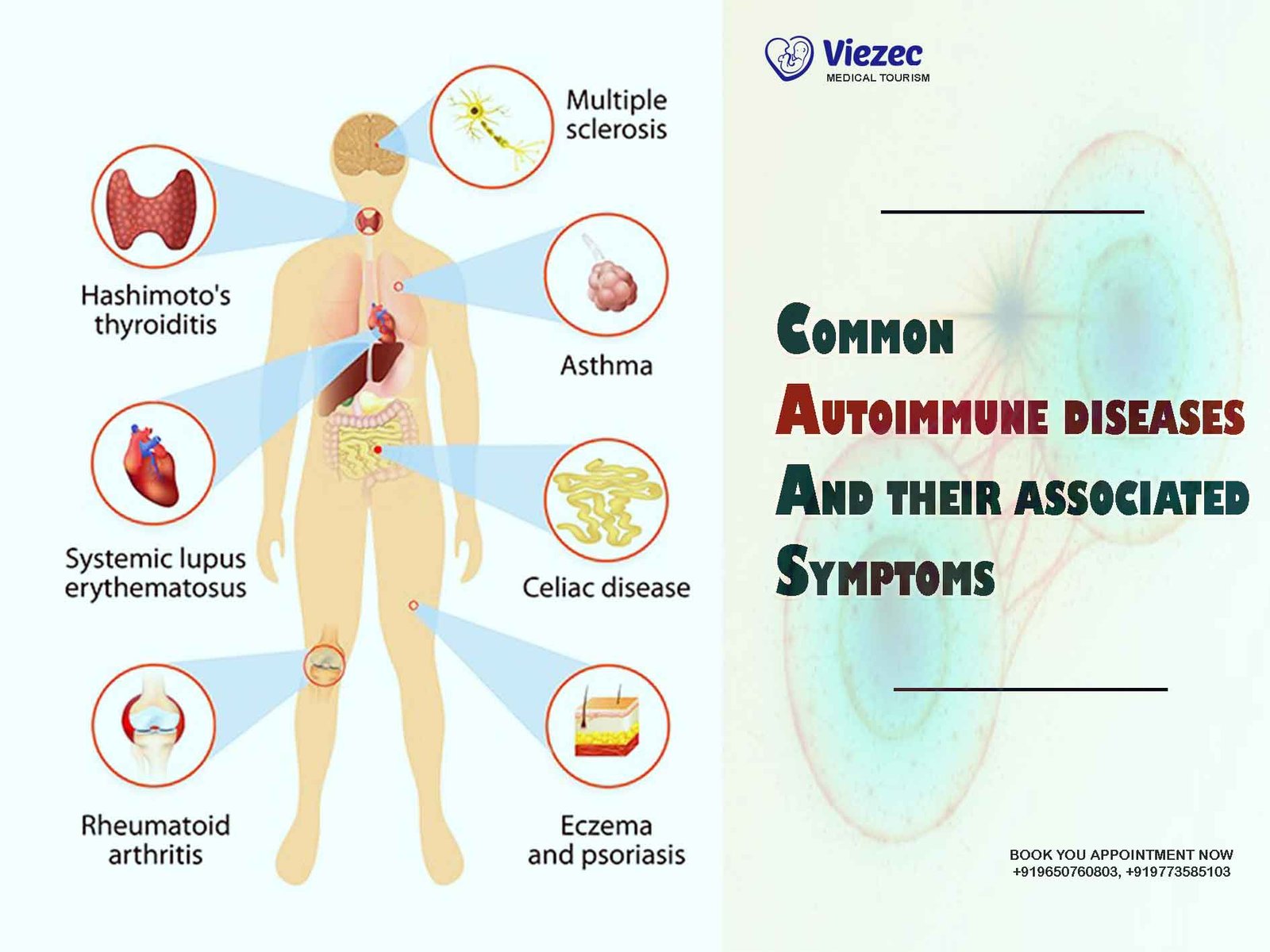
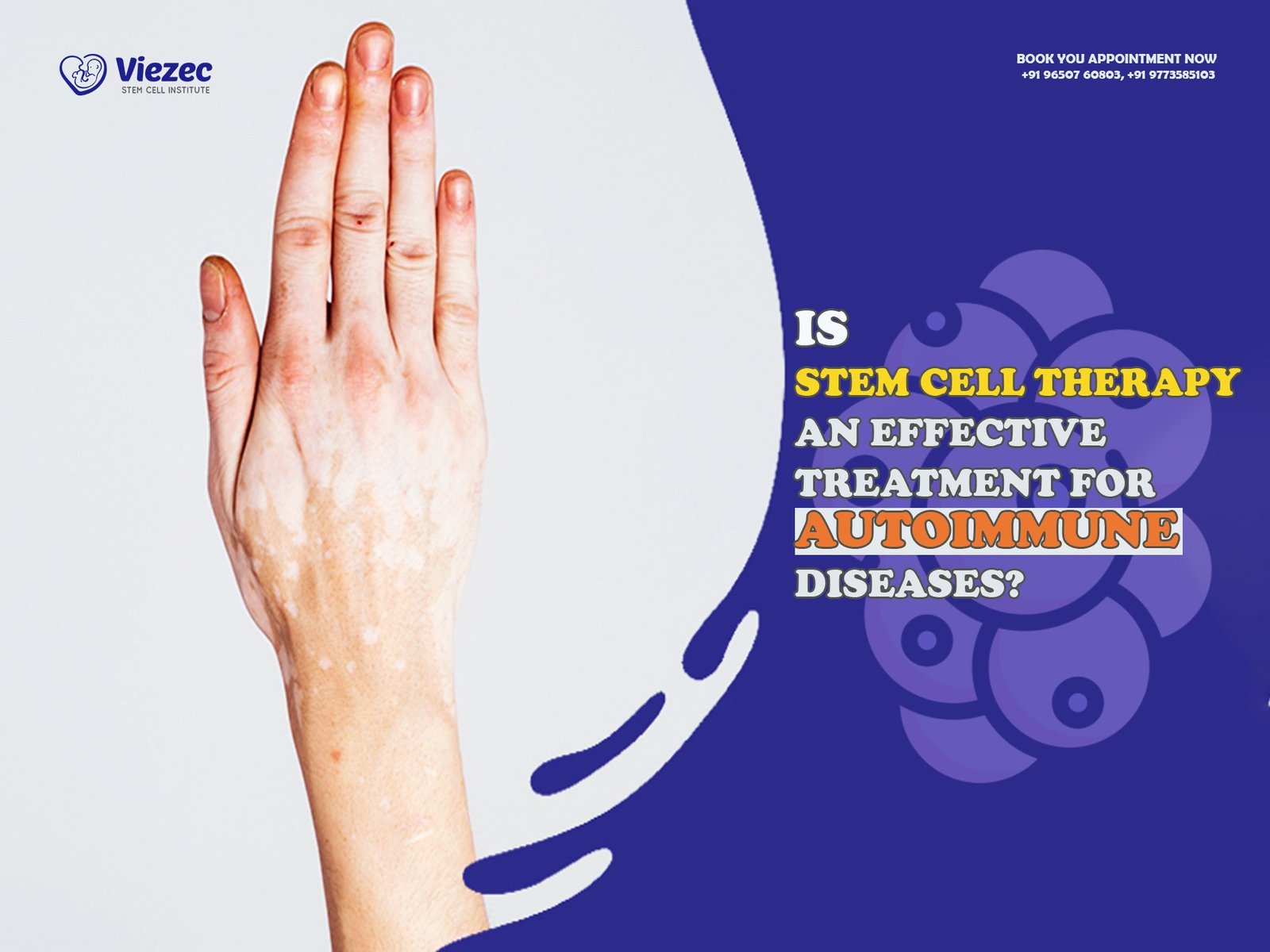
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy cells, tissues, and organs. These conditions can affect various parts of the body and cause a wide range of symptoms, often making diagnosis challenging. In this article, we will explore some of the most common autoimmune diseases, their associated symptoms, and how they impact the body.
Understanding Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system, which is designed to protect against harmful substances like viruses and bacteria, mistakenly attacks healthy cells. This can lead to inflammation, tissue damage, and organ dysfunction. While the exact cause of autoimmune diseases is not fully understood, factors such as genetics, environmental triggers, and hormonal imbalances may play a role in their development.
Common Autoimmune Diseases
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Symptoms:
- Joint pain and swelling, typically affecting the hands, wrists, knees, and feet
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity
- Fatigue
- Loss of joint function and deformity over time
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the joints but can also involve other organs such as the lungs and heart. It occurs when the immune system attacks the synovium, the lining of the membranes that surround the joints.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Symptoms:
- Butterfly-shaped rash on the face (malar rash)
- Joint pain and swelling
- Fatigue and weakness
- Fever
- Sensitivity to sunlight
- Raynaud’s phenomenon (fingers turning white or blue in response to cold)
Systemic lupus erythematosus, commonly known as lupus, is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, and brain. It is characterized by periods of flare-ups and remission, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe.
Type 1 Diabetes
Symptoms:
- Excessive thirst and urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Increased appetite
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. As a result, the body cannot produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels, leading to high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) and various symptoms.
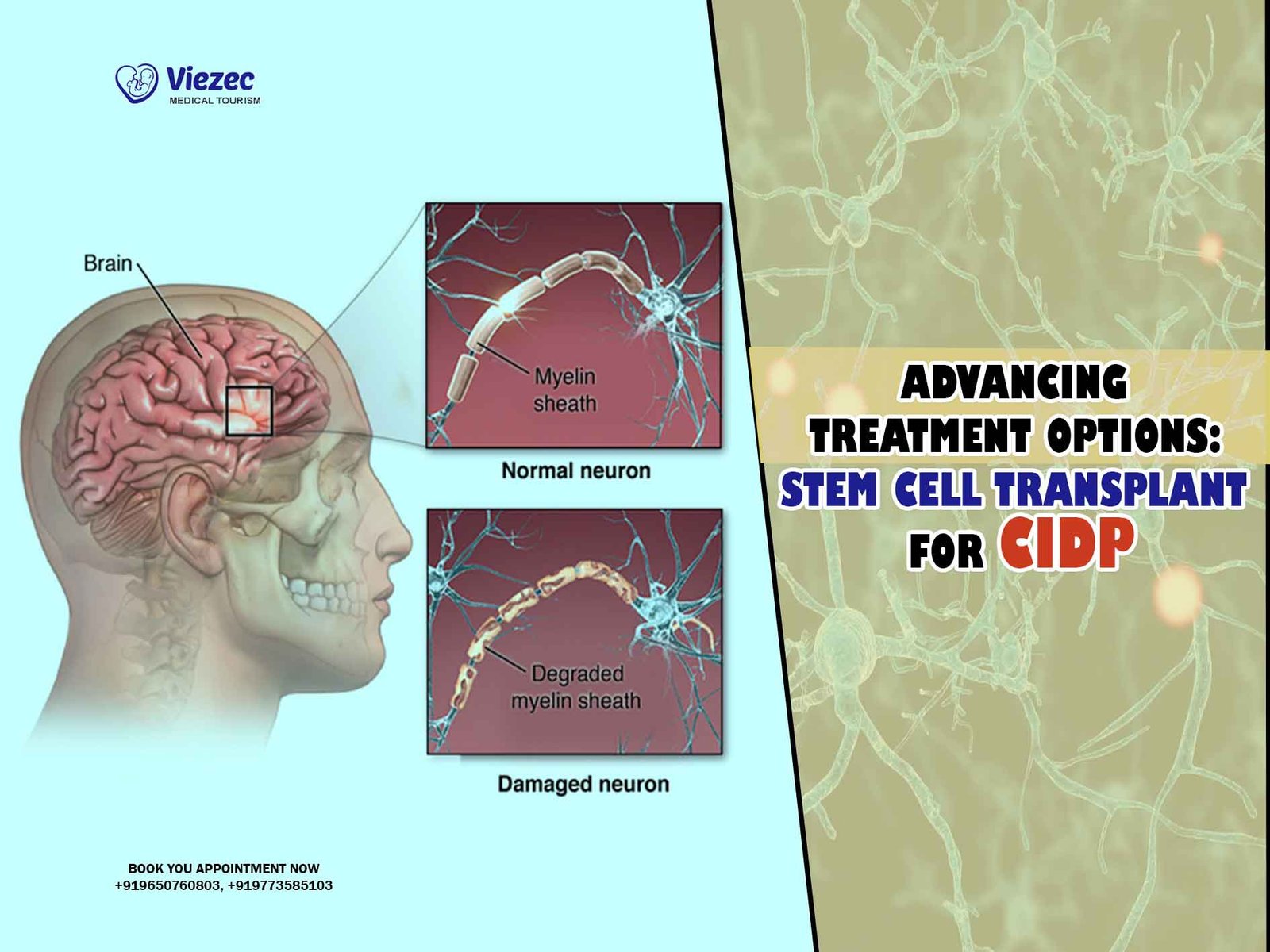
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Numbness or weakness in one or more limbs
- Tingling or pain in various parts of the body
- Vision problems, such as blurred or double vision
- Difficulty with coordination and balance
- Cognitive impairment
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord. It occurs when the immune system attacks the protective myelin sheath that covers nerve fibers, leading to communication problems between the brain and the rest of the body.
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Constipation
- Dry skin and hair
- Depression
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation of the thyroid gland, leading to an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism). It occurs when the immune system mistakenly targets and attacks the thyroid tissue, disrupting hormone production and metabolism.
Plan Your Stem Cell Therapy Procedure in India
Graves’ Disease
Symptoms:
- Weight loss
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
- Tremors
- Anxiety and irritability
- Bulging eyes (exophthalmos)
- Heat intolerance
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder that causes the overproduction of thyroid hormones, leading to hyperthyroidism. It occurs when the immune system produces antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland, resulting in increased metabolism and various symptoms.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Symptoms:
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Diarrhea, sometimes with blood or mucus
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
Inflammatory bowel disease is a group of chronic inflammatory disorders of the digestive tract, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. While the exact cause is unknown, it is believed to involve an abnormal immune response to environmental triggers in genetically susceptible individuals.
Psoriasis
Symptoms:
- Red, inflamed patches of skin covered with silvery scales
- Itching or burning sensation
- Thickened, pitted, or ridged nails
- Stiff and swollen joints (psoriatic arthritis)
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the skin, causing red, scaly patches to appear on the surface. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly speeds up the skin cell turnover process, resulting in the rapid buildup of cells on the skin’s surface.
Contact us for free online appointment
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing autoimmune diseases can be challenging due to the variability of symptoms and the overlap between different conditions. Healthcare providers typically use a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests, imaging studies, and biopsy to make an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment for autoimmune diseases aims to control symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent further damage to affected tissues and organs. This often involves a combination of medication, lifestyle modifications, and therapies such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, and counseling.
Autoimmune diseases are a diverse group of conditions that can affect virtually any part of the body, causing a wide range of symptoms and complications. While these diseases can be challenging to diagnose and manage, early detection and appropriate treatment can help individuals lead fulfilling lives despite their condition. By raising awareness and investing in research, we can better understand autoimmune diseases and improve outcomes for those affected by them.
Related post:-
Potential Benefits of Stem Cell Treatment for Autoimmune Disorders
Promise of Stem Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Conditions
Stem Cell Therapy as a Novel Approach to Treating Scleroderma