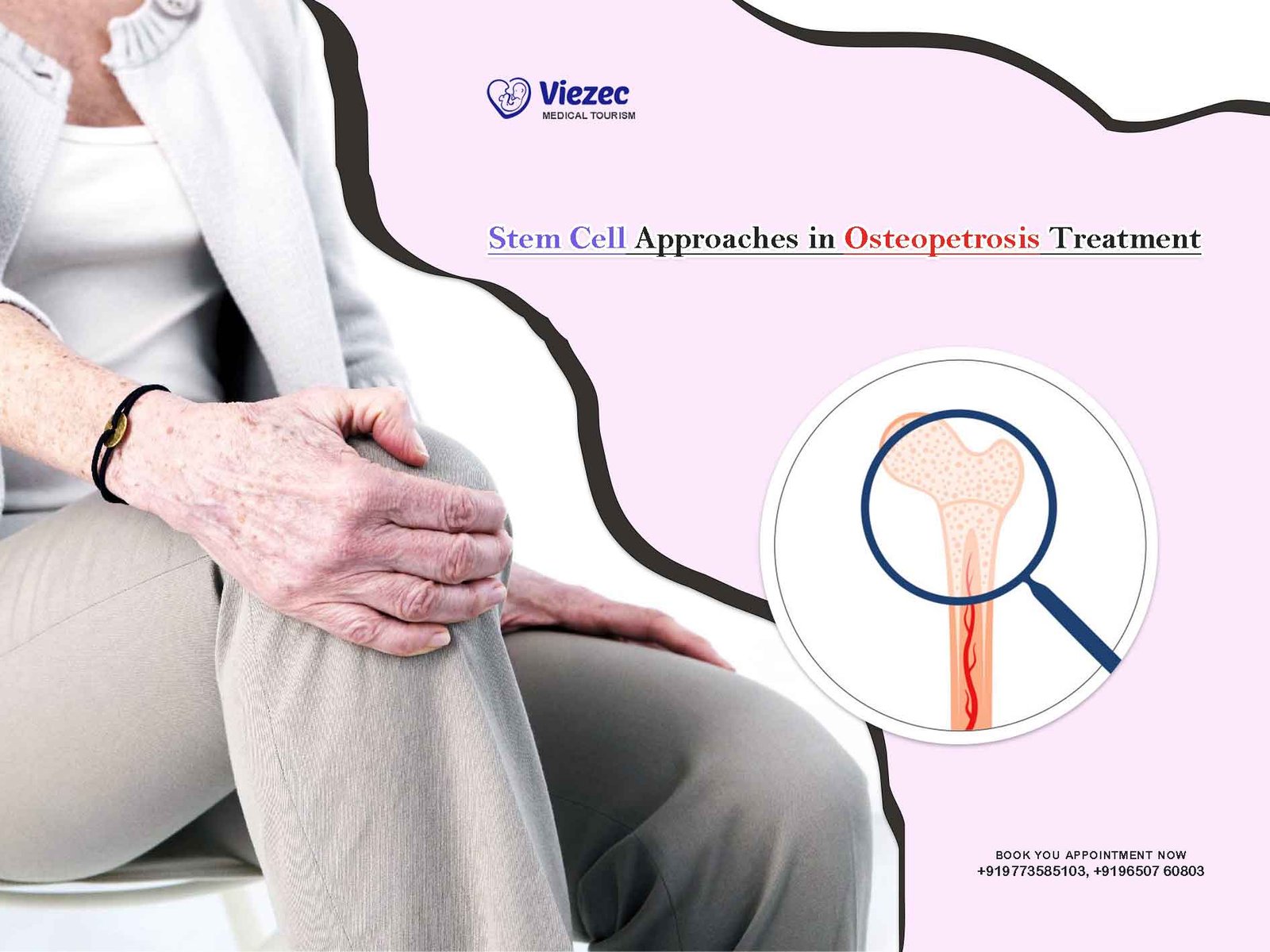
Osteopetrosis, a rare genetic disorder characterized by increased bone density, poses significant challenges in treatment due to its complexity and varied manifestations. Stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising avenue for addressing this condition, offering potential avenues for both symptom management and even curative interventions. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the mechanisms of osteopetrosis, the limitations of current treatment modalities, and the exciting prospects of stem cell approaches in transforming the landscape of osteopetrosis management.
Understanding Osteopetrosis
What is Osteopetrosis?
Osteopetrosis, also known as marble bone disease or Albers-Schönberg disease, is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the abnormal thickening and hardening of bones. This condition arises due to defects in the differentiation or function of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone resorption, leading to impaired bone remodeling. As a result, excessive bone formation occurs, resulting in dense, brittle bones prone to fractures and deformities.
Types of Osteopetrosis
Osteopetrosis manifests in several forms, ranging from mild to severe, with varying onset and severity of symptoms. The classification includes:
1. Autosomal Recessive Osteopetrosis (ARO)
ARO, the most severe form of osteopetrosis, typically presents in infancy or early childhood. It is caused by mutations in genes such as TCIRG1, CLCN7, and OSTM1, which encode proteins crucial for osteoclast function. Patients with ARO experience life-threatening complications, including bone marrow failure, neurological impairment, and recurrent infections.
2. Autosomal Dominant Osteopetrosis (ADO)
ADO usually presents later in childhood or adulthood and is less severe compared to ARO. Mutations in genes such as CLCN7 and PLEKHM1 underlie this form of osteopetrosis. While symptoms may vary, individuals with ADO often exhibit fractures, osteomyelitis, and dental abnormalities.
3. Intermediate Osteopetrosis
Intermediate osteopetrosis encompasses a spectrum of presentations between ARO and ADO in terms of severity and age of onset. It may result from mutations in genes such as CLCN7, CAII, or TNFSF11, among others.
Current Treatment Challenges
1. Symptomatic Management
Traditional approaches to managing osteopetrosis primarily focus on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. This often involves a combination of supportive measures such as analgesics for pain management, orthopedic interventions for fractures, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) in severe cases to address bone marrow failure.
2. Limitations of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
While HSCT offers the potential for cure in some cases of severe osteopetrosis by providing functional osteoclasts derived from donor stem cells, it is associated with significant risks, including graft-versus-host disease, transplant rejection, and long-term complications. Additionally, finding suitable donors can be challenging, particularly in the absence of compatible siblings.
Stem Cell Therapy: A Paradigm Shift in Osteopetrosis Treatment
Mechanisms of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy holds immense promise in addressing the root cause of osteopetrosis by replenishing defective osteoclasts or modulating bone metabolism. Several approaches are being explored:
1. Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) Therapy
MSCs, multipotent cells capable of differentiating into various cell types, including osteoblasts and osteoclasts, offer a versatile platform for osteopetrosis treatment. By introducing healthy MSCs into affected individuals, it is possible to enhance bone remodeling and restore bone homeostasis.
2. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPSC) Technology
iPSCs, generated by reprogramming somatic cells into a pluripotent state, hold immense potential in personalized medicine for osteopetrosis. Patient-specific iPSCs can be differentiated into osteoclast precursor cells, offering a tailored approach to treatment while minimizing the risk of immune rejection.
3. Gene Therapy
Advancements in gene editing technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9 present opportunities for correcting genetic mutations underlying osteopetrosis. By precisely targeting and repairing defective genes in patient-derived stem cells, it is conceivable to generate functional osteoclasts capable of normal bone remodeling.
Preclinical and Clinical Insights
1. Preclinical Studies
Preclinical investigations utilizing animal models of osteopetrosis have demonstrated the efficacy of stem cell-based approaches in ameliorating skeletal abnormalities and improving bone strength. Studies employing MSCs, iPSCs, and gene-edited stem cells have shown promising outcomes, paving the way for clinical translation.
2. Clinical Trials
While clinical trials specific to stem cell therapy in osteopetrosis are limited, ongoing research in related fields such as bone marrow disorders and genetic bone diseases provides valuable insights. Early-phase trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of MSC-based therapies are underway, with preliminary results showcasing encouraging outcomes in terms of bone density improvement and symptom relief.
Challenges and Future Directions
1. Immunogenicity and Engraftment
One of the foremost challenges in stem cell therapy for osteopetrosis is ensuring the long-term engraftment and functionality of transplanted cells, particularly in the context of immune-mediated rejection. Strategies to enhance immunomodulation and promote graft acceptance are imperative for the success of these approaches.
2. Safety Concerns
The safety profile of stem cell-based interventions warrants thorough assessment, encompassing the risk of tumorigenesis, ectopic tissue formation, and off-target effects associated with gene editing technologies. Rigorous preclinical evaluation and close monitoring of patients are essential to mitigate potential adverse events.
3. Translational Hurdles
Translating promising preclinical findings into clinically viable therapies necessitates addressing various translational hurdles, including scalability, standardization of manufacturing processes, regulatory approvals, and cost-effectiveness. Collaborative efforts involving academia, industry, and regulatory bodies are essential to expedite the transition from bench to bedside.
Make informed Decision
Stem cell therapy represents a paradigm shift in the management of osteopetrosis, offering novel avenues for targeted intervention and personalized treatment strategies. While considerable challenges lie ahead, the convergence of stem cell biology, regenerative medicine, and gene editing technologies holds immense promise in transforming the outlook for individuals affected by this debilitating disorder. By harnessing the regenerative potential of stem cells and advancing our understanding of bone biology, we embark on a journey towards realizing the vision of effective and curative therapies for osteopetrosis.