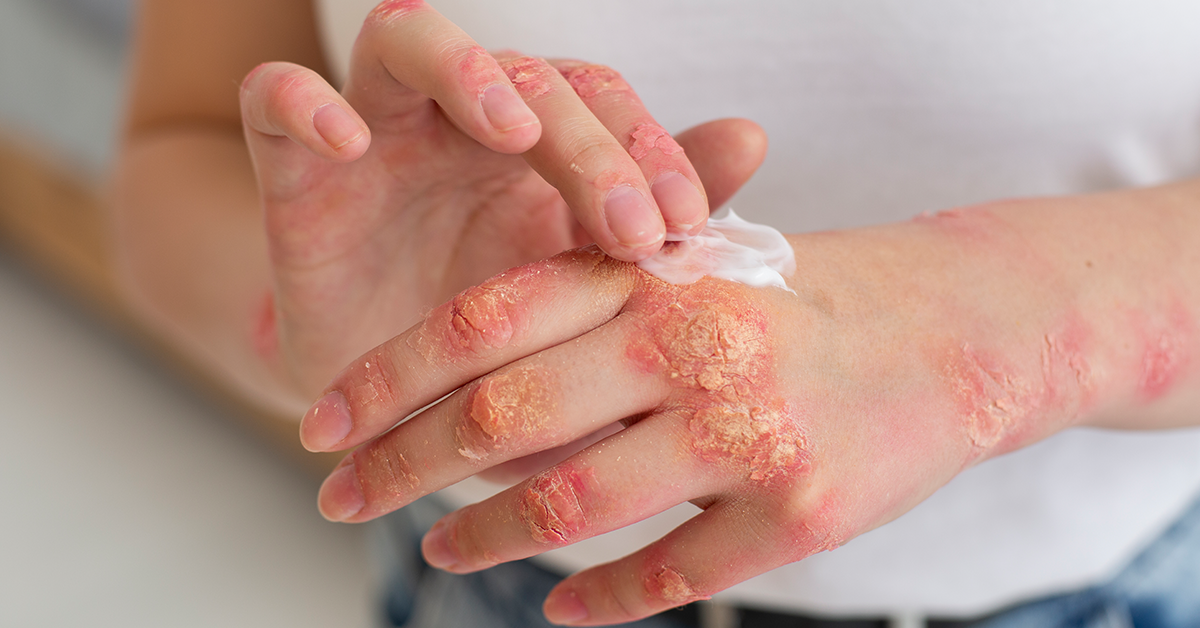
Key Takeaways
- 01. Treatment approach explained:
The therapy uses adult mesenchymal stem cells (often from umbilical-cord tissue) to modulate immune activity and reduce skin inflammation rather than replace skin permanently. - 02. Symptom improvement potential:
Some patients reportedly experienced fewer flare-ups, reduced scaling and redness, and slower disease progression after stem-cell administration. - 03. Therapy remains experimental:
The article clarifies that stem-cell therapy for psoriasis is not a defined cure. It still lacks large-scale clinical trials and should be considered alongside conventional treatments. - 04. Treatment logistics vary:
Protocols differ in terms of cell source, delivery method, cost, and stay duration in India. Patients should review these factors carefully and note that insurance typically does not cover this therapy.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin, causing cells to multiply too quickly. This results in thick, red patches covered with silvery scales. These patches can appear anywhere on the body, but they are most commonly found on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. Psoriasis varies greatly in severity, from small patches to large areas of the body being affected.
The condition tends to have cycles, where flare-ups of symptoms are followed by periods of remission. During flare-ups, the skin can become dry, cracked, and even bleed. The rate of skin cell turnover is drastically increased, and new skin cells form rapidly, which can lead to the build-up of dead skin cells on the surface.
Psoriasis can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, both physically and emotionally. The visible nature of the condition often leads to self-esteem issues and social stigma. Many people with psoriasis experience discomfort or itching, which can further exacerbate the emotional distress associated with the condition.
Aside from the physical effects, psoriasis has been linked to other health issues. For example, those with psoriasis may be at a higher risk of developing other autoimmune disorders or joint problems, such as psoriatic arthritis. In some cases, psoriasis has been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Living with psoriasis often involves managing flare-ups and finding effective ways to cope with the emotional and psychological impacts. People with psoriasis may choose lifestyle changes that support skin health and seek therapies that help control flare-ups. Social support and a good understanding of the condition can also be beneficial in managing the impact of psoriasis on daily life.
It’s important to note that psoriasis is not contagious, meaning it cannot be spread through physical contact. Despite this, individuals with psoriasis may face challenges in social situations due to misconceptions or a lack of understanding about the condition.
Although psoriasis cannot be cured, many people find ways to manage it effectively, leading to improved skin health and a better overall quality of life.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes the skin cells to multiply too quickly. The underlying cause of psoriasis is not entirely understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, immune system, and environmental factors.
- Genetic Factors: Genetics play a significant role in the development of psoriasis. If a person has a family history of psoriasis or other autoimmune diseases, they may have a higher risk of developing the condition. Certain genes, such as the HLA-Cw6 gene, have been linked to psoriasis, suggesting a hereditary component to the disease. However, not everyone with a genetic predisposition develops psoriasis, indicating that other factors are involved.
- Immune System Dysfunction: Psoriasis is primarily an autoimmune disorder. The immune system, which normally protects the body from infections, mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. In psoriasis, T-cells, a type of white blood cell, become overactive and trigger inflammation. This results in the rapid turnover of skin cells. Instead of shedding the normal amount of dead skin cells, the body produces new skin cells in a matter of days, rather than weeks, leading to a build-up of skin cells on the surface, forming thick, scaly patches.
- Environmental Triggers: Environmental factors can trigger or exacerbate psoriasis in people who are genetically predisposed. These triggers can include:
- Infections: Certain infections, particularly streptococcal throat infections, have been linked to the onset of psoriasis, especially in children. Infections can stimulate the immune system, leading to flare-ups of the disease.
- Stress: Emotional or physical stress is one of the most common triggers for psoriasis. Stress can weaken the immune system and promote inflammation, triggering flare-ups in those predisposed to the condition.
- Skin Injury: Physical trauma to the skin, such as cuts, scrapes, sunburn, or insect bites, can lead to the development of new psoriasis lesions in a phenomenon known as the Koebner phenomenon.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as lithium, antimalarial drugs, and beta-blockers, can trigger or worsen psoriasis in some individuals.
- Weather: Cold, dry weather can dry out the skin and cause flare-ups, while sunny weather can sometimes improve symptoms, as sunlight helps reduce inflammation.
- Smoking and Alcohol: Smoking is a known risk factor for psoriasis and can increase the severity of the condition. Excessive alcohol consumption can also exacerbate psoriasis flare-ups.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty or menopause, can trigger psoriasis. For example, many women experience flare-ups during pregnancy or when starting or stopping birth control. This is thought to be due to changes in the body’s immune response during these times.
- Other Autoimmune Conditions: People with other autoimmune diseases, such as Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, or celiac disease, are at higher risk of developing psoriasis. These conditions also involve the immune system mistakenly attacking the body’s tissues, which could contribute to the development of psoriasis.
Overall, the causes of psoriasis are complex and multifactorial, with genetic predisposition and immune system dysfunction at the core, while environmental and lifestyle factors can play a significant role in triggering or exacerbating the condition.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that primarily affects the skin, causing the rapid growth of skin cells. This rapid turnover leads to the formation of thick, scaly patches. The symptoms can vary greatly from person to person, and their severity can range from mild to severe.
- Red, Raised Patches of Skin: One of the most recognizable symptoms of psoriasis is the appearance of red, inflamed patches on the skin. These patches are often covered with silvery-white scales, which are dead skin cells that accumulate due to the rapid growth of skin cells. The patches can appear anywhere on the body but are most common on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back.
- Itching and Pain: Psoriasis can be itchy, with affected areas often feeling dry or tight. In more severe cases, the patches may become painful or even crack and bleed. This can lead to discomfort and interfere with daily activities.
- Thickened or Pitted Nails: Psoriasis can affect the nails, causing them to become thickened, discolored, or pitted. The nails may also separate from the nail bed in more severe cases. These nail changes are particularly common in people with psoriatic arthritis.
- Scalp Psoriasis: Psoriasis on the scalp can cause itching, flaking, and dandruff-like symptoms. The scales may be thick and difficult to remove. In severe cases, hair loss can occur due to the inflammation and damage caused by the scales.
- Dry or Cracked Skin: People with psoriasis often experience dry and cracked skin, especially in areas with active lesions. This can lead to further irritation, bleeding, or the formation of new lesions. Skin may become more sensitive to harsh weather conditions or skincare products.
- Swollen or Stiff Joints (Psoriatic Arthritis): In some cases, psoriasis is associated with psoriatic arthritis, a type of arthritis that causes joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. The joints most commonly affected are those in the fingers, toes, knees, and lower back. Psoriatic arthritis can lead to permanent joint damage if not managed properly.
- Burning Sensation: Some people with psoriasis report a burning sensation on the affected skin areas. This is especially common during flare-ups when the skin becomes inflamed.
- Guttate Psoriasis: This form of psoriasis causes small, drop-shaped patches to appear suddenly, often following a bacterial or viral infection, like a strep throat. The patches are typically red and covered with scales, often affecting the trunk, arms, and legs.
- Inverse Psoriasis: This type of psoriasis occurs in skin folds such as under the breasts, in the groin, or in the armpits. The lesions are typically smooth and red, and they are less scaly than in other types of psoriasis, but they can still be painful or itchy.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: Although rare, erythrodermic psoriasis is a severe form that covers the entire body with large, red, peeling patches. It can cause a burning sensation and can be life-threatening. This form of psoriasis requires immediate medical attention, as it can lead to severe dehydration and infections.
These symptoms can flare up and subside over time. The severity and duration of flare-ups can vary depending on the type of psoriasis and individual health factors. While there is no cure for psoriasis, treatments such as topical creams, systemic medications, and phototherapy can help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of flare-ups.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that results in rapid skin cell turnover, leading to thick, scaly patches on the skin. Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. The process typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and, in some cases, additional tests.
1. Physical Examination
The primary method of diagnosing psoriasis is through a physical exam. Dermatologists look for characteristic symptoms, including raised, red patches of skin with silvery scales. These patches are commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. The doctor may also check for other features such as thickened nails, pitted nails, or joint pain, which could indicate psoriatic arthritis.
2. Medical History
A detailed medical history is essential for diagnosis. The doctor will ask about your family history of psoriasis or other autoimmune conditions, as genetics play a significant role in the disease. They will also inquire about any triggers you’ve experienced, such as infections, stress, or medications that could worsen symptoms.
3. Skin Biopsy
In some cases, the doctor may take a small sample of the affected skin (skin biopsy) to examine it under a microscope. This helps rule out other skin conditions that may resemble psoriasis, such as eczema or fungal infections. A biopsy can confirm the diagnosis and provide information about the specific type of psoriasis.
4. Blood Tests
Although there is no specific blood test to diagnose psoriasis, blood tests can help rule out other conditions and check for signs of inflammation or infection. Tests may include a complete blood count (CBC) or liver function tests, particularly if you are taking medications that affect the liver.
5. Scalp Examination
Psoriasis often affects the scalp, which can sometimes be difficult to distinguish from dandruff or other scalp conditions. A dermatologist may examine the scalp closely to check for scales, redness, or hair loss. If the condition is severe, a biopsy may be performed.
6. Psoriatic Arthritis Screening
In cases where joint pain or stiffness is present, the doctor may screen for psoriatic arthritis, a related condition that affects the joints. This could involve joint examinations, X-rays, or MRI scans to check for signs of inflammation and joint damage.
7. Differential Diagnosis
Several other skin conditions can mimic the appearance of psoriasis, so it is essential to distinguish between them. Conditions such as eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, or fungal infections can present with similar symptoms. A dermatologist will use a combination of clinical observation and testing to make an accurate diagnosis.
8. Diagnostic Challenges
In some cases, diagnosing psoriasis can be challenging, particularly in people with atypical symptoms or those with a mild form of the disease. It may take time to gather enough evidence through observation, tests, and a comprehensive history. Nonetheless, early and accurate diagnosis can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
9. Genetic Testing
While not routine, genetic testing may be considered in certain cases. This can help determine if specific gene mutations are present, although it’s generally used for research purposes or in rare cases where the diagnosis is unclear.
10. Psychological Evaluation
Psoriasis can significantly affect mental health, causing stress, anxiety, or depression due to visible symptoms. In some cases, a psychological evaluation may be suggested to help manage the emotional impact of the disease.
Early diagnosis of psoriasis can significantly improve treatment outcomes and quality of life. If you suspect you have psoriasis, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Identifying the specific type and severity of psoriasis helps tailor the most effective therapies.
Stem cell therapy is emerging as a potential treatment for psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune condition that causes skin cells to multiply rapidly, leading to the formation of scaly patches. While traditional treatments like topical creams, phototherapy, and systemic medications provide relief, stem cell treatment offers a new approach by targeting the underlying causes of psoriasis.
Understanding Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin disorder characterized by an overactive immune system that speeds up the production of skin cells. Normally, skin cells mature and shed within a 28-30 day cycle, but in psoriasis, this process occurs in just a few days, leading to the accumulation of cells on the skin’s surface, forming scaly patches. Common triggers include infections, stress, and genetics. The severity can vary, from mild patches to large, inflamed lesions that cover much of the body.
What is Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cells are unique cells with the ability to differentiate into a variety of cell types. They have regenerative properties, which means they can help repair or replace damaged tissues. In the context of psoriasis, stem cells could potentially restore normal immune function and skin cell production by reducing inflammation and correcting the abnormal cell turnover associated with the condition.
Types of Stem Cells Used for Psoriasis Treatment
There are several types of stem cells that might be used to treat psoriasis, including:
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): These cells, derived from bone marrow, fat tissue, or umbilical cord blood, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. MSCs can modulate the immune system and have been shown to reduce the symptoms of autoimmune diseases like psoriasis.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): iPSCs are adult cells reprogrammed to behave like embryonic stem cells. They offer a potentially limitless source of cells for therapy without ethical concerns related to using embryonic stem cells.
- Autologous Stem Cells: Stem cells taken from the patient’s own body, often from fat tissue or bone marrow, may be used in treatments to avoid the risk of immune rejection.
How Stem Cells Can Help Treat Psoriasis
Stem cell therapy for psoriasis aims to correct the underlying immune system dysfunction that causes abnormal skin cell production. Here’s how stem cells might help:
- Reducing Inflammation: Stem cells can secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines that suppress the immune system’s overactive response, thereby decreasing inflammation and skin irritation.
- Regulating Immune Responses: By modulating the immune system, stem cells can help reset the immune response, preventing the overproduction of skin cells.
- Promoting Skin Regeneration: Stem cells might help regenerate healthy skin by promoting the growth of new skin cells that are properly differentiated and functional.
Treatment Process
The process typically involves harvesting stem cells from the patient or a donor, which are then cultured and prepared for injection or topical application. The stem cells are introduced into the affected areas or injected into the bloodstream. These cells migrate to the areas with the most significant tissue damage, where they begin to work on reducing inflammation, promoting tissue repair, and regulating immune responses.
Potential Benefits of Stem Cell Treatment for Psoriasis
- Long-term Relief: Stem cell therapy has the potential to provide long-lasting results by addressing the root cause of psoriasis rather than just alleviating symptoms.
- Reduced Reliance on Medications: Since stem cells work by regulating the immune system and reducing inflammation, patients may experience fewer flare-ups and reduced dependence on traditional psoriasis medications.
- Improved Skin Health: Stem cells may promote the regeneration of healthy skin, improving the appearance and texture of the skin and reducing scarring.
Stem cell therapy represents an exciting frontier in the treatment of psoriasis, offering the potential for long-term relief and a cure for this challenging condition. However, it is important to approach this treatment with caution, as the technology is still in its early stages. Patients should consult with dermatologists or specialists in regenerative medicine to learn more about the current status of stem cell treatments for psoriasis and whether they are a suitable option for them.
Stem cell therapy for psoriasis in India has become an increasingly popular treatment option, offering hope to those suffering from this chronic autoimmune skin condition. Psoriasis causes rapid skin cell turnover, leading to scaling and inflammation. Traditional treatments like topical creams or phototherapy may not always provide long-term relief, which is why many are exploring stem cell-based therapies.
In India, stem cell therapy is typically administered through injections or intravenous methods. The goal is to harness the regenerative properties of stem cells to help modulate the immune system, reduce inflammation, and repair damaged skin cells. By using stem cells, either derived from the patient’s own body or from other sources such as umbilical cords, the treatment can potentially offer lasting improvement by addressing the root cause of the disease rather than just the symptoms.
While stem cell therapy is still considered an emerging treatment for psoriasis, initial reports indicate promising results, with many patients experiencing significant improvement in skin health and quality of life.. The cost of such treatments in India is generally more affordable compared to many Western countries, making it an attractive option for international patients seeking advanced care
To explore this treatment further, a detailed consultation with a specialist is necessary to understand the potential benefits and risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stem cell treatment for psoriasis?
Stem cell treatment for psoriasis involves using regenerative cells to modulate the immune system, reduce inflammation, and promote skin healing, potentially improving symptoms and preventing flare-ups.
Who is eligible for stem cell therapy for psoriasis?
Patients with moderate to severe psoriasis who have not responded well to conventional treatments, such as topical creams or biologics, may be considered eligible after a thorough medical evaluation.
How is stem cell therapy administered for psoriasis?
Stem cells are typically administered intravenously or injected directly into affected areas under medical supervision, using minimally invasive procedures to ensure safety and efficacy.
Is stem cell therapy safe for psoriasis patients?
When performed in certified clinics with experienced specialists, stem cell therapy is generally safe. Temporary side effects may include mild fever, fatigue, or localized swelling at the injection site.
How long does it take to see results?
Results vary per individual, but improvements in skin lesions and reduction in flare-ups may be noticed over several weeks to months following therapy.
How many sessions are required for optimal effect?
The number of sessions depends on the severity of psoriasis, individual response, and treatment goals. Typically, 1–3 sessions are recommended with follow-up assessments to track progress.
Can stem cell therapy replace conventional treatments?
Stem cell therapy is usually used alongside standard treatments like topical agents, phototherapy, or biologics rather than as a complete replacement. It may enhance overall treatment outcomes.
How can I schedule a consultation for stem cell therapy?
You can schedule a consultation by contacting our clinic via phone, email, or the online appointment form. Our specialists will assess your condition and create a personalized treatment plan.
For more questions, visit our FAQs page or request an evaluation with our expert team.
How Much Does Stem Cell Therapy Cost for Psoriasis?
The cost of stem cell therapy for psoriasis depends on several factors including the extent and severity of skin involvement, patient’s overall health, number of sessions required, and the type of stem cells used. Prices also vary significantly between countries due to differences in healthcare systems, technology, and medical infrastructure. Below is a general cost comparison across major countries for a complete stem cell therapy program for psoriasis.
Cost Comparison: Select Countries
The following table provides estimated cost ranges reported by international regenerative medicine clinics for a full psoriasis treatment program, including cell processing, administration, lab work, and medical supervision.
| Country | Average Cost (in USD) | Average Cost (in INR) |
|---|---|---|
| United States 🇺🇸 | $18,000 – $30,000 | ₹14,90,000 – ₹24,80,000 |
| United Kingdom 🇬🇧 | $14,000 – $25,000 | ₹11,60,000 – ₹20,60,000 |
| Germany 🇩🇪 | $16,000 – $27,000 | ₹13,20,000 – ₹22,30,000 |
| Singapore 🇸🇬 | $12,000 – $20,000 | ₹9,90,000 – ₹16,50,000 |
While treatment in countries like the USA, UK, and Germany offers advanced technologies and clinical infrastructure, it also comes at a significantly higher cost due to expensive operational systems, healthcare labor, and insurance overheads.
In comparison, India provides equally effective stem cell therapy for psoriasis at a fraction of the international cost. The lower pricing is mainly due to favorable exchange rates, cost-efficient healthcare delivery, and reduced hospital overheads — without any compromise on medical quality or safety standards.
Many top hospitals in India operate GMP-certified laboratories and employ internationally trained regenerative medicine experts, offering patients reliable, ethical, and affordable treatment options.
Why Choose Viezec?
Viezec collaborates with accredited hospitals and expert doctors to provide world-class regenerative treatment for psoriasis. We emphasize transparency in pricing, patient safety, and international standards of care to ensure you receive the best possible results.
Get a Personalized Cost Estimate
Every patient’s condition is unique. Contact our team to get a personalized quotation and customized treatment plan based on your specific psoriasis condition and medical history.
At Viezec, quality control during the stem cell procedure for psoriasis is a crucial aspect of ensuring patient safety and treatment effectiveness. The clinic follows stringent protocols to maintain the highest standards throughout the process. Here’s an in-depth look at how quality control is managed:
1. Patient Assessment and Screening
Before the stem cell procedure begins, a thorough evaluation of the patient is conducted. This includes a detailed medical history review, assessing the severity of psoriasis, and identifying any underlying conditions that could impact the treatment’s success. Viezec ensures that only eligible patients, who meet specific criteria, undergo the procedure. This initial assessment is essential to minimize risks and tailor the treatment to the individual’s needs.
2. Stem Cell Source Selection
Viezec prioritizes the use of high-quality stem cells, sourced from reputable facilities that adhere to international standards. The stem cells used for psoriasis treatment are typically derived from either the patient’s own body (autologous) or a donor (allogenic), depending on the patient’s condition and specific treatment plan. Every stem cell batch is tested for viability and purity to ensure no contamination or abnormalities that could affect the treatment’s success.
3. Laboratory Standards and Certification
Viezec partners with accredited stem cell laboratories that follow good manufacturing practices (GMP). These laboratories are certified for stem cell culture and processing. Each batch of stem cells undergoes a series of tests to confirm their quality, including viability testing, sterility checks, and assessments for any genetic abnormalities. The lab maintains stringent environmental conditions, ensuring that the cells are stored and handled properly to maintain their potency.
4. Stem Cell Preparation and Processing
Once the stem cells are harvested, they are processed in state-of-the-art facilities under the supervision of skilled professionals. The cells are isolated, cultured, and expanded under controlled conditions. This stage is crucial to ensure that only the healthiest, most viable stem cells are used for the procedure. During this phase, extensive quality control checks are implemented, including microscopic examinations and tests to detect any contaminants.
5. Infection Control and Sterility Measures
Viezec follows strict infection control protocols to minimize the risk of infection during the stem cell procedure. The clinic uses sterile equipment, and the entire procedure is conducted in a controlled, sterile environment. All staff members undergo regular training in aseptic techniques to prevent cross-contamination. Every tool, syringe, and container used in the process is sterilized to the highest standards.
6. Monitoring and Tracking of Stem Cell Viability
To ensure that the stem cells remain viable throughout the treatment process, Viezec employs advanced monitoring systems. The cells are stored in temperature-controlled incubators, with real-time tracking of conditions such as temperature and humidity. These conditions are continuously monitored and adjusted to optimize the stem cell’s health, ensuring they remain potent by the time of injection.
7. Pre-Procedure Preparations and Patient Consent
The clinic ensures that all patients are fully informed about the procedure, including potential risks and benefits. Consent forms are provided, and patients are given the opportunity to ask questions. This transparency is vital to patient safety and compliance with ethical standards. Pre-procedure care includes ensuring the patient is in optimal health, free of infections, and has no contraindications for stem cell therapy.
8. During the Procedure: Precision and Accuracy
The stem cell procedure itself is carefully managed. Viezec employs highly skilled medical professionals who are trained in administering stem cell treatments. The cells are injected precisely into the affected areas of the skin, where they can work to regenerate tissue, reduce inflammation, and alleviate psoriasis symptoms. During the procedure, real-time monitoring ensures the right volume and concentration of stem cells are applied for maximum effectiveness.
9. Post-Procedure Monitoring and Follow-Up
After the procedure, the patient is closely monitored for any signs of complications or adverse reactions. Viezec schedules follow-up visits to assess the patient’s progress and determine the effectiveness of the treatment. The clinic uses advanced imaging and diagnostic tools to track improvements in skin condition, ensuring that the stem cells are producing the desired results.
10. Data Collection and Outcome Analysis
Viezec is committed to tracking the long-term outcomes of stem cell treatments for psoriasis. Data from each patient is collected, including their response to treatment and any side effects. This helps improve the procedure and refine the protocols used. Quality control is also linked to research, where findings contribute to enhancing treatment methods.
11. Continuous Training and Quality Audits
To maintain the highest standards, Viezec implements regular audits and ongoing staff training. This ensures that all team members are up-to-date with the latest advancements in stem cell therapy and quality control measures. The clinic also participates in industry-specific quality assurance programs to guarantee that international guidelines are followed.
At Viezec, quality control is integrated into every aspect of the stem cell procedure for psoriasis, from patient evaluation to post-procedure follow-up. The clinic’s commitment to using only the highest quality stem cells, maintaining strict sterility, and employing highly trained professionals ensures the best possible outcomes for patients. Quality control is not just a standard but a continuous process aimed at improving patient satisfaction and treatment efficacy.
Stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising treatment option for various autoimmune diseases, including psoriasis. Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by rapid skin cell turnover, leading to the formation of scaly, inflamed patches. Traditional treatments like topical creams, phototherapy, and systemic medications may provide relief, but stem cell therapy offers a novel approach by addressing the underlying causes of the disease at a cellular level.
How Stem Cell Therapy Works for Psoriasis
Stem cell therapy aims to harness the regenerative potential of stem cells to repair damaged tissue and modulate the immune system. The therapy involves injecting or transplanting stem cells—often derived from the patient’s own body (autologous stem cells) or from a donor—into areas affected by psoriasis. These cells have the ability to differentiate into various types of cells, including skin cells, and can promote healing by reducing inflammation and regulating the immune response.
Reduction in Inflammation
One of the primary benefits observed after stem cell therapy for psoriasis is a significant reduction in inflammation. Psoriasis is driven by an overactive immune response, where T-cells (a type of white blood cell) mistakenly attack the skin, leading to the rapid turnover of skin cells. Stem cells have immunomodulatory properties that can suppress this autoimmune reaction. Research has shown that stem cells can decrease the activity of these T-cells and reduce the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are key players in the development of psoriasis.
Improvement in Skin Appearance
Patients often notice visible improvements in the appearance of their skin after undergoing stem cell therapy. The skin becomes less red, swollen, and scaly, and new, healthy skin cells begin to grow in place of the damaged ones. In some cases, patients may experience near-complete clearing of psoriasis plaques, particularly when stem cells are used in combination with other therapies. The regenerative potential of stem cells accelerates the healing of the skin, leading to smoother and healthier-looking skin.
Long-Term Effects and Maintenance
While the effects of stem cell therapy for psoriasis can vary from patient to patient, many individuals report long-term improvement in the condition. For some, the therapy provides lasting remission, while others may require periodic treatments to maintain the results. Unlike conventional treatments that only provide temporary relief, stem cell therapy targets the root causes of psoriasis, offering a potential for more sustained outcomes.
Reduced Need for Conventional Medications
A notable advantage of stem cell therapy is the potential to reduce or eliminate the need for long-term use of conventional psoriasis medications, which often come with side effects. Medications like corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologics can be effective in managing symptoms but may cause unwanted side effects, such as skin thinning, infections, and other systemic issues. By promoting the body’s natural healing processes, stem cell therapy offers a potentially safer, more natural treatment option.
Pain and Itch Relief
Psoriasis is often accompanied by discomfort, including pain, itching, and a burning sensation. Stem cell therapy has been reported to alleviate these symptoms significantly. By reducing inflammation and promoting skin regeneration, patients experience less irritation and an improvement in their quality of life. The restoration of normal skin function helps prevent further episodes of itching and pain, leading to enhanced comfort for the patient.
Stem cell therapy for psoriasis represents a significant advancement in the treatment of this chronic condition. The therapy has shown potential to reduce inflammation, improve skin appearance, and offer long-term relief from psoriasis symptoms. Though still under investigation, the regenerative and immunomodulatory properties of stem cells make them an exciting avenue for future psoriasis treatments. For those suffering from psoriasis, stem cell therapy may one day provide a more effective and sustainable solution, offering a better quality of life with fewer side effects than traditional therapies.
Stem cell therapy offers a promising approach to treating psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by rapid skin cell turnover, leading to the formation of thick, scaly patches. The mechanism of action behind stem cells in treating psoriasis involves several key biological processes aimed at reducing inflammation, regulating immune responses, and repairing damaged tissues. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how stem cells can help manage psoriasis:
1. Regulation of Immune Response
Psoriasis is fundamentally driven by an overactive immune system, where T cells (a type of white blood cell) mistakenly attack healthy skin cells, triggering inflammation. Stem cells, particularly mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), have immunomodulatory properties. When injected into the body, MSCs can help dampen the overactive immune response. They interact with T cells and other immune cells, promoting a more balanced immune response by reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This helps in minimizing the inflammatory cascade that drives psoriasis flare-ups.
2. Anti-inflammatory Effects
Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of psoriasis, contributing to the skin damage and scarring associated with the condition. Stem cells, especially MSCs, release anti-inflammatory cytokines like interleukin-10 (IL-10) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β). These cytokines work by downregulating the production of pro-inflammatory molecules such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukins that promote skin inflammation. By reducing inflammation, stem cells can help to alleviate symptoms like redness, itching, and scaling.
3. Promotion of Tissue Repair and Regeneration
In psoriasis, the skin’s natural regeneration process is disrupted, with skin cells multiplying too quickly and accumulating on the surface. Stem cells can aid in repairing damaged tissues by stimulating the regeneration of healthy skin cells. Stem cells possess the unique ability to differentiate into various types of cells, including keratinocytes, the primary cell type in the epidermis. By enhancing tissue repair, stem cells can help restore the skin’s normal structure and function, reducing the thickness and scaling of psoriasis plaques.
4. Angiogenesis
Psoriasis can lead to abnormal blood vessel formation in the affected areas of the skin. This can exacerbate inflammation and make the condition worse. Stem cells can stimulate angiogenesis, the process of new blood vessel formation. This helps to improve the blood supply to the affected skin, promoting healing and better oxygenation of the tissues. Increased blood flow also helps in the delivery of nutrients that are crucial for skin cell regeneration.
5. Modulation of Skin Cell Proliferation
One of the key issues in psoriasis is the rapid turnover of skin cells. Normally, skin cells shed and renew themselves in a controlled manner, but in psoriasis, this process is accelerated, leading to the formation of thick, scaly patches. Stem cells can help regulate the growth and differentiation of skin cells, reducing the overproduction of keratinocytes. By balancing cell proliferation and apoptosis (programmed cell death), stem cells can restore normal skin turnover, reducing the buildup of scales and improving the overall appearance of the skin.
6. Cell Communication and Signal Modulation
Stem cells communicate with surrounding cells through a complex network of signaling molecules. These signals can influence the behavior of both immune and skin cells, promoting a more coordinated response. For instance, stem cells release exosomes (tiny vesicles containing proteins, lipids, and RNA) that carry messages to other cells. This form of cellular communication can help modify the skin’s response to inflammation and help regulate the activity of immune cells involved in psoriasis.
7. Therapeutic Potential of Different Stem Cell Types
Several types of stem cells have been studied for their potential in treating psoriasis, including:
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): MSCs are derived from tissues like bone marrow, adipose (fat) tissue, and the umbilical cord. They are known for their immunomodulatory and regenerative properties, making them the most common stem cell type used in psoriasis treatments.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): iPSCs are laboratory-created stem cells that have the potential to differentiate into any type of cell, including skin cells. These cells can be generated from the patient’s own tissues, reducing the risk of immune rejection.
- Epidermal Stem Cells: These stem cells are found in the basal layer of the skin and are responsible for producing new skin cells. Their potential for regenerating damaged skin in psoriasis patients is an exciting area of research.
8. Potential for Personalized Treatment
One of the major advantages of stem cell therapy for psoriasis is its potential for personalized medicine. Since stem cells can be derived from the patient’s own tissues, there is a reduced risk of immune rejection, and the treatment can be tailored to the individual’s specific needs. For example, stem cells could be harvested from a patient’s adipose tissue, cultured, and then reinjected into the affected areas of the skin to promote healing.
Stem cell therapy offers a multifaceted approach to treating psoriasis by addressing the underlying immune dysfunction, reducing inflammation, and promoting tissue regeneration. While research is still ongoing, the potential of stem cells to treat psoriasis represents a promising avenue for future therapies, particularly for those with moderate to severe forms of the condition that do not respond well to traditional treatments. However, more clinical trials and studies are needed to fully understand the safety and effectiveness of stem cells in treating psoriasis on a broad scale.
At Viezec Stem Cell Institute, we understand how psoriasis can greatly affect your quality of life. Our stem cell treatment for psoriasis promises to provide advanced, personalized care to improve your symptoms and overall well-being. We commit to using innovative medical techniques, experienced specialists, and high-quality standards to give you the best possible outcome.
Advanced and Safe Technology
Our promise includes the use of cutting-edge stem cell technology, ensuring a safe and effective treatment. We use mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), renowned for their regenerative and anti-inflammatory properties. These stem cells have been studied for their effectiveness in addressing the root cause of psoriasis, helping to regenerate damaged tissues and modulate the immune system.
Highly Qualified Medical Team
At Viezec, we boast a team of experienced, internationally trained specialists. Our doctors and medical staff are dedicated to providing the highest level of care. We constantly stay updated with the latest research in stem cell therapy, applying the best practices to each case. From initial consultation to the final treatment, our experts work with you every step of the way.
Personalized Treatment Plans
We know that every patient is unique, which is why our approach to psoriasis treatment is highly personalized. After a thorough assessment of your medical history and current health status, we develop a tailored treatment plan to address your specific needs. This customized approach ensures that your treatment targets the underlying issues contributing to your condition.
Minimally Invasive and Painless
Our stem cell procedures are minimally invasive, providing a less painful experience compared to traditional treatments. This means shorter recovery times and a lower risk of complications. The treatment is administered via infusion or targeted injections, both of which are simple and well-tolerated methods. Our promise includes making your comfort and safety a top priority.
Enhanced Quality of Life
Our ultimate goal is to enhance your quality of life by effectively managing your psoriasis symptoms. Stem cells have the potential to reduce inflammation and improve skin regeneration, providing long-lasting relief. Many patients report a significant improvement in their skin condition and a reduced need for ongoing medications.
Transparent and Supportive Care
We promise transparency throughout your treatment journey. Our team takes the time to explain each step, ensuring you understand what to expect. We are also committed to providing continuous support and follow-ups even after your treatment is complete. Our staff is available to answer any questions and offer guidance as you recover.
Ethical and Regulated Treatment
We strictly adhere to all medical and ethical guidelines for stem cell therapy. Our procedures are conducted in state-of-the-art facilities, ensuring that we maintain the highest standards of cleanliness and safety. At Viezec, we are committed to ethical practices and uphold a patient-first philosophy.
Global and Accessible Healthcare
Viezec welcomes patients from around the world. We offer comprehensive medical tourism packages, including airport transfers, accommodation, and language support to make your experience stress-free. Our commitment is to make advanced psoriasis treatment accessible to as many patients as possible, regardless of location.
Positive Outcomes and Testimonials
Our patients have experienced positive outcomes, which motivates us to continue our mission of delivering excellence in healthcare. We invite you to read our success stories and testimonials from individuals who have benefited from our stem cell therapy for psoriasis. Hearing from others can give you hope and assurance in our treatment approach.
Your Well-being is Our Priority
At Viezec, your well-being is at the core of everything we do. We promise to walk this journey with you, providing compassionate care and the best possible outcomes. By choosing our stem cell procedure for psoriasis, you are placing your trust in a dedicated team that genuinely cares about your health and happiness.
For more information or to schedule a consultation, visit our website and take the first step toward a healthier, psoriasis-free life.
Stem cell therapy for psoriasis is an innovative approach that holds significant promise for improving patients’ quality of life. Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by rapid skin cell turnover, causing red, scaly patches on the skin. Traditional treatments primarily manage symptoms, but stem cell therapy aims to address the root cause by modulating the immune system and promoting healing.
How Stem Cell Therapy Works for Psoriasis
Stem cells, particularly mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), have immunomodulatory and regenerative properties. When introduced into the body, these cells can reduce inflammation and reprogram the immune system to stop attacking the skin. This treatment addresses the excessive immune response that leads to the accelerated skin cell production seen in psoriasis. Stem cells can also promote tissue regeneration, potentially healing damaged skin areas.
Results Observed After Stem Cell Treatment for Psoriasis
Patients who undergo stem cell therapy for psoriasis have reported various positive outcomes. The severity and duration of these improvements depend on factors such as the patient’s overall health, the type of stem cells used, and the disease stage. The results generally include:
- Reduction in Psoriatic Plaques: One of the most noticeable effects is a reduction in the thickness and size of psoriatic plaques. This results from the anti-inflammatory action of stem cells, which calms the hyperactive immune response.
- Improved Skin Appearance: Patients often report smoother skin, with reduced redness and scaling. Stem cells aid in tissue regeneration, helping the skin return to a healthier state.
- Longer Remission Periods: Traditional treatments may lead to periods of improvement, but stem cell therapy has shown potential for longer-lasting remission. Some patients experience extended periods without flare-ups, as the underlying immune dysregulation is addressed.
- Decreased Itching and Discomfort: The therapy reduces the discomfort associated with psoriasis, such as itching and burning sensations, leading to better quality of life and improved sleep patterns.
Timeline of Results
- Immediate Effects: Right after the procedure, patients may not observe immediate changes. The body takes time to respond to the regenerative signals from the stem cells.
- Short-Term Results (Weeks 1-4): Inflammation often starts to decrease, and symptoms like itching and scaling become less severe.
- Mid-Term Results (1-3 Months): Significant skin improvement is often noticed during this period. Plaques become less pronounced, and the overall appearance of the skin improves.
- Long-Term Results (6 Months and Beyond): Some patients experience continued improvement over several months, with fewer or no flare-ups. The immune system may exhibit a more balanced response, leading to longer remission periods.
Variability in Results
While many patients benefit from stem cell therapy, results can vary. Factors influencing outcomes include the patient’s age, severity of psoriasis, and any underlying health conditions. Some patients may experience only partial relief, while others achieve significant and lasting improvement.
Studies and Evidence
Several clinical studies have shown promising results for stem cell treatment in psoriasis. Research indicates that stem cells can reduce the activity of specific immune cells involved in psoriasis, such as T-cells, and promote an anti-inflammatory environment.
Stem cell therapy offers hope for psoriasis patients seeking long-term relief. With its ability to address the immune system and promote skin regeneration, it stands out from traditional treatments. While more research is necessary to fully establish its efficacy, many patients have reported significant improvements in their symptoms and quality of life. If you’re considering this treatment, consult a healthcare professional to discuss its potential benefits and risks.
Ahead of undergoing this process; a patient needs to understands that stem cell therapy is an experimental therapy that might not work at certain times. At the time of procedure, a patient might be refused the treatment or the proposed protocol might change depending on the patient’s health condition.
At Viezec Stem Cell Institute, our main motive is to give the best technology and safety available; of which has been proven across the globe.
As with any medical treatment, there are no guarantees or claims of cures are made as to the extent of the response to treatment. Every patient has different internal status of body; hence results vary from patient to patient, even with a similar diagnosis. This means that we cannot offer, infer or suggest that there is any certainty of a given outcome. For our any treatment we do not use embryonic or fetal cells.
Testimonials
Arjun K. – Delhi, India – January 2020 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆
“Psoriasis made my skin itchy and painful. After Viezec’s stem cell therapy, my flare-ups reduced, and my skin looks much healthier.”
Emma R. – London, UK – June 2020 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
“I lived with psoriasis patches for years. Post-treatment at Viezec, the redness and scaling decreased, and I feel confident again.”
Ahmed M. – Cairo, Egypt – November 2020 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆
“My son’s psoriasis was spreading quickly. After stem cell therapy, his skin cleared significantly, and he feels more comfortable.”
Isabella P. – Rome, Italy – March 2021 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
“Psoriasis caused constant embarrassment. Thanks to Viezec, my flare-ups reduced, and my skin feels smooth and pain-free.”
George S. – Athens, Greece – September 2021 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆
“I had painful plaques on my arms. After Viezec’s stem cell treatment, they healed faster, and my itching reduced.”
Hannah W. – Toronto, Canada – February 2022 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
“Living with psoriasis was frustrating. Stem cell therapy at Viezec gave me clearer skin and boosted my self-esteem.”
Omar H. – Amman, Jordan – August 2022 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆
“My psoriasis flare-ups were frequent. After therapy at Viezec, the outbreaks reduced, and my skin condition is stable now.”
Maria L. – Madrid, Spain – April 2023 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
“I tried many treatments with little success. Stem cell therapy at Viezec gave lasting relief, and my psoriasis symptoms are under control.”
Daniel K. – Sydney, Australia – October 2023 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆
“Psoriasis had affected my confidence at work. After Viezec’s therapy, my skin cleared, and I feel normal again.”
Fatima Y. – Istanbul, Turkey – May 2025 – ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
“Psoriasis made daily life uncomfortable. Thanks to Viezec’s stem cell therapy, my skin is smoother, and flare-ups are rare now.”
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy for psoriasis offers a promising and innovative approach by targeting the underlying immune dysfunction rather than just managing surface symptoms. At Viezec, we prioritize patient safety, clinical precision, and ethical medical practices to ensure every individual receives personalized care tailored to their condition. Our advanced regenerative treatment aims to restore skin health, reduce inflammation, and minimize relapse rates—helping patients achieve lasting relief and improved quality of life. With India emerging as a trusted destination for cutting-edge stem cell therapy, Viezec stands as your reliable healthcare partner in the journey toward healthier, clearer skin. Get in touch with our experts today to explore your treatment options with confidence and care.
Our Testimonials
Related Videos
Recent Blog Posts
4.8 average based on 654 reviews.






