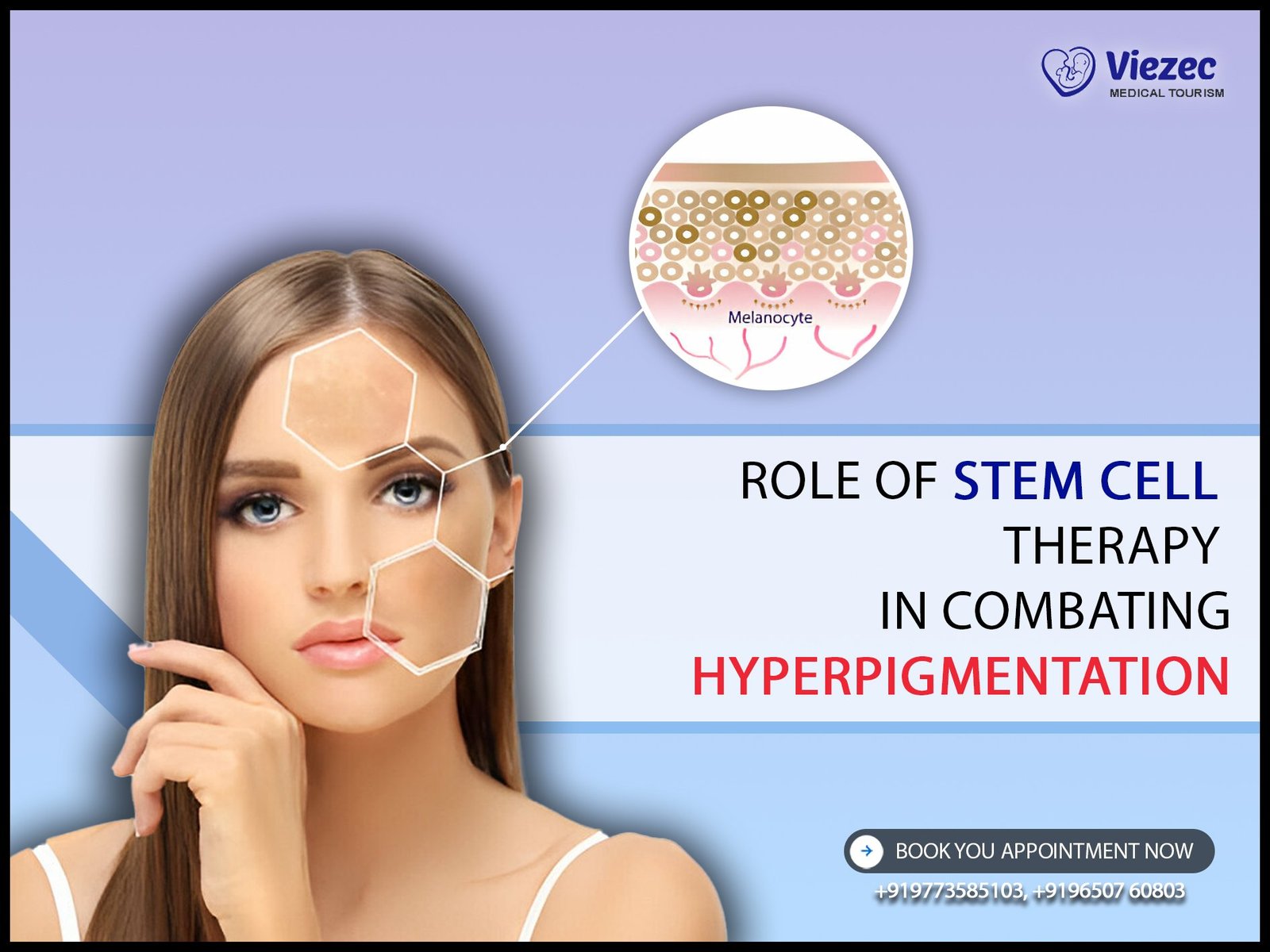
Hyperpigmentation refers to the darkening of the skin caused by the overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin coloration. This condition can manifest in various forms, including melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, and age spots. The development of hyperpigmentation is influenced by factors such as sun exposure, hormonal changes, inflammation, and genetic predisposition.
Definition and Types of Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation encompasses a spectrum of skin discoloration disorders, each with distinct characteristics and underlying causes. Melasma, commonly triggered by hormonal fluctuations, presents as irregular patches of brown or grayish pigmentation on sun-exposed areas like the face. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation arises as a result of skin trauma or inflammation, leading to localized darkening of the skin. Age spots, also known as liver spots or solar lentigines, emerge due to cumulative sun exposure and typically appear as small, flat brown patches on areas exposed to sunlight.
Causes and Risk Factors
The development of hyperpigmentation is influenced by various internal and external factors. Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy or with the use of oral contraceptives, can stimulate melanin production and contribute to conditions like melasma. Sun exposure is a major external trigger, as ultraviolet (UV) radiation stimulates melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin. Inflammation resulting from conditions like acne, eczema, or allergic reactions can also lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Current Treatment Options and Limitations
Current treatment modalities for hyperpigmentation include topical agents, chemical peels, laser therapy, and light-based treatments. These approaches aim to either inhibit melanin production, accelerate its turnover, or target pigmented cells selectively. However, these treatments often yield variable results and may be associated with adverse effects such as irritation, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, or hypopigmentation. Moreover, some individuals may not achieve satisfactory outcomes despite undergoing multiple treatment sessions.
Ready to Transform Your Skin?
Understanding Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy represents a promising approach for addressing various dermatological conditions, including hyperpigmentation. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells capable of self-renewal and differentiation into specialized cell types. Their unique properties enable them to contribute to tissue repair and regeneration.
Basics of Stem Cells
Stem cells can be broadly classified into embryonic stem cells, derived from early-stage embryos, and adult stem cells, found in mature tissues. Embryonic stem cells possess pluripotent capabilities, meaning they can differentiate into any cell type in the body. Adult stem cells, also known as somatic or tissue-specific stem cells, are multipotent and can generate a limited range of cell types within their tissue of origin.
Types of Stem Cells Used in Therapy
In the context of dermatological applications, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from sources such as adipose tissue, bone marrow, or umbilical cord blood have garnered significant attention. These MSCs exhibit immunomodulatory properties and can differentiate into various cell lineages, including those relevant to skin regeneration.
Mechanisms of Stem Cell Action in Tissue Regeneration
Stem cells exert their therapeutic effects through multiple mechanisms, including direct differentiation, paracrine signaling, and immunomodulation. Upon administration, stem cells can migrate to injured sites within the skin and differentiate into keratinocytes, fibroblasts, and melanocytes, contributing to tissue repair. Additionally, stem cells release bioactive factors such as growth factors, cytokines, and extracellular vesicles, which promote cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and extracellular matrix remodeling. Moreover, stem cells can modulate the immune response, suppressing inflammation and facilitating tissue healing.
Hyperpigmentation: A Dermatological Perspective
Pathophysiology of Hyperpigmentation
The pathogenesis of hyperpigmentation involves dysregulation of melanin synthesis and distribution within the skin. Melanocytes, residing in the basal layer of the epidermis, produce melanin through a series of enzymatic reactions involving tyrosinase. Various factors, including hormonal changes, UV exposure, and inflammatory mediators, can upregulate tyrosinase activity, leading to increased melanin production. Furthermore, aberrant melanosome transfer from melanocytes to keratinocytes can result in uneven distribution of melanin and the formation of hyperpigmented lesions.
Impact on Skin Health and Aesthetics
Hyperpigmentation not only affects the aesthetic appearance of the skin but also has psychological implications, impacting individuals’ self-esteem and quality of life. Moreover, certain forms of hyperpigmentation, such as melasma, may be associated with underlying hormonal imbalances or medical conditions, necessitating comprehensive evaluation and management.
Challenges in Hyperpigmentation Management
Despite the availability of various treatment modalities, managing hyperpigmentation can be challenging due to factors such as treatment resistance, recurrence, and adverse effects. Additionally, the diverse etiology and clinical presentation of hyperpigmentation underscore the need for personalized treatment approaches tailored to individual patient characteristics and preferences.
Role of Stem Cells in Skin Regeneration
Stem cell therapy holds immense potential for promoting skin regeneration and addressing hyperpigmentation through multiple mechanisms.
Stem Cell Migration and Homing to Injured Sites
Following administration, stem cells have the capacity to migrate to sites of tissue injury or inflammation within the skin. This targeted homing response enables stem cells to exert their reparative effects directly at the site of pathology, facilitating tissue regeneration and functional restoration.
Differentiation into Skin-specific Cell Types
Stem cells possess the ability to differentiate into various cell lineages relevant to skin regeneration, including keratinocytes, fibroblasts, and melanocytes. By replenishing damaged or dysfunctional cells, stem cell-derived progeny contribute to tissue repair and restoration of normal skin architecture.
Paracrine Effects and Modulation of Skin Microenvironment
In addition to their direct differentiation potential, stem cells secrete a myriad of bioactive molecules that modulate the local microenvironment and facilitate tissue healing. These paracrine factors exert anti-inflammatory, pro-angiogenic, and immunomodulatory effects, promoting a favorable milieu for tissue regeneration and melanocyte function.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Stem Cell Therapy
Numerous preclinical and clinical studies have provided compelling evidence supporting the efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy for hyperpigmentation.
Clinical Studies on Stem Cell Treatment for Hyperpigmentation
Clinical trials investigating the use of stem cells for hyperpigmentation have demonstrated promising outcomes, including reduction in pigmented lesions, improvement in skin texture, and enhancement of overall skin quality. These studies have highlighted the potential of stem cell therapy as a novel and effective approach for addressing hyperpigmentation refractory to conventional treatments.
Histological and Immunohistochemical Findings
Histological analysis of skin biopsies from patients treated with stem cell therapy has revealed structural improvements, including increased epidermal thickness, collagen deposition, and neovascularization. Immunohistochemical studies have further elucidated the mechanisms underlying stem cell-mediated tissue regeneration, documenting enhanced expression of markers associated with keratinocyte proliferation, extracellular matrix synthesis, and angiogenesis.
Get Personalized Stem Cell Solutions!
Patient-reported Outcomes and Long-term Effects
Patient-reported outcomes, including subjective assessments of pigmentation improvement, satisfaction with treatment outcomes, and quality of life measures, have been consistently positive in studies evaluating stem cell therapy for hyperpigmentation. Furthermore, long-term follow-up data have indicated sustained efficacy and safety profiles, with minimal risk of adverse events or treatment-related complications.
Advantages of Stem Cell Therapy Over Conventional Treatments
Stem cell therapy offers several distinct advantages over conventional treatments for hyperpigmentation, making it an attractive option for patients and clinicians alike.
Targeted Approach to Melanocyte Restoration
Unlike topical agents or light-based therapies that target superficial pigmentary changes, stem cell therapy offers a targeted approach to melanocyte restoration by replenishing dysfunctional or depleted melanocytes within the skin. This enables more comprehensive and long-lasting correction of hyperpigmentation, addressing both the underlying pathology and associated aesthetic concerns.
Reduced Risk of Hypopigmentation and Scarring
Stem cell therapy minimizes the risk of hypopigmentation, a common complication associated with traditional treatments such as laser therapy or chemical peels. By promoting physiological tissue repair and regeneration, stem cells facilitate gradual and natural improvement in pigmentation, minimizing the likelihood of dyspigmentation or scarring.
Potential for Personalized Treatment Strategies
Stem cell therapy offers the flexibility to tailor treatment strategies to individual patient needs and characteristics. From selecting an optimal cell source to optimizing treatment protocols and dosing regimens, stem cell-based interventions can be customized to maximize efficacy while minimizing risks and adverse effects.
Challenges and Limitations in Stem Cell Therapy
While stem cell therapy holds tremendous promise for hyperpigmentation management, several challenges and limitations must be addressed to optimize its clinical utility and accessibility.
A. Immunogenicity and Rejection Risks
The potential for immunogenicity and immune rejection remains a concern with allogeneic stem cell-based therapies, particularly when utilizing cells derived from unrelated donors. Strategies to mitigate immune responses, such as immunosuppressive regimens or patient-specific cell sources, may be necessary to enhance treatment safety and efficacy.
B. Standardization of Stem Cell Preparation and Administration
Achieving consistency and reproducibility in stem cell isolation, expansion, and administration poses technical challenges that must be addressed to ensure uniformity of treatment outcomes. Standardized protocols for cell processing, quality control, and delivery are essential to minimize variability and optimize therapeutic efficacy.
C. Cost-effectiveness and Accessibility Concerns
The high cost of stem cell therapy, coupled with limited insurance coverage and reimbursement, poses barriers to widespread adoption and accessibility. Addressing cost-effectiveness considerations and exploring alternative financing models are crucial steps toward making stem cell-based treatments more affordable and equitable for patients across diverse socioeconomic backgrounds.
Case Studies and Clinical Applications
Real-world case studies provide valuable insights into the clinical utility and effectiveness of stem cell therapy for hyperpigmentation.
Successful Cases of Stem Cell Therapy in Hyperpigmentation Treatment
Clinical case reports and series have documented successful outcomes following stem cell therapy for various forms of hyperpigmentation, including melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, and solar lentigines. These cases underscore the potential of stem cell-based interventions to achieve meaningful and sustained improvements in pigmentation and skin quality.
Comparative Analysis with Traditional Treatments
Comparative studies evaluating the efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy versus conventional treatments for hyperpigmentation offer valuable insights into the relative merits and limitations of each approach. By systematically assessing treatment outcomes, adverse event profiles, and patient satisfaction levels, these studies inform evidence-based decision-making and guide treatment selection for individual patients.
Patient Selection Criteria and Treatment Outcomes
Optimal patient selection is critical for maximizing the likelihood of treatment success and minimizing potential risks associated with stem cell therapy. Factors such as skin type, underlying etiology, treatment history, and patient preferences should be carefully considered when determining candidacy for stem cell-based interventions. Long-term follow-up and comprehensive outcome assessment are essential for evaluating treatment efficacy, durability, and safety over time.
Patient Education and Counseling
Patient education and counseling are integral components of the treatment process, empowering individuals to make informed decisions and actively participate in their care.
Pre-treatment Assessment and Expectation Management
Prior to undergoing stem cell therapy, patients should undergo thorough pre-treatment assessment, including medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic evaluation as indicated. Clinicians should discuss treatment goals, potential risks and benefits, expected outcomes, and alternative treatment options with patients to ensure realistic expectations and informed consent.
Post-treatment Care and Follow-up Protocols
Following stem cell therapy, patients should adhere to prescribed post-treatment care regimens to optimize healing and maximize treatment outcomes. This may include topical medications, sun protection measures, and lifestyle modifications aimed at promoting skin health and minimizing pigmentation recurrence. Regular follow-up visits allow clinicians to monitor treatment response, address any concerns or complications, and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Lifestyle Modifications for Long-term Skin Health
In addition to undergoing medical interventions, patients can enhance the efficacy of hyperpigmentation treatments by adopting healthy lifestyle practices. This may include minimizing sun exposure, practicing sun-safe behaviors, maintaining a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and nutrients, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and managing stress effectively. By incorporating these lifestyle modifications into their daily routine, patients can support the regeneration of healthy, radiant skin and prolong the benefits of stem cell therapy.
Unlock Clearer, Healthier Skin with Stem Cells
Global Perspectives on Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy for hyperpigmentation represents a rapidly evolving field with global implications, transcending geographical boundaries and cultural contexts.
Adoption and Integration into Dermatological Practices Worldwide
Stem cell-based treatments for hyperpigmentation have gained traction across diverse geographical regions, with dermatologists and aesthetic practitioners incorporating these innovative therapies into their clinical armamentarium. Collaborative research efforts and knowledge exchange initiatives facilitate the dissemination of best practices and foster international collaboration in advancing the field of regenerative dermatology.
Regional Disparities in Access to Stem Cell Treatments
Despite the growing popularity of stem cell therapy, disparities in access persist, reflecting differences in healthcare infrastructure, regulatory frameworks, and socioeconomic factors across regions. Efforts to address barriers to access, such as improving healthcare infrastructure, enhancing regulatory oversight, and expanding insurance coverage, are essential for ensuring equitable distribution of stem cell-based treatments and maximizing patient benefit.
Collaborative Efforts in Research and Knowledge Sharing
Collaborative endeavors among academia, industry, and regulatory agencies play a crucial role in driving innovation and translating scientific discoveries into clinical applications. By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and facilitating data sharing, these initiatives accelerate the pace of research, enhance treatment development, and ultimately improve patient outcomes worldwide.
Ethical and Legal Implications
As with any emerging therapeutic modality, stem cell therapy for hyperpigmentation raises important ethical and legal considerations that must be carefully navigated.
Informed Consent and Patient Rights
Informed consent is paramount in stem cell therapy, ensuring that patients are fully informed about the nature of the treatment, potential risks and benefits, and alternative options available to them. Clinicians must engage in open and transparent communication with patients, respecting their autonomy and upholding their right to make informed decisions about their care.
Regulatory Frameworks for Stem Cell Therapy
Regulatory oversight is essential to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of stem cell-based treatments for hyperpigmentation. Regulatory agencies play a pivotal role in establishing clear guidelines for stem cell research, clinical trials, and commercialization, safeguarding patient welfare and promoting public trust in emerging therapies.
Addressing Ethical Concerns and Misconceptions
Public perception of stem cell therapy can be influenced by ethical concerns, misconceptions, and misinformation propagated by media outlets and internet sources. Clinicians and researchers have a responsibility to engage in public outreach and education initiatives, dispelling myths, addressing ethical concerns, and fostering informed discourse about the potential benefits and limitations of stem cell-based interventions.
Public Perception and Media Coverage
Media portrayal of stem cell therapy for hyperpigmentation can shape public attitudes and perceptions, influencing patient decision-making and healthcare practices.
Media Portrayal of Stem Cell Therapy for Hyperpigmentation
Media coverage of stem cell therapy often emphasizes its potential for revolutionary breakthroughs and transformative outcomes, sparking public interest and curiosity. However, sensationalized reporting and lack of context can contribute to unrealistic expectations and misconceptions about the safety, efficacy, and accessibility of stem cell-based treatments.
Public Awareness Campaigns and Education Initiatives
Educational campaigns and public awareness initiatives play a vital role in providing accurate information about stem cell therapy, addressing misconceptions, and empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their health. By leveraging various media platforms, healthcare organizations, advocacy groups, and regulatory agencies can disseminate evidence-based information, promote responsible use of stem cell therapies, and foster trust in the scientific community.
Debunking Myths and Dispelling Misinformation
Efforts to debunk myths and dispel misinformation surrounding stem cell therapy require collaboration among healthcare professionals, researchers, policymakers, and media stakeholders. By engaging in proactive communication strategies, providing credible sources of information, and encouraging critical thinking, stakeholders can mitigate the spread of false narratives and promote a more nuanced understanding of stem cell-based interventions among the public.
Expert Opinions and Perspectives
Insights from leading dermatologists, researchers, and clinicians provide valuable perspectives on the current state and future directions of stem cell therapy for hyperpigmentation.
Interviews with Leading Dermatologists and Researchers
Interviews with key opinion leaders in dermatology shed light on emerging trends, challenges, and opportunities in stem cell-based treatments for hyperpigmentation. By sharing their expertise and experiences, these experts offer valuable insights into best practices, treatment protocols, and areas for future research and innovation.
Clinician Insights on Integrating Stem Cell Therapy into Practice
Clinicians who have implemented stem cell therapy in their practice provide firsthand accounts of treatment outcomes, patient experiences, and practical considerations for incorporating these therapies into clinical workflows. Their perspectives offer valuable guidance for colleagues considering the adoption of stem cell-based interventions and highlight the importance of multidisciplinary collaboration in delivering optimal patient care.
Predictions and Areas of Focus in Hyperpigmentation Research
Looking ahead, dermatologists and researchers envision exciting opportunities for advancing the field of hyperpigmentation research and treatment. From exploring novel stem cell sources and delivery methods to elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying melanocyte biology and pigmentation regulation, ongoing efforts aim to unlock new therapeutic targets and refine treatment strategies for hyperpigmentation and related dermatological conditions.
In conclusion, stem cell therapy holds immense promise for addressing hyperpigmentation, offering a targeted, regenerative approach to skin rejuvenation and pigmentation correction. While challenges and limitations remain, ongoing research and clinical advancements continue to expand the therapeutic landscape and improve patient outcomes in dermatology.