Stem cell therapy is revolutionizing the medical field with its potential to treat a variety of conditions, including chronic pain. At its core, stem cell therapy involves using undifferentiated cells, which have the ability to develop into different types of cells, to repair or replace damaged tissues. This innovative approach aims to harness the body’s own repair mechanisms, offering a promising alternative to traditional pain management strategies that often rely on medications or invasive surgeries. As research and technology advance, stem cell therapy continues to evolve, opening new avenues for more effective and long-lasting pain relief.
Evolution of Stem Cell Use in Pain Treatment
The journey of stem cell therapy from experimental research to clinical application has been remarkable. Initially, stem cells were primarily studied in the context of regenerative medicine, focusing on their potential to repair organs and tissues. Over the past decade, however, there has been a growing interest in their application for pain management. This shift has been driven by a deeper understanding of pain mechanisms and the discovery that stem cells can modulate inflammatory responses and promote tissue healing. Today, stem cell therapy is being integrated into pain treatment protocols, offering hope to patients suffering from conditions that were previously deemed untreatable.
Understanding Pain Mechanisms and Stem Cell Interaction
Mechanisms of Chronic Pain
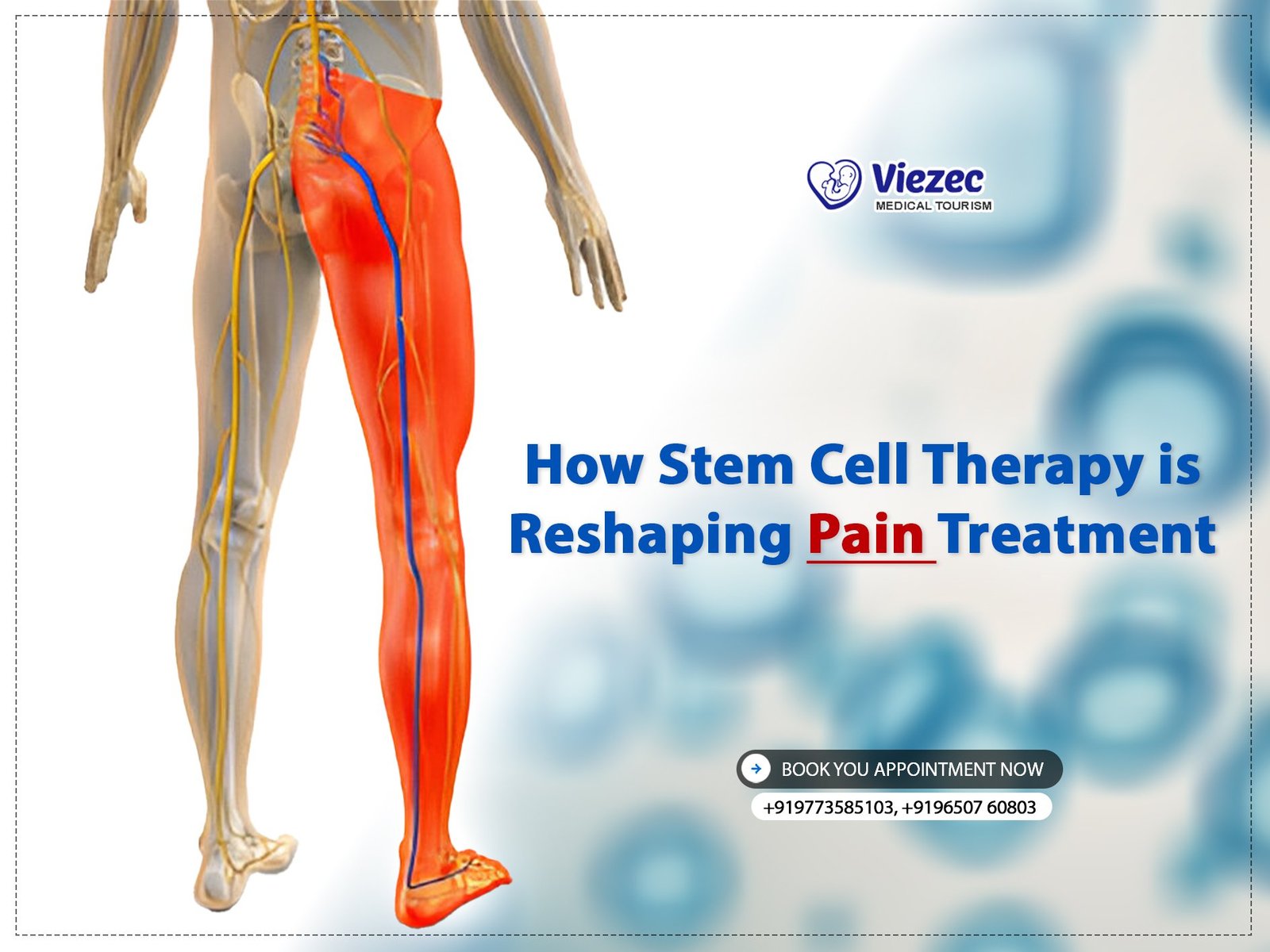
Chronic pain is a complex condition that can result from various underlying causes, including injury, inflammation, and nerve damage. Unlike acute pain, which serves as a protective response to immediate harm, chronic pain persists for extended periods, often without a clear cause. It involves changes in the nervous system that enhance pain perception, making even non-painful stimuli feel painful. This condition can significantly impair a person’s quality of life, leading to physical, emotional, and psychological distress. Understanding the mechanisms of chronic pain is crucial for developing effective treatments, and this is where stem cell therapy shows significant promise.
Role of Stem Cells in Pain Reduction
Stem cells have emerged as a powerful tool in pain management due to their unique properties. They possess anti-inflammatory capabilities, which are essential for reducing pain associated with inflammation. Additionally, stem cells can modulate immune responses, thereby decreasing the hypersensitivity that contributes to chronic pain. Their ability to differentiate into various cell types allows them to repair damaged tissues, further alleviating pain. By addressing the root causes of pain rather than just the symptoms, stem cell therapy offers a more comprehensive and potentially long-lasting solution for patients suffering from chronic pain conditions.
Anti-inflammatory Properties of Stem Cells
One of the key mechanisms by which stem cells alleviate pain is through their anti-inflammatory properties. Inflammation is a common contributor to pain, especially in conditions like arthritis and tendonitis. Stem cells secrete various bioactive molecules that can reduce inflammation, thereby decreasing pain and promoting tissue healing. These anti-inflammatory effects help to create a more conducive environment for tissue regeneration and repair, which is essential for sustained pain relief. This ability to target inflammation directly makes stem cell therapy a promising option for treating various chronic pain conditions.
Modulation of Immune Responses
Stem cells also play a crucial role in modulating the body’s immune responses. In chronic pain conditions, the immune system often becomes dysregulated, leading to persistent inflammation and pain. Stem cells can help restore balance by regulating immune cell activity and reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This immunomodulatory effect not only helps in reducing pain but also aids in preventing further tissue damage. By targeting the immune system, stem cell therapy offers a novel approach to pain management that goes beyond mere symptom control, aiming to address the underlying causes of chronic pain.
Types of Stem Cells Used in Pain Management
Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs)
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are derived from early-stage embryos and have the unique ability to differentiate into any cell type in the body. This pluripotency makes them incredibly versatile and valuable for research and potential therapeutic applications. In the context of pain management, ESCs have shown promise in preclinical studies for their ability to regenerate damaged tissues and reduce inflammation. However, their use in clinical settings is limited due to ethical concerns and the potential for tumorigenesis. Despite these challenges, ongoing research continues to explore the safe and effective use of ESCs in treating chronic pain conditions.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are among the most widely studied and utilized stem cells in pain management. They can be sourced from various tissues, including bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood. MSCs are known for their anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties, making them ideal candidates for treating chronic pain. They can differentiate into a variety of cell types, including bone, cartilage, and muscle cells, which is particularly beneficial for repairing damaged tissues. MSCs have demonstrated efficacy in reducing pain and improving function in conditions such as osteoarthritis, tendonitis, and spinal cord injuries.
Sources of MSCs (Bone Marrow, Adipose Tissue, etc.)
MSCs can be harvested from several sources, each with its own advantages. Bone marrow-derived MSCs (BM-MSCs) are well-established and have been extensively studied for their therapeutic potential. Adipose tissue-derived MSCs (AD-MSCs) are easier to obtain in larger quantities and have shown similar regenerative capabilities. Umbilical cord-derived MSCs (UC-MSCs) offer a non-invasive source and are abundant in young, potent cells. The choice of MSC source depends on various factors, including the patient’s condition, availability of tissue, and the specific therapeutic goals. Each source provides unique benefits, contributing to the versatility of MSC therapy in pain management.
Characteristics and Benefits in Pain Therapy
MSCs are characterized by their ability to migrate to sites of injury, where they can exert their therapeutic effects. Their anti-inflammatory properties help reduce pain by decreasing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Additionally, MSCs secrete growth factors that promote tissue repair and regeneration, which is crucial for long-term pain relief. Their immunomodulatory effects further enhance their therapeutic potential, as they can modulate the activity of immune cells to prevent chronic inflammation. These characteristics make MSCs an attractive option for treating a wide range of chronic pain conditions, offering a multifaceted approach to pain management.
Applications of Stem Cell Therapy in Different Types of Pain
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Regeneration
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Traditional treatments focus on symptom relief but do not address the underlying cause of cartilage degradation. Stem cell therapy, particularly using MSCs, offers a promising alternative by promoting cartilage regeneration and reducing inflammation. MSCs can differentiate into chondrocytes, the cells responsible for cartilage formation, thereby aiding in the repair of damaged cartilage. Clinical studies have shown that stem cell therapy can improve joint function and reduce pain in patients with OA, offering a potential long-term solution.
Neuropathic Pain Conditions
Neuropathic pain results from damage to the nervous system and can be particularly challenging to treat. Conditions such as spinal cord injuries and peripheral neuropathy often result in chronic pain that is resistant to conventional treatments. Stem cell therapy has shown promise in these conditions by promoting nerve regeneration and modulating pain pathways. MSCs, in particular, have demonstrated the ability to reduce neuropathic pain through their anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. By addressing the underlying nerve damage and reducing inflammation, stem cell therapy offers hope for patients suffering from debilitating neuropathic pain.
Spinal Cord Injury
Spinal cord injuries (SCI) often result in severe, chronic pain that significantly impacts quality of life. Stem cell therapy offers a novel approach to treating SCI-related pain by promoting nerve regeneration and reducing inflammation. MSCs have been shown to support the repair of damaged spinal cord tissues, potentially restoring function and reducing pain. Clinical studies are ongoing to determine the optimal methods and timing for stem cell administration in SCI patients. Early results are promising, indicating that stem cell therapy could become a key component in the treatment of spinal cord injuries and associated pain.
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often caused by diabetes or chemotherapy, involves damage to the peripheral nerves, leading to pain, numbness, and weakness. Stem cell therapy has emerged as a potential treatment option, offering pain relief and nerve regeneration. MSCs can enhance nerve repair by secreting growth factors and reducing inflammation. Clinical trials are exploring the efficacy of stem cell therapy in alleviating the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy. Preliminary findings suggest that stem cell therapy can improve nerve function and reduce pain, offering a promising alternative to current treatments that mainly focus on symptom management.
Clinical Studies and Evidence Supporting Stem Cell Efficacy
Review of Clinical Trials
Numerous clinical trials have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy of stem cell therapy in pain management. These studies have investigated a range of conditions, including osteoarthritis, intervertebral disc degeneration, and tendinopathies. Overall, the results have been promising, with many patients experiencing significant pain reduction and improved function. However, it is important to note that not all studies have been successful, and further research is needed to refine treatment protocols and optimize outcomes.
Key Findings and Success Rates
The key findings from clinical trials highlight the potential of stem cell therapy to provide long-lasting pain relief and functional improvement. Success rates vary depending on the condition treated, the type of stem cells used, and the delivery method. For example, studies on osteoarthritis have reported success rates ranging from 60% to 80%, while trials on intervertebral disc degeneration have shown pain reduction in up to 70% of patients. These results underscore the need for continued research to identify the most effective treatment approaches.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the promising results, there are several challenges and limitations associated with stem cell therapy. One major challenge is the variability in treatment outcomes, which can be influenced by factors such as patient age, disease severity, and stem cell quality. Additionally, there are concerns about the long-term safety of stem cell treatments, particularly regarding the risk of tumorigenesis and immunogenicity. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for the widespread adoption of stem cell therapy in pain management.
Techniques and Procedures in Stem Cell Administration
Injection Methods and Delivery Systems
The success of stem cell therapy largely depends on the method of administration. There are several injection methods and delivery systems used to administer stem cells, each with its advantages and limitations. Common methods include direct injections into the affected area and intravenous infusions. The choice of method depends on the condition being treated and the desired therapeutic outcome.
Direct Injections vs. Intravenous Infusions
Direct injections involve delivering stem cells directly into the affected tissue, such as joints, tendons, or intervertebral discs. This method allows for a high concentration of stem cells at the target site, potentially enhancing therapeutic efficacy. On the other hand, intravenous infusions involve injecting stem cells into the bloodstream, allowing them to travel to the affected area via the circulatory system. This approach can be beneficial for systemic conditions but may result in a lower concentration of stem cells at the target site.
Customization of Treatment Plans
Personalized treatment plans are essential for optimizing the outcomes of stem cell therapy. Factors such as the patient’s medical history, the severity of the condition, and the type of stem cells used must be considered when developing a treatment plan. Customization may involve selecting the appropriate stem cell source, determining the optimal delivery method, and adjusting the treatment schedule based on the patient’s response. By tailoring the therapy to the individual, clinicians can maximize the chances of a successful outcome.
Safety, Ethics, and Regulatory Considerations
Safety Profiles of Stem Cell Therapies
Safety is a critical concern in the development and application of stem cell therapies. While many studies have demonstrated the safety of these treatments, there are potential risks that must be carefully managed. Common safety concerns include the risk of tumorigenesis, immunogenicity, and infection. Ensuring the highest standards of quality and safety in stem cell processing and administration is essential to minimize these risks.
Risk of Tumorigenesis and Immunogenicity
The risk of tumorigenesis, or the formation of tumors, is a significant concern with stem cell therapy. This risk can arise from the uncontrolled proliferation of transplanted stem cells. Similarly, immunogenicity, or the potential for an immune response against the transplanted cells, can also pose challenges. To mitigate these risks, researchers are developing techniques to ensure the purity and safety of stem cell preparations, such as rigorous screening and genetic modification to prevent abnormal growth.
Patient Selection and Informed Consent
Careful patient selection is crucial to the success of stem cell therapy. Not all patients are suitable candidates for these treatments, and thorough screening is necessary to identify those who are most likely to benefit. Additionally, obtaining informed consent is a vital ethical consideration. Patients must be fully informed about the potential risks and benefits of the therapy, as well as alternative treatment options, to make an informed decision about their care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What conditions can stem cell therapy treat?
Stem cell therapy can treat a variety of conditions, particularly those involving chronic pain and tissue damage. Common applications include osteoarthritis, intervertebral disc degeneration, and chronic tendinopathies. Research is ongoing to expand the range of conditions that can be effectively treated with stem cell therapy.
How long does it take to see results from stem cell therapy?
The time it takes to see results from stem cell therapy can vary depending on the condition being treated and the individual’s response to the therapy. Some patients may experience improvements within a few weeks, while others may take several months to notice significant changes. It’s important to have realistic expectations and follow the treatment plan prescribed by the healthcare provider.
Are there any side effects associated with stem cell therapy?
While stem cell therapy is generally considered safe, there are potential side effects to be aware of. These can include mild pain or swelling at the injection site, infection, and, in rare cases, an immune response or tumor formation. Patients should discuss the potential risks with their healthcare provider before undergoing treatment.
How can I determine if I am a candidate for stem cell therapy?
To determine if you are a candidate for stem cell therapy, you should consult with a healthcare provider who specializes in regenerative medicine. They will conduct a thorough evaluation of your medical history, current condition, and treatment goals to determine if stem cell therapy is a suitable option for you. This process may include imaging studies, laboratory tests, and a review of previous treatments.
For more information on stem cell therapy and to find a qualified provider, visit us online.