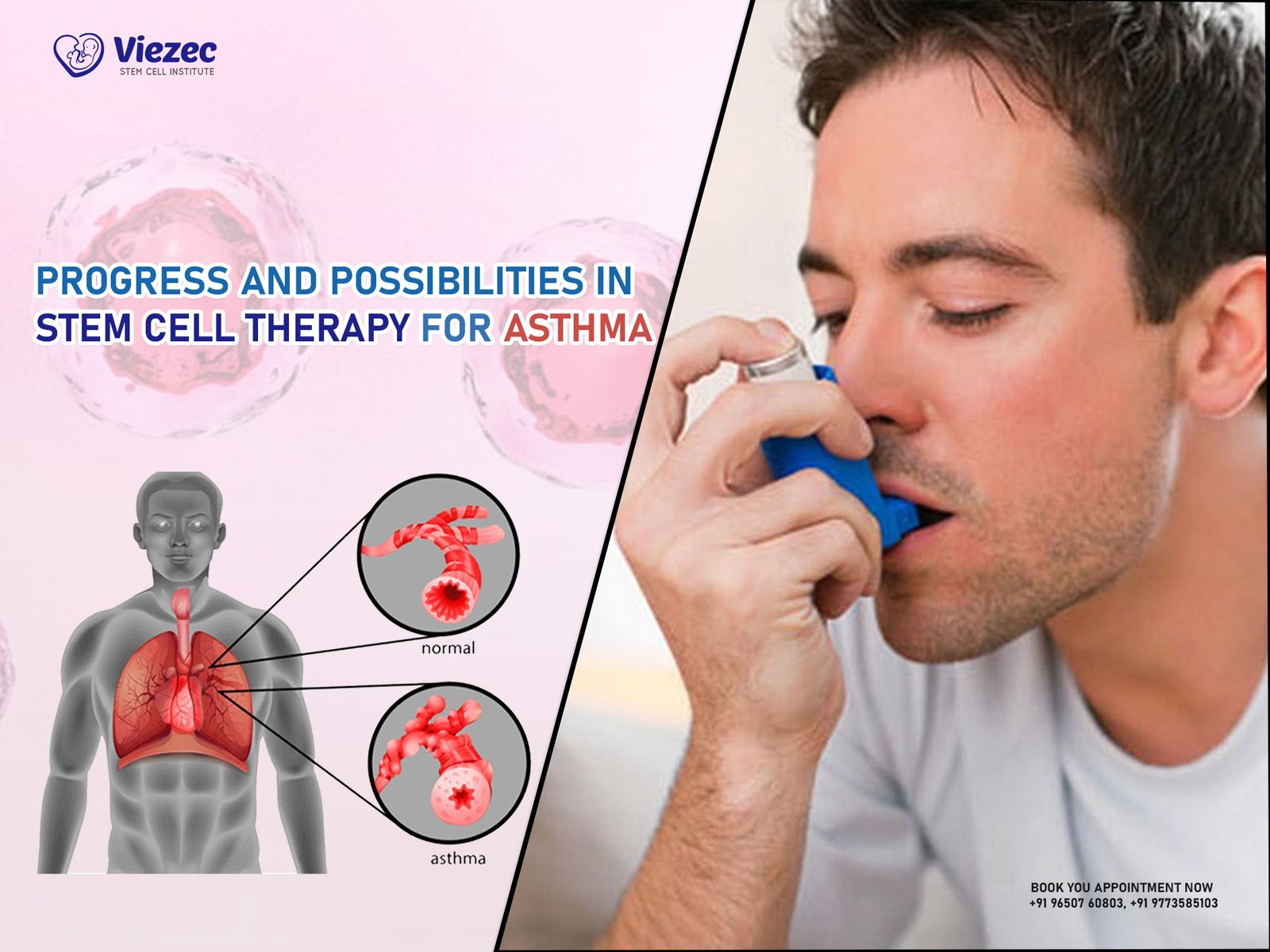
In recent years, the field of stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising avenue for medical treatment across various domains. Stem cells possess the remarkable ability to differentiate into different cell types and have the potential to regenerate damaged tissues. One area of particular interest is the enhancement of the immune system through stem cell therapy. The immune system plays a crucial role in protecting the body against infections and diseases, and any enhancement in its function can have profound implications for healthcare. In this article, we will explore the potential of stem cell therapy in enhancing the immune system, the current state of research in this field, and the challenges and opportunities it presents.
Understanding Stem Cell Therapy
What are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells with the unique ability to develop into specialized cell types. They serve as the body’s internal repair system, capable of replenishing cells that are damaged or lost due to injury, disease, or normal wear and tear. There are several types of stem cells, including embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Each type has its own characteristics and potential applications in medical treatment.
Mechanisms of Action
Stem cell therapy works through various mechanisms to enhance the immune system. One of the primary mechanisms is the ability of stem cells to differentiate into different immune cell types, such as T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells. These cells are instrumental in detecting and eliminating pathogens, infected cells, and abnormal cells, thereby bolstering the body’s defense mechanisms.
Additionally, stem cells possess immunomodulatory properties, meaning they can regulate the activity of the immune system. This modulation can involve suppressing excessive immune responses in conditions like autoimmune diseases or enhancing immune responses to combat infections or cancer. Stem cells achieve this modulation through the secretion of cytokines, growth factors, and other signaling molecules that regulate immune cell function.
Potential Applications of Stem Cell Therapy in Immune System Enhancement
Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues in the body, leading to inflammation and tissue damage. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and lupus are examples of autoimmune diseases with significant morbidity and limited treatment options. Stem cell therapy holds promise for treating autoimmune diseases by modulating the immune response and promoting tissue repair.
Clinical trials have demonstrated the potential of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in managing autoimmune conditions. MSCs have been shown to suppress aberrant immune responses and promote the generation of regulatory T cells, which help maintain immune tolerance. In diseases like multiple sclerosis, MSC therapy has shown improvements in symptoms and disease progression, offering hope for effective treatments in the future.
Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases pose a significant threat to global health, and the emergence of drug-resistant pathogens underscores the need for innovative treatment strategies. Stem cell therapy offers a novel approach to combat infectious diseases by enhancing the body’s immune response.
One promising application of stem cell therapy in infectious diseases is the development of engineered immune cells with enhanced antiviral or antibacterial properties. For example, scientists have engineered T cells to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) targeting specific pathogens, such as HIV or influenza. These engineered T cells have shown potent antiviral activity in preclinical studies and offer a potential strategy for controlling viral infections.
Cancer Immunotherapy
Cancer immunotherapy harnesses the power of the immune system to target and destroy cancer cells. While traditional cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy can be effective, they often come with significant side effects and may not eradicate all cancer cells. Stem cell therapy has the potential to augment existing cancer immunotherapy approaches and improve outcomes for cancer patients.
One approach involves using stem cells to generate immune cells capable of recognizing and eliminating cancer cells. For example, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) can be used to replace a patient’s immune system with donor-derived immune cells, which may have enhanced antitumor activity. Additionally, advances in gene editing technologies allow for the engineering of immune cells with improved tumor-targeting capabilities, paving the way for more effective cancer immunotherapies.
Standardization and Optimization
Another challenge is the standardization and optimization of stem cell-based therapies. The variability in stem cell sources, isolation techniques, and administration protocols can affect treatment outcomes and hinder the reproducibility of results. Standardization efforts are needed to establish guidelines for the manufacturing, characterization, and delivery of stem cell products, ensuring their safety and efficacy in clinical settings.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
The ethical and regulatory considerations surrounding stem cell research remain complex and contentious. Issues such as the use of embryonic stem cells, informed consent, and oversight of clinical trials raise important ethical questions that must be addressed. Furthermore, regulatory frameworks must keep pace with advancements in stem cell technology to ensure patient safety and facilitate the translation of research findings into clinical practice.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research efforts continue to advance our understanding of stem cell biology and its applications in immune system enhancement. Future directions in this field may include the development of personalized stem cell therapies tailored to individual patient characteristics, the refinement of gene editing techniques for precise immune cell engineering, and the exploration of novel stem cell sources with unique immunomodulatory properties.
Make informed Decision
Stem cell therapy holds tremendous promise for enhancing the immune system and revolutionizing the treatment of various diseases. By harnessing the regenerative and immunomodulatory properties of stem cells, researchers are exploring innovative approaches to boost immune function, combat infections, and improve outcomes for patients with autoimmune diseases and cancer. While significant challenges remain, continued investment in stem cell research and collaborative efforts across disciplines are essential for realizing the full potential of this groundbreaking technology in immune system enhancement.
As we unlock the mysteries of stem cell biology and translate scientific discoveries into clinical applications, we move closer to a future where personalized stem cell therapies offer new hope for patients battling immune-related disorders and infectious diseases. With further advancements in technology and a commitment to rigorous scientific inquiry, the potential of stem cell therapy in immune system enhancement may soon become a reality.