Depression is a silent epidemic that continues to grow globally, affecting millions of people across all age groups and demographics. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 280 million people worldwide suffer from depression, making it one of the leading causes of disability. Despite advancements in mental health treatments, many individuals struggle to find relief through conventional therapies such as psychotherapy and antidepressant medications. These treatments, while beneficial for some, often come with limitations, including side effects, variable efficacy, and the risk of relapse. This has led researchers to explore alternative approaches, and one of the most promising breakthroughs in recent years is stem cell therapy. Stem cells, particularly those derived from cord blood, have shown immense potential in regenerating damaged tissues and modulating the immune system, offering new hope for those battling depression. This blog delves into the science behind stem cell therapy, its potential to revolutionize mental health treatment, and the role of cord blood in this groundbreaking field.
Understanding Depression: A Silent Epidemic
Depression is more than just feeling sad or going through a rough patch; it is a complex mental health disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest in daily activities. It can severely impact a person’s ability to function, affecting their relationships, work, and overall quality of life. Globally, depression is a leading cause of disability, with an estimated 5% of adults suffering from the condition. In India, the situation is equally alarming, with over 56 million people affected by depression. The emotional toll of depression is immense, but its impact extends beyond the individual. Families, communities, and economies bear the brunt of this condition, with lost productivity and increased healthcare costs adding to the burden. Despite its prevalence, depression often goes undiagnosed or untreated due to stigma, lack of awareness, and limited access to mental health services. This underscores the urgent need for innovative and effective treatments that can address the root causes of depression and provide lasting relief.
Current Treatments for Depression
The current treatment landscape for depression primarily revolves around psychotherapy and antidepressant medications. Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), helps patients identify and change negative thought patterns, while medications like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) aim to balance brain chemicals. However, these treatments are not without their challenges. Many patients experience side effects from medications, including weight gain, insomnia, and sexual dysfunction, which can lead to discontinuation. Additionally, not all patients respond to these treatments, and some may experience only partial relief. The risk of relapse is also high, with many individuals experiencing recurring episodes of depression despite ongoing treatment. These limitations have spurred interest in alternative therapies, particularly those that target the underlying biological mechanisms of depression. Stem cell therapy, with its ability to repair and regenerate damaged tissues, has emerged as a promising candidate for addressing the root causes of depression and providing long-lasting relief.
What Are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are unique cells with the remarkable ability to develop into different types of cells in the body. They serve as a repair system, capable of dividing and renewing themselves to replace damaged or diseased tissues. There are several types of stem cells, including embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Each type has its own potential and limitations, but all share the common ability to differentiate into specialized cells. Stem cells are particularly valuable in regenerative medicine, where they are used to treat a wide range of conditions, from spinal cord injuries to heart disease. Their regenerative potential has also sparked interest in their application for mental health disorders, including depression. By repairing damaged brain tissue and promoting neurogenesis (the growth of new neurons), stem cells offer a novel approach to treating depression that goes beyond symptom management to address the underlying causes of the condition.
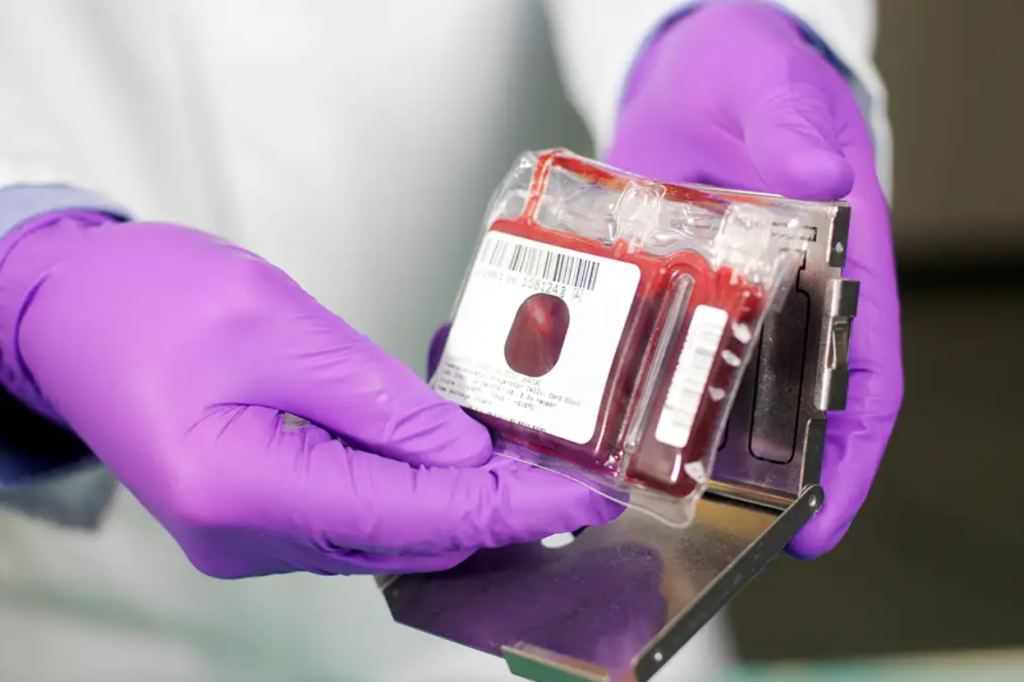
Cord Blood Stem Cells: A Valuable Resource
Cord blood, the blood collected from the umbilical cord and placenta after childbirth, is a rich source of stem cells. These stem cells, known as hematopoietic stem cells, have the ability to develop into various types of blood cells and have been used for decades in the treatment of blood disorders like leukemia. However, recent research has revealed that cord blood also contains other types of stem cells, including mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which have potent anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties. Unlike embryonic stem cells, which are derived from embryos, cord blood stem cells are obtained ethically and non-invasively, making them a more acceptable option for many. The process of collecting and storing cord blood is simple and painless, and it can be done at the time of birth. Once collected, the cord blood is cryogenically preserved in cord blood banks, where it can be stored for decades and used for future medical treatments. This makes cord blood a valuable resource not only for the child but also for family members who may benefit from its therapeutic potential.
Science Behind Stem Cells and Mental Health
The potential of stem cells to treat depression lies in their ability to repair and regenerate brain tissue. Depression has been linked to reduced neurogenesis (the growth of new neurons) and increased inflammation in the brain. Stem cells, particularly mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) found in cord blood, have been shown to promote neurogenesis and reduce inflammation, addressing two key factors associated with depression. Studies have demonstrated that stem cells can modulate the immune system, reducing the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines that contribute to brain inflammation. Additionally, stem cells release growth factors that support the survival and function of existing neurons, further enhancing brain health. Research on animal models has shown promising results, with stem cell therapy leading to improvements in depressive-like behaviors. These findings have paved the way for clinical trials in humans, offering hope for a new and effective treatment for depression.
Stem Cell Therapy for Depression: How It Works
Stem cell therapy for depression involves the administration of stem cells, typically through intravenous infusion, to target the underlying causes of the condition. Once in the body, these stem cells migrate to the brain, where they exert their therapeutic effects. They promote neurogenesis, reduce inflammation, and modulate the immune system, leading to improvements in mood and cognitive function. Unlike traditional treatments that focus on managing symptoms, stem cell therapy addresses the root causes of depression, offering the potential for long-lasting relief. Early clinical trials have shown promising results, with patients experiencing significant improvements in their symptoms and quality of life. For example, a study conducted in Japan found that patients with treatment-resistant depression showed marked improvements after receiving stem cell therapy. These findings suggest that stem cell therapy could be a game-changer for individuals who have not responded to conventional treatments.
 Global Advances in Stem Cell Therapy for Depression
Global Advances in Stem Cell Therapy for Depression
Stem cell therapy for depression is a rapidly evolving field, with researchers around the world making significant strides. In the United States, clinical trials are underway to evaluate the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapy for treatment-resistant depression. Japan, a leader in regenerative medicine, has approved stem cell therapies for various conditions and is actively researching their application for mental health disorders. India, too, is emerging as a key player in stem cell research, with several institutions conducting cutting-edge studies on the use of stem cells for depression. Success stories from patients who have undergone stem cell therapy highlight its potential to transform lives. For instance, a patient in the USA who had struggled with depression for decades reported significant improvements in mood and energy levels after receiving stem cell therapy. These global advances underscore the potential of stem cell therapy to revolutionize the treatment of depression and offer hope to millions of patients worldwide.
Stem Cell Therapy in India: A Growing Frontier
India is making significant contributions to the field of stem cell research, with several institutions and hospitals conducting pioneering studies. The country’s large population and high prevalence of depression make it an ideal setting for research and clinical trials. Indian researchers are exploring the use of stem cells derived from various sources, including cord blood, to treat depression and other mental health disorders. Cord blood banking is also gaining popularity in India, with more parents opting to store their baby’s cord blood for future medical use. However, challenges remain, including the need for greater awareness, regulatory oversight, and funding for research. Despite these hurdles, India’s progress in stem cell research holds great promise for the future of mental health treatment in the country and beyond.
Cord Blood Banking: A Lifeline for Future Therapies
Cord blood banking is a proactive step that parents can take to secure their child’s future health. By preserving cord blood at birth, families gain access to a valuable resource that can be used for a wide range of medical treatments, including stem cell therapy for depression. The process of cord blood banking is simple and painless, involving the collection of blood from the umbilical cord and placenta after childbirth. The collected blood is then processed and cryogenically stored in specialized facilities. While the initial cost of cord blood banking can be high, the potential benefits far outweigh the expense, especially considering the growing applications of stem cells in medicine. Ethical considerations, such as informed consent and transparency, are also important factors to consider when opting for cord blood banking. Public awareness campaigns are needed to educate families about the benefits of cord blood banking and its potential to save lives.
Promise of Cord Blood Stem Cells for Depression
Cord blood stem cells are particularly well-suited for treating depression due to their unique properties. Unlike other types of stem cells, cord blood stem cells are young and highly potent, with a greater capacity for differentiation and regeneration. They also have strong anti-inflammatory properties, making them ideal for addressing the brain inflammation associated with depression. Compared to embryonic stem cells, which raise ethical concerns, cord blood stem cells are obtained ethically and non-invasively. Additionally, cord blood stem cells are less likely to be rejected by the recipient’s immune system, reducing the risk of complications. Ongoing research is exploring the full potential of cord blood stem cells for treating depression, with promising results so far. As our understanding of stem cell biology advances, the possibilities for using cord blood stem cells to treat depression and other mental health disorders will continue to grow.
Challenges in Stem Cell Therapy for Depression
Despite its promise, stem cell therapy for depression faces several challenges. Scientifically, there is still much to learn about the mechanisms by which stem cells exert their effects and how to optimize their use for mental health conditions. Technical hurdles, such as ensuring the survival and integration of stem cells in the brain, also need to be addressed. Regulatory and ethical concerns, particularly regarding the use of embryonic stem cells, continue to be a topic of debate. Additionally, the high cost of stem cell therapy and limited accessibility pose significant barriers for many patients. Addressing these challenges will require continued research, collaboration, and investment in the field. Public and private sector support will be crucial in overcoming these obstacles and making stem cell therapy a viable option for depression treatment.
Role of Government and Policy in Stem Cell Research
Government support and policy play a crucial role in advancing stem cell research and therapy. In countries like the USA, Japan, and India, government funding and regulatory frameworks have facilitated the development of stem cell therapies for various conditions. However, more needs to be done to support research on stem cell therapy for mental health disorders. Policies that promote ethical research, ensure patient safety, and increase funding for clinical trials are essential for advancing the field. Public-private partnerships can also play a key role in accelerating research and making stem cell therapy more accessible. By fostering a supportive environment for stem cell research, governments can help unlock the full potential of this groundbreaking technology.
Public Perception and Awareness of Stem Cell Therapy
Public perception and awareness of stem cell therapy are critical for its acceptance and adoption. Despite its potential, many people have misconceptions about stem cells, often confusing them with embryonic stem cells or viewing them as experimental and unsafe. Educating the public about the science behind stem cells, their therapeutic potential, and the ethical considerations involved is essential for building trust and acceptance. Awareness campaigns, patient testimonials, and transparent communication from researchers and healthcare providers can help dispel myths and inform the public about the benefits of stem cell therapy. By fostering a better understanding of stem cells, we can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and treatment options.
The Future of Stem Cell Therapy for Depression
The future of stem cell therapy for depression is bright, with emerging technologies and innovations paving the way for more effective treatments. Advances in stem cell biology, such as the development of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and gene editing techniques, hold great promise for personalized medicine. These technologies could enable the creation of patient-specific stem cells, tailored to address the unique biological factors contributing to their depression. Long-term prospects for curing depression using stem cell therapy are also encouraging, with ongoing research exploring the potential for complete remission of symptoms. As our understanding of stem cells and their applications continues to grow, the possibilities for treating depression and other mental health disorders will expand, offering new hope for patients worldwide.
Integrating Stem Cell Therapy with Other Treatments
Stem cell therapy is not a standalone treatment but rather a complementary approach that can be integrated with other therapies for depression. Combining stem cell therapy with psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes can provide a holistic approach to mental health. For example, psychotherapy can help patients address the psychological factors contributing to their depression, while stem cell therapy targets the biological underpinnings of the condition. Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management, can further support the therapeutic effects of stem cells. By taking a comprehensive approach to treatment, patients can achieve better outcomes and improve their overall well-being.
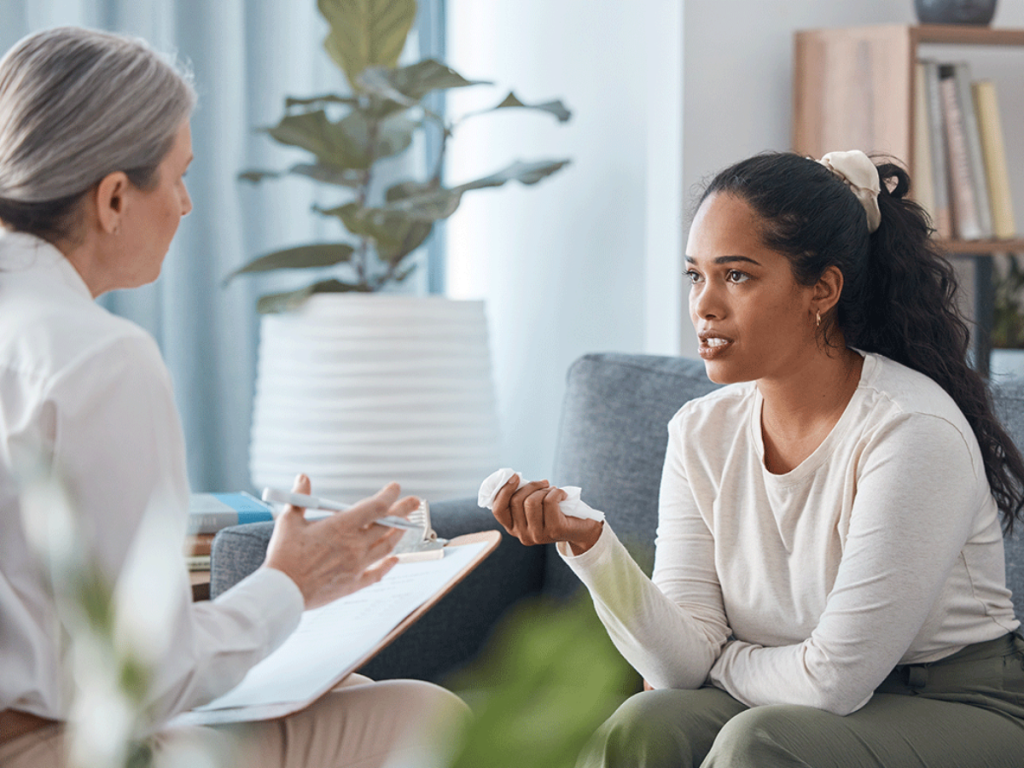
How to Access Stem Cell Therapy for Depression
Accessing stem cell therapy for depression requires careful consideration and research. Patients interested in exploring this option should start by consulting with a healthcare provider who specializes in stem cell therapy. It is important to choose a reputable clinic or research center with a track record of success in stem cell treatments. Patients should also be aware of the costs and risks involved, as stem cell therapy can be expensive and is not yet widely covered by insurance. Understanding the potential benefits and limitations of stem cell therapy is crucial for making an informed decision. By taking these steps, patients can explore the potential of stem cell therapy as a treatment option for depression.
A New Hope for Depression Patients
Stem cell therapy, particularly using cord blood stem cells, offers a new hope for individuals battling depression. By addressing the root causes of the condition and promoting brain repair and regeneration, stem cell therapy has the potential to provide lasting relief and improve quality of life. While challenges remain, ongoing research and innovation are paving the way for more effective and accessible treatments. The promise of stem cell therapy underscores the importance of continued investment in research and public awareness. For those struggling with depression, stem cell therapy represents a beacon of hope, offering the possibility of a brighter, healthier future.
Call to Action
If you or a loved one is considering stem cell therapy for depression, take the first step by educating yourself about the potential benefits and risks. Consider cord blood banking as a proactive measure to secure future health options. Support stem cell research and mental health initiatives by advocating for increased funding and awareness. Together, we can unlock the full potential of stem cell therapy and transform the lives of millions battling depression.


 Global Advances in Stem Cell Therapy for Depression
Global Advances in Stem Cell Therapy for Depression