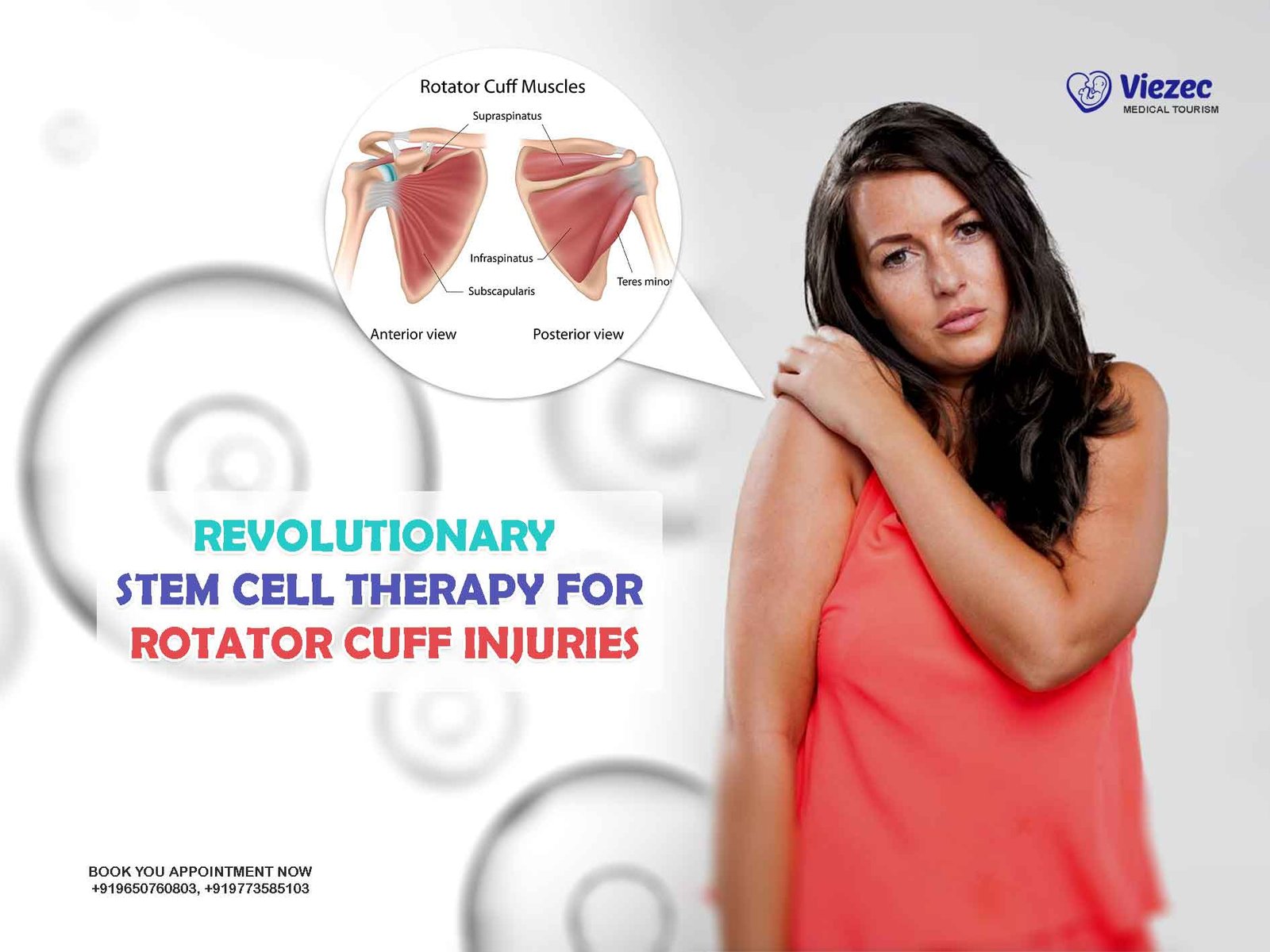
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint, providing stability and enabling a wide range of movements. Comprising four primary muscles—supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis—the rotator cuff is crucial for lifting and rotating the arm. These muscles work in unison to stabilize the head of the humerus firmly within the shallow socket of the shoulder. When the rotator cuff is injured, it can lead to pain, weakness, and reduced range of motion, significantly impacting daily activities and quality of life.
Common Causes of Rotator Cuff Injuries
Rotator cuff injuries can arise from various factors, including acute trauma, repetitive motion, and degenerative changes. Acute injuries often occur due to sudden movements or heavy lifting, leading to tears or strains. Repetitive overhead activities, such as those performed by athletes and manual laborers, can cause overuse injuries. Degenerative changes, which are more common in older adults, result from the gradual wearing down of the tendons. Other contributing factors include poor posture, inadequate warm-up before exercise, and genetic predisposition. Understanding these causes is vital for prevention and effective treatment.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common symptoms of rotator cuff injuries include shoulder pain, particularly when lifting the arm, weakness, and a crackling sensation during movement. Pain may be persistent and worsen at night, especially when lying on the affected side. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical examination, patient history, and imaging studies such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound. During the physical exam, the doctor may perform specific maneuvers to assess the range of motion, strength, and areas of tenderness. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the most appropriate treatment approach.
Traditional Treatment Options
Traditional treatments for rotator cuff injuries range from conservative methods to surgical interventions. Conservative treatments include rest, ice application, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy to strengthen the surrounding muscles and improve flexibility. Corticosteroid injections may also be administered to reduce inflammation and pain. In cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical options such as arthroscopic repair, tendon transfer, or shoulder replacement may be considered. While these treatments can be effective, they often involve prolonged recovery periods and carry risks of complications.
Stem Cell Therapy: A New Horizon
What Are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are unique cells with the ability to develop into various specialized cell types in the body. They play a critical role in growth, development, and tissue repair. Stem cells can be broadly categorized into embryonic stem cells, which are derived from early-stage embryos, and adult stem cells, found in various tissues such as bone marrow and fat. These cells have the potential to differentiate into specific cell types and regenerate damaged tissues, making them a promising tool in regenerative medicine.
Types of Stem Cells Used in Therapy
In the context of rotator cuff injuries, two primary types of stem cells are utilized: mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs). MSCs are typically harvested from bone marrow and have demonstrated the ability to differentiate into bone, cartilage, and muscle cells. ADSCs, obtained from adipose (fat) tissue, are abundant and relatively easy to collect. Both types of stem cells have shown promise in promoting tissue regeneration and reducing inflammation, making them suitable candidates for treating rotator cuff injuries.
Mechanisms of Stem Cell Healing
Stem cells contribute to healing through several mechanisms. They can differentiate into the specific cell types needed for tissue repair, such as tendon or muscle cells. Additionally, stem cells secrete various growth factors and cytokines that promote tissue regeneration, reduce inflammation, and enhance blood flow to the injured area. These paracrine effects help create a favorable environment for healing. Furthermore, stem cells can modulate the immune response, reducing the risk of chronic inflammation and fibrosis, which can impede recovery.
Advantages of Stem Cell Therapy Over Traditional Treatments
Non-Invasive Nature
One of the significant advantages of stem cell therapy is its minimally invasive nature. Unlike surgical interventions, which require incisions and prolonged recovery times, stem cell therapy involves simple injections. These injections can be performed under local anesthesia, reducing the risks associated with general anesthesia and surgical procedures. This non-invasive approach allows patients to return to their daily activities more quickly and with fewer complications. Additionally, the reduced need for hospitalization and physical therapy further enhances the appeal of stem cell therapy.
Faster Recovery Times
Stem cell therapy has been shown to accelerate the healing process compared to traditional treatments. By promoting tissue regeneration and reducing inflammation, stem cells can help repair damaged tissues more efficiently. Patients often experience a quicker return to normal function and a significant reduction in pain. This faster recovery time is particularly beneficial for athletes and individuals with physically demanding jobs, as it allows them to resume their activities with minimal downtime. The expedited healing process also contributes to a better overall patient experience.
Reduced Risk of Complications
Traditional treatments for rotator cuff injuries, especially surgical interventions, carry a risk of complications such as infections, blood clots, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. In contrast, stem cell therapy has a lower risk profile. Since the therapy uses the patient’s cells, the risk of immune rejection is minimal. Additionally, the non-invasive nature of the procedure reduces the likelihood of surgical complications. This improved safety profile makes stem cell therapy an attractive option for patients seeking effective and safe treatment alternatives.
Procedure for Stem Cell Therapy in Rotator Cuff Injuries
Patient Evaluation and Selection
The first step in stem cell therapy for rotator cuff injuries is a thorough patient evaluation. This involves assessing the patient’s medical history, current health status, and the severity of the injury. Imaging studies such as MRI or ultrasound are often used to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the extent of tendon damage. Not all patients are suitable candidates for stem cell therapy; factors such as age, overall health, and the presence of other medical conditions must be considered. A comprehensive evaluation ensures that only patients who are likely to benefit from the therapy are selected.
Harvesting Stem Cells
Once a patient is deemed suitable for stem cell therapy, the next step is harvesting the stem cells. For mesenchymal stem cells, this typically involves extracting bone marrow from the hip bone using a needle and syringe. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. Adipose-derived stem cells are obtained through liposuction, a minimally invasive procedure that removes fat tissue from areas such as the abdomen or thighs. The harvested tissue is then processed to isolate and concentrate the stem cells, preparing them for injection.
Preparation of Stem Cells
After harvesting, the stem cells undergo a preparation process to ensure they are ready for therapeutic use. This involves isolating the stem cells from the harvested tissue, which may include centrifugation and filtration techniques. The concentrated stem cells are then combined with a solution that enhances their viability and effectiveness. In some cases, additional growth factors or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) may be added to further boost the regenerative potential of the stem cells. The prepared stem cell solution is now ready for injection into the injured rotator cuff.
Injection Procedure
The final step in the stem cell therapy process is the injection procedure. Under ultrasound or fluoroscopic guidance, the prepared stem cell solution is precisely injected into the damaged area of the rotator cuff. This targeted delivery ensures that the stem cells reach the site of injury, where they can exert their regenerative effects. The procedure is typically performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day. Post-procedure care may include rest, physical therapy, and follow-up visits to monitor progress and ensure optimal outcomes.
Clinical Evidence and Research Studies
Overview of Key Clinical Trials
Several clinical trials have been conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of stem cell therapy for rotator cuff injuries. These studies have provided valuable insights into the potential benefits and limitations of the therapy. For instance, a randomized controlled trial published in the “American Journal of Sports Medicine” demonstrated that patients who received stem cell injections experienced significant improvements in pain and function compared to those who underwent traditional treatments. Other studies have shown promising results in terms of tendon healing and reduced re-tear rates.
Success Rates and Outcomes
The success rates of stem cell therapy for rotator cuff injuries have been encouraging. Research indicates that a substantial percentage of patients experience significant pain relief, improved shoulder function, and enhanced quality of life following treatment. For example, a study published in the “Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery” reported that over 70% of patients achieved satisfactory outcomes one year after receiving stem cell therapy. These positive results highlight the potential of stem cell therapy as an effective treatment option for rotator cuff injuries.
Long-term Benefits and Follow-Up
Long-term follow-up studies have shown that the benefits of stem cell therapy can be sustained over time. Patients often report continued improvements in pain and function several years after the initial treatment. This durability of results suggests that stem cell therapy not only promotes short-term healing but also supports long-term tissue regeneration. Regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor progress and address any potential issues. Ongoing research continues to explore the long-term outcomes and potential enhancements to stem cell therapy protocols.
Global Perspective on Stem Cell Therapy for Rotator Cuff Injuries
Adoption in North America
In North America, stem cell therapy for rotator cuff injuries has gained considerable traction. Leading medical centers and sports medicine clinics offer this innovative treatment to patients seeking alternatives to traditional surgery. The regulatory environment in the United States and Canada supports the use of autologous stem cells, allowing physicians to provide these therapies with appropriate oversight. Insurance coverage for stem cell therapy varies, but increasing recognition of its benefits is driving broader acceptance and availability across the region.
European Practices and Innovations
Europe has been at the forefront of stem cell research and application, with numerous clinical trials and studies conducted in countries such as Germany, the United Kingdom, and Spain. European regulatory bodies have established stringent guidelines to ensure the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapies. Innovative practices, such as the use of combined stem cell and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatments, have shown promising results in enhancing tissue regeneration. The collaboration between research institutions and clinical practitioners continues to advance the field in Europe.
Advancements in Asia, including India
Asia, including India, has witnessed significant advancements in stem cell therapy for rotator cuff injuries. Countries like Japan, South Korea, and India are investing heavily in stem cell research and clinical applications. In India, the growing acceptance of regenerative medicine has led to the establishment of specialized clinics offering stem cell treatments. Indian researchers are also contributing to global knowledge through pioneering studies and publications. The accessibility and affordability of stem cell therapy in Asia make it an attractive option for patients seeking cutting-edge treatments.
Case Studies and Patient Testimonials
Success Stories
Numerous success stories highlight the transformative impact of stem cell therapy for rotator cuff injuries. For instance, a professional athlete suffering from a severe rotator cuff tear was able to return to competitive sports within months of receiving stem cell injections. Another case involved an elderly patient with chronic shoulder pain who experienced significant pain relief and improved mobility following treatment. These stories underscore the potential of stem cell therapy to deliver remarkable outcomes for patients with varying degrees of injury severity.
Challenges and Lessons Learned
Despite the successes, there are challenges associated with stem cell therapy for rotator cuff injuries. Variability in patient responses, the need for precise injection techniques, and the importance of patient selection are critical factors influencing outcomes. Some patients may not respond as expected, necessitating alternative treatments. Lessons learned from clinical experiences emphasize the importance of thorough evaluation, proper technique, and realistic patient expectations. Ongoing research and refinement of protocols aim to address these challenges and enhance the overall effectiveness of the therapy.
Patient Experiences from India
Patient experiences from India provide valuable insights into the practical aspects of stem cell therapy. Many patients report positive outcomes, including reduced pain, improved shoulder function, and enhanced quality of life. The affordability and accessibility of treatment in India make it a viable option for both domestic and international patients. Testimonials from Indian patients highlight the compassionate care provided by medical professionals and the state-of-the-art facilities available in the country. These experiences contribute to the growing recognition of India as a hub for regenerative medicine.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Regulatory Framework in India
The regulatory framework for stem cell therapy in India is evolving to ensure patient safety and treatment efficacy. The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) have established guidelines for the clinical use of stem cells. These guidelines outline the requirements for clinical trials, patient consent, and quality control. Adherence to these regulations is essential for maintaining the credibility of stem cell therapies and protecting patients from unproven or unsafe treatments.
Ethical Concerns and Guidelines
Ethical considerations play a significant role in the application of stem cell therapy. Ensuring informed consent, maintaining transparency in patient communication, and adhering to ethical guidelines are paramount. The use of autologous stem cells, which are derived from the patient’s body, mitigates ethical concerns related to donor cells. However, ethical challenges remain, particularly in balancing innovation with patient safety. Ongoing dialogue among medical professionals, researchers, and regulatory bodies is crucial for addressing these concerns and advancing the ethical use of stem cell therapy.
Legal Status of Stem Cell Therapy in India
The legal status of stem cell therapy in India is guided by regulations set forth by the ICMR and CDSCO. These regulations classify stem cell therapy as a form of regenerative medicine, requiring rigorous clinical evaluation and approval. Clinics offering stem cell treatments must comply with these standards to ensure patient safety and treatment efficacy. Legal oversight aims to prevent the proliferation of unproven therapies and protect patients from potential risks. Continued regulatory advancements are expected to enhance the legal framework and support the responsible use of stem cell therapy.
Cost and Accessibility
Cost Comparison with Traditional Treatments
Stem cell therapy for rotator cuff injuries can be more cost-effective compared to traditional surgical treatments. While the initial cost of stem cell therapy may be higher, the reduced need for hospitalization, physical therapy, and extended recovery periods can lead to overall cost savings. Additionally, the non-invasive nature of the procedure minimizes the risk of complications, further reducing healthcare expenses. A detailed cost comparison helps patients make informed decisions based on their financial situation and treatment preferences.
Insurance and Coverage Options
Insurance coverage for stem cell therapy varies widely, with some providers offering partial or full reimbursement for the procedure. In India, insurance policies are gradually evolving to include regenerative medicine treatments, reflecting the growing acceptance of these therapies. Patients are encouraged to consult with their insurance providers to understand the extent of coverage available for stem cell therapy. Efforts to expand insurance coverage can enhance the accessibility of this innovative treatment for a broader patient population.
Accessibility of Stem Cell Therapy in Various Regions
Accessibility to stem cell therapy varies across different regions, influenced by factors such as availability of specialized clinics, regulatory environment, and economic conditions. In North America and Europe, the presence of advanced medical facilities and supportive regulations enhances accessibility. In contrast, regions with limited healthcare infrastructure may face challenges in providing widespread access to stem cell treatments. Efforts to improve accessibility include expanding healthcare infrastructure, training medical professionals, and raising awareness about the benefits of stem cell therapy.
Technological Advances Enhancing Stem Cell Therapy
Innovations in Stem Cell Harvesting
Technological advancements have significantly improved the harvesting of stem cells. Techniques such as automated cell isolation and minimally invasive extraction methods enhance the efficiency and safety of the harvesting process. These innovations reduce patient discomfort and increase the yield of viable stem cells. Continued research and development in stem cell harvesting technology are expected to further optimize the procedure, making it more accessible and effective for patients with rotator cuff injuries.
Improved Delivery Methods
Innovations in delivery methods are enhancing the precision and effectiveness of stem cell therapy. Techniques such as ultrasound-guided injections and targeted delivery systems ensure that stem cells are precisely placed at the site of injury. Additionally, advancements in biomaterials and scaffolding technologies provide supportive environments for stem cell growth and differentiation. These improved delivery methods contribute to better treatment outcomes and pave the way for further advancements in regenerative medicine.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How long does it take to see results from stem cell therapy for rotator cuff injuries?
Results can vary, but many patients begin to notice improvements in pain and function within a few weeks to months following the procedure. Full recovery and maximum benefits may take several months as the stem cells continue to promote tissue regeneration.
2. Is stem cell therapy covered by insurance?
Insurance coverage for stem cell therapy varies. Some insurance providers offer partial or full coverage, while others may not. Patients should consult with their insurance providers to understand their specific coverage options.
3. Are there any risks associated with stem cell therapy?
Stem cell therapy is generally considered safe, especially when using autologous stem cells. However, as with any medical procedure, there are risks, including infection, bleeding, and an adverse reaction to the injection. Discuss potential risks with your healthcare provider.
4. Who is a suitable candidate for stem cell therapy?
Suitable candidates for stem cell therapy are typically individuals with mild to moderate rotator cuff injuries who have not responded to conservative treatments. A thorough evaluation by a medical professional is necessary to determine candidacy.