Stem cell therapy has quickly become one of the most promising advancements in modern medicine. With ongoing research and technological breakthroughs, these treatments are becoming more accessible and widely recognized. Stem cell therapies hold significant potential for treating a broad range of diseases, offering hope for patients with conditions that traditional treatments can’t address. From chronic degenerative diseases to life-threatening illnesses, stem cell therapy provides new possibilities for healing and recovery. Despite its promise, many wonder about the effectiveness of these therapies. This article will delve into how stem cell therapy works, the diseases it can treat, its benefits, and the risks involved. We’ll also examine the success rates of stem cell treatments to help you understand its true potential. By the end of this guide, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of how stem cell therapy may be a viable treatment option for various medical conditions.
What Is Stem Cell Therapy?
Definition of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy involves using stem cells to treat or prevent a disease or condition. Stem cells are unique because they have the ability to develop into different types of cells in the body, such as muscle cells, nerve cells, and blood cells. This regenerative potential makes stem cell therapy an attractive option for treating various diseases and injuries.
Types of Stem Cells Used in Therapy
There are several types of stem cells used in therapy, including:
-
Embryonic Stem Cells – These stem cells are derived from early-stage embryos. They are pluripotent, meaning they can become any type of cell in the body, making them highly versatile for treatment.
-
Adult Stem Cells – Found in tissues like bone marrow, these cells are multipotent, meaning they can turn into a limited range of cell types but are still useful for regenerating damaged tissues.
-
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs) – These are adult stem cells that have been genetically reprogrammed to behave like embryonic stem cells. They have the potential to develop into nearly any cell type, offering exciting therapeutic possibilities.
How Stem Cell Therapy Works
Stem cell therapy works by introducing stem cells into the body, either to replace damaged cells or to stimulate the body’s healing process. The stem cells can be delivered directly to the affected area or injected into the bloodstream, depending on the disease being treated. These cells then begin to differentiate and help regenerate damaged tissues, improve function, and in some cases, even reverse disease progression.
How Effective Is Stem Cell Therapy for Treating Specific Diseases?
Stem cell therapy is showing promise in the treatment of various diseases. Here’s a look at how it works for some common conditions:
Stem Cell Therapy for Arthritis
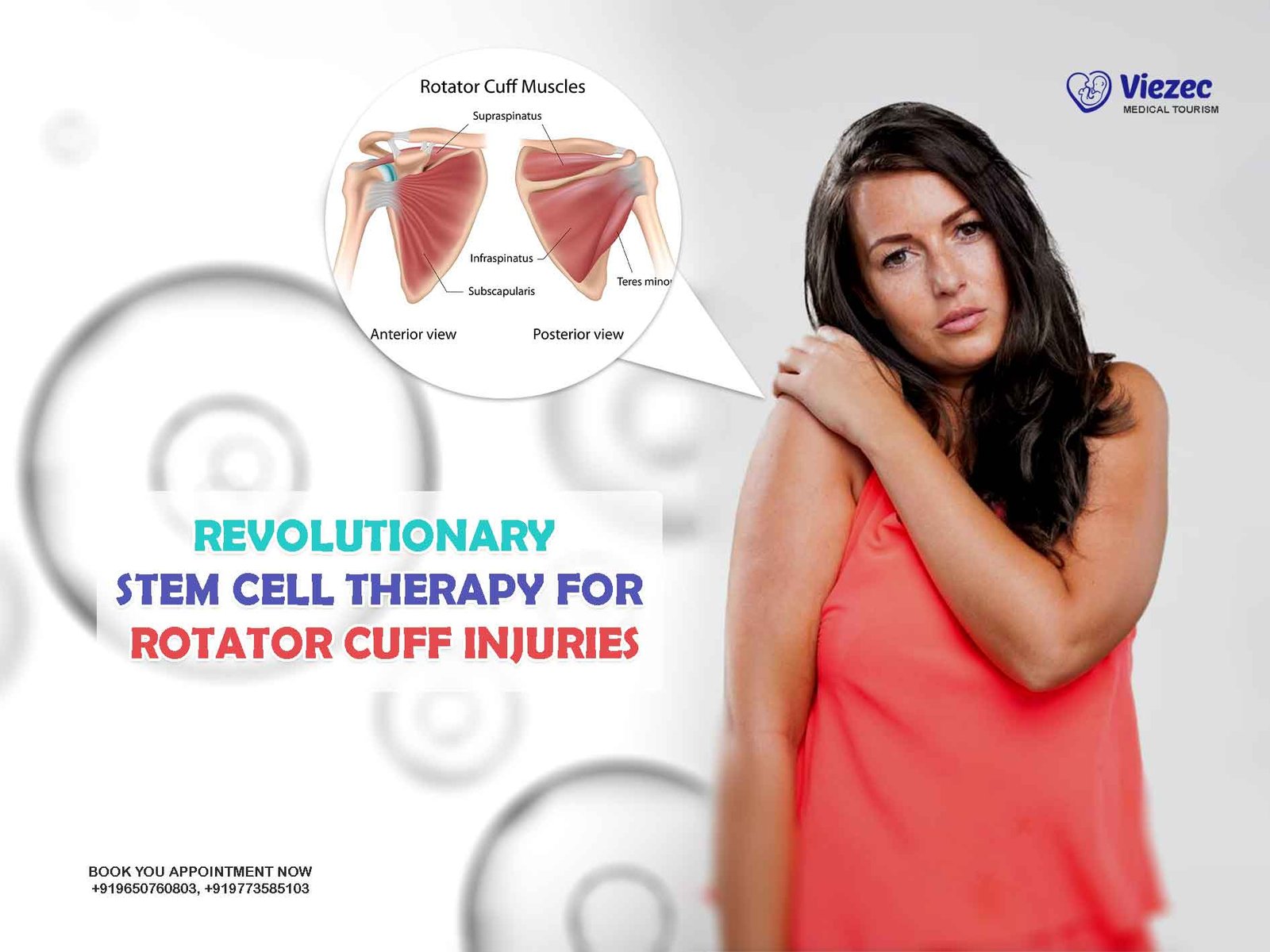
Arthritis is a degenerative disease that affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Stem cell therapy offers a potential treatment by regenerating cartilage and tissue within the joints. Several studies have shown that stem cell injections can reduce inflammation and promote healing in arthritic joints, offering long-term relief for patients.
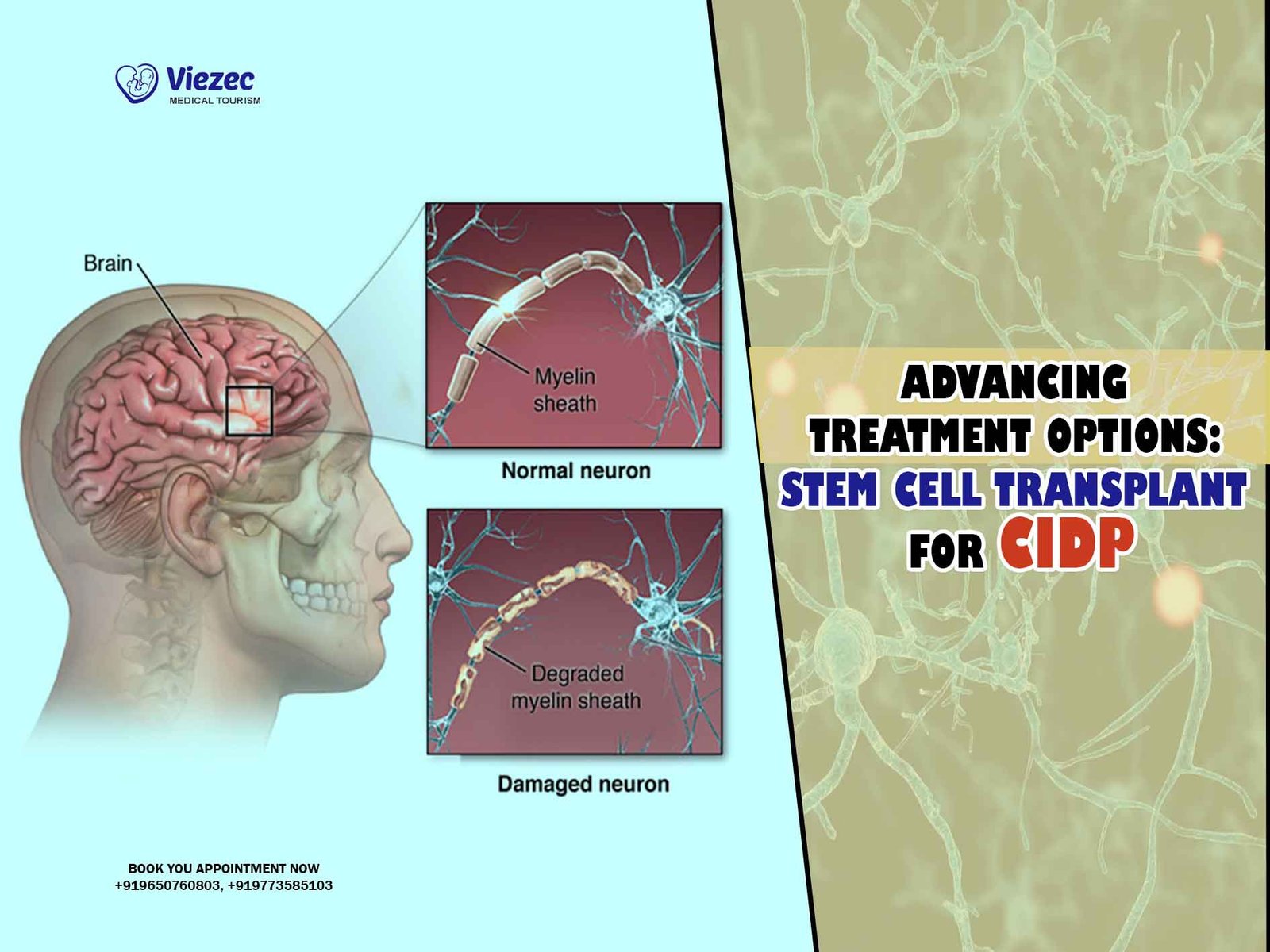
Stem Cell Therapy for Neurological Disorders (e.g., Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s)
Neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s are among the most challenging conditions to treat. Stem cell therapy is being explored as a way to regenerate damaged brain cells, reduce neuroinflammation, and potentially slow or halt disease progression. Early clinical trials have shown positive results, with some patients experiencing improvements in motor function and cognition.
Stem Cell Therapy for Heart Disease
Heart disease is a leading cause of death worldwide, and stem cell therapy offers a promising solution. By injecting stem cells into the heart muscle, doctors aim to regenerate damaged tissue, improve heart function, and reduce the risk of heart failure. Some studies have demonstrated improvements in heart function and reduced scarring after stem cell therapy, though more research is needed to confirm long-term effectiveness.
Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetes
Stem cell therapy is being investigated as a potential treatment for type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The goal is to use stem cells to regenerate insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, potentially offering a cure for diabetes. While this therapy is still in the experimental stage, initial studies have shown encouraging results, particularly in animal models.
Stem Cell Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury
Stem cells have the potential to repair damaged spinal cord tissue and restore function in patients with paralysis. In clinical trials, stem cells have been shown to improve mobility and sensation in some individuals with spinal cord injuries, though these results are still in early stages.
Stem Cell Therapy for Cancer Treatment
Stem cell therapy is also being explored as a complementary treatment for cancer. Researchers are investigating the use of stem cells to enhance the effectiveness of chemotherapy, promote the regeneration of healthy tissue after cancer treatment, and even use stem cells to attack cancer cells directly. While this area of research is still developing, the potential for stem cell-based cancer therapies is enormous.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy in Disease Treatment
Stem cell therapy offers a wide array of potential benefits for treating diseases, focusing on regeneration, healing, and personalized care.
Regenerative Potential
One of the most exciting aspects of stem cell therapy is its regenerative potential. Stem cells can help repair or replace damaged tissues, promoting healing in affected areas. This regenerative capability offers patients the possibility of recovery from previously untreatable conditions. Over time, stem cells could significantly improve the overall quality of life for individuals suffering from chronic conditions.
Minimally Invasive Treatment
Unlike traditional surgeries, stem cell therapy is a minimally invasive treatment. The process typically involves injections or small incisions that are less traumatic to the body. This reduces the risk of complications and speeds up recovery, allowing patients to return to normal activities more quickly. As a result, stem cell therapy is seen as a more patient-friendly alternative to conventional surgical treatments.
Potential for Personalized Medicine
Stem cell therapy can be customized to the individual, offering a more personalized treatment experience. By using the patient’s own stem cells, the treatment is less likely to trigger immune rejection. This personalized approach allows for more precise targeting of specific medical issues, improving the chances of successful outcomes. Additionally, tailoring stem cell therapy to each patient ensures that the treatment is both safe and effective for their unique needs.
Risks and Limitations of Stem Cell Therapy
While stem cell therapy holds great promise, it is not without its risks:
Possible Side Effects
Although generally considered safe, stem cell therapy can have side effects, including infection, inflammation, or even tumor formation in rare cases. These risks are minimized by careful screening and using cells derived from the patient’s own body.
Ethical Considerations
The use of embryonic stem cells raises ethical concerns due to the destruction of embryos required for obtaining these cells. This has sparked debate within the medical and ethical communities, leading many researchers to focus on alternatives like iPSCs.
Regulatory and Safety Concerns
Stem cell therapy is not yet universally regulated, and in some countries, treatments are being offered without proper clinical testing or oversight. Patients should ensure that they are receiving therapy from licensed and reputable providers to minimize risks.
Success Rates of Stem Cell Therapy
Key Factors That Influence Success
The success of stem cell therapy depends on various factors, including the type of disease being treated, the patient’s overall health, and the quality of the stem cells used. For instance, younger patients or those with less severe conditions tend to have better outcomes.
Scientific Studies on Stem Cell Therapy Success
Numerous studies have shown promising results in stem cell therapy. For example, clinical trials have demonstrated that stem cell injections can reduce pain and improve function in patients with osteoarthritis. However, it’s important to note that results can vary, and more long-term studies are needed to establish consistent success rates.
How to Determine If Stem Cell Therapy Is Right For You
Consultations with Healthcare Providers
Before opting for stem cell therapy, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider. They will evaluate your medical history, overall health, and the specifics of your condition. A healthcare provider can help you determine if you’re a suitable candidate for stem cell therapy. They will guide you through potential treatment options and ensure you’re fully informed about the therapy’s benefits and risks.
Factors to Consider Before Choosing Stem Cell Therapy
Consider the type of disease you’re dealing with and how advanced it is. Understanding whether stem cell therapy is an approved treatment or still experimental for your condition is crucial. You should also research different providers to ensure they are reputable and experienced. Finally, be sure to assess the costs, risks, and potential benefits before making a decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Diseases Can Be Treated with Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cell therapy has been investigated for treating a wide variety of conditions, including arthritis, neurological disorders, heart disease, diabetes, spinal cord injuries, and cancer.
Is Stem Cell Therapy Safe?
While stem cell therapy is generally considered safe, it does come with some risks, including infection and possible tumor formation. The safety of the therapy largely depends on the type of stem cells used and the experience of the medical provider.
How Much Does Stem Cell Therapy Cost?
The cost of stem cell therapy can vary widely depending on the condition being treated, the type of stem cells used, and the country in which the therapy is administered. In general, treatments can range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars.
How Long Does It Take to See Results from Stem Cell Therapy?
Results can vary, but many patients start to notice improvements within a few weeks to months after treatment. Some conditions may require multiple sessions to achieve optimal results.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy holds immense promise in treating a variety of diseases, from arthritis to cancer. While it is not without risks, its regenerative potential and ability to personalize treatment make it a compelling option for many patients. Ongoing research continues to expand our understanding of stem cell therapy’s effectiveness, and as science progresses, these treatments may become more widely available and effective. If you’re considering stem cell therapy, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if it’s the right option for you.
Interested in learning more about stem cell therapy? Schedule a consultation with one of our experts to explore how this innovative treatment could help you. Download our free guide to stem cell therapy for more information and take the first step towards better health today!