Stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising treatment option for a variety of medical conditions, ranging from degenerative diseases to injuries and chronic pain. But what exactly is stem cell therapy, and does it involve the use of your own stem cells? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of stem cell therapy, exploring its mechanisms of action, the different types of stem cells used, and whether the therapy utilizes your own stem cells for treatment.
Understanding Stem Cell Therapy
What is Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cell therapy, also known as regenerative medicine, involves the use of stem cells to promote tissue repair, regeneration, and healing within the body. Stem cells are unique cells with the remarkable ability to differentiate into various cell types and replace damaged or dysfunctional cells, making them an attractive option for treating a wide range of medical conditions.
Mechanisms of Action
Stem cell therapy works by harnessing the regenerative potential of stem cells to repair and regenerate damaged tissues and organs. When introduced into the body, stem cells can migrate to injured or diseased areas, differentiate into specialized cell types, and promote tissue repair through various mechanisms, including:
- Differentiation: Stem cells can differentiate into specific cell types, such as muscle cells, nerve cells, or cartilage cells, depending on the tissue’s needs.
- Secretion of Growth Factors: Stem cells secrete a variety of growth factors and cytokines that stimulate tissue regeneration, reduce inflammation, and promote healing.
- Modulation of the Immune System: Stem cells can modulate the immune response, suppressing inflammation and promoting tissue tolerance, which is beneficial for conditions involving autoimmune or inflammatory processes.
Types of Stem Cells Used in Therapy
Embryonic Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells are derived from the inner cell mass of early-stage embryos and have the potential to develop into any cell type in the body. Due to their pluripotent nature, embryonic stem cells are valuable for research and therapeutic purposes but raise ethical concerns related to their derivation from embryos.
Adult Stem Cells
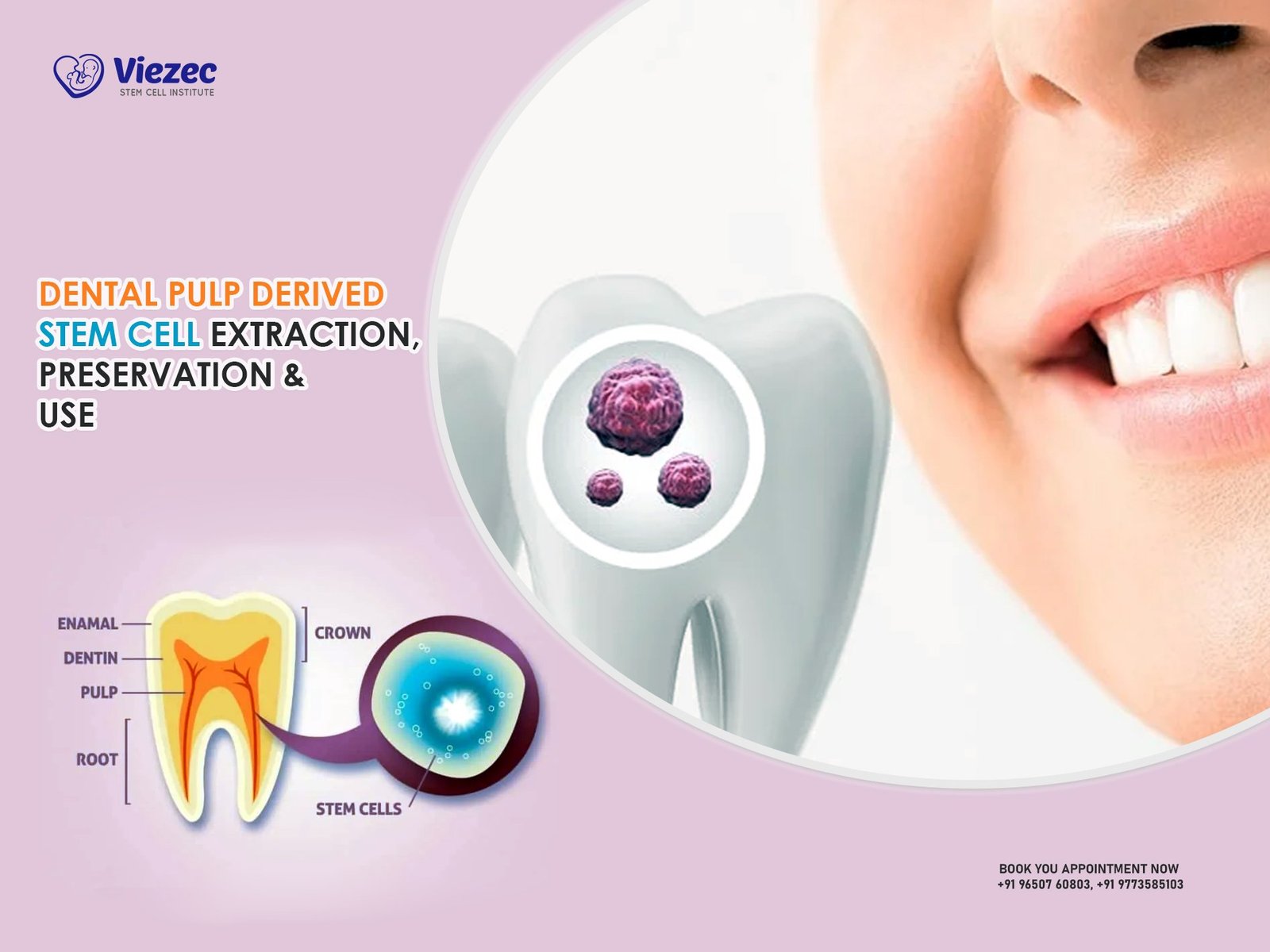
Adult stem cells, also known as somatic or tissue-specific stem cells, are found in various tissues throughout the body, such as bone marrow, adipose tissue, and blood. Unlike embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells are multipotent or tissue-specific, meaning they can differentiate into a limited range of cell types related to their tissue of origin.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are adult cells that have been reprogrammed into a pluripotent state, similar to embryonic stem cells. iPSCs offer the potential to generate patient-specific stem cell lines without the ethical concerns associated with embryonic stem cells, making them an attractive option for personalized medicine and regenerative therapies.
Does Stem Cell Therapy Utilize Your Own Stem Cells?
The answer to whether stem cell therapy utilizes your own stem cells depends on the type of stem cell therapy being administered:
Autologous Stem Cell Therapy
Autologous stem cell therapy involves the use of a patient’s own stem cells for treatment. In this approach, stem cells are harvested from the patient’s bone marrow, adipose tissue, or blood, processed and purified, and then reintroduced into the body at the site of injury or disease. Autologous stem cell therapy offers several advantages, including:
- Reduced Risk of Rejection: Since the stem cells are derived from the patient’s own body, there is minimal risk of rejection or immune reaction.
- Personalized Treatment: Using the patient’s own stem cells allows for personalized treatment tailored to their specific needs and biology.
- Ethical Considerations: Autologous stem cell therapy avoids ethical concerns associated with the use of embryonic stem cells or donor-derived cells.
Allogeneic Stem Cell Therapy
Allogeneic stem cell therapy involves the use of stem cells obtained from a donor, typically from umbilical cord blood or bone marrow. These donor-derived stem cells are processed, purified, and then transplanted into the patient’s body for therapeutic purposes. Allogeneic stem cell therapy offers several advantages, including:
- Availability: Donor-derived stem cells are readily available and can be obtained from healthy, screened donors.
- Standardization: Allogeneic stem cell products can be standardized and manufactured in large quantities for widespread use.
- Broader Compatibility: Donor-derived stem cells may be suitable for patients who are unable to undergo autologous stem cell therapy due to medical reasons or limitations.
Applications of Stem Cell Therapy
Orthopedic Conditions
Stem cell therapy has shown promise in treating orthopedic conditions, such as osteoarthritis, tendon injuries, and joint degeneration. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow or adipose tissue can be injected directly into the affected joint or tissue to promote cartilage repair, reduce inflammation, and improve joint function.
Neurological Disorders
Stem cell therapy holds potential for treating neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and spinal cord injuries. Neural stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells can be used to replace damaged neurons, promote neural regeneration, and restore neurological function in affected individuals.
Cardiovascular Diseases
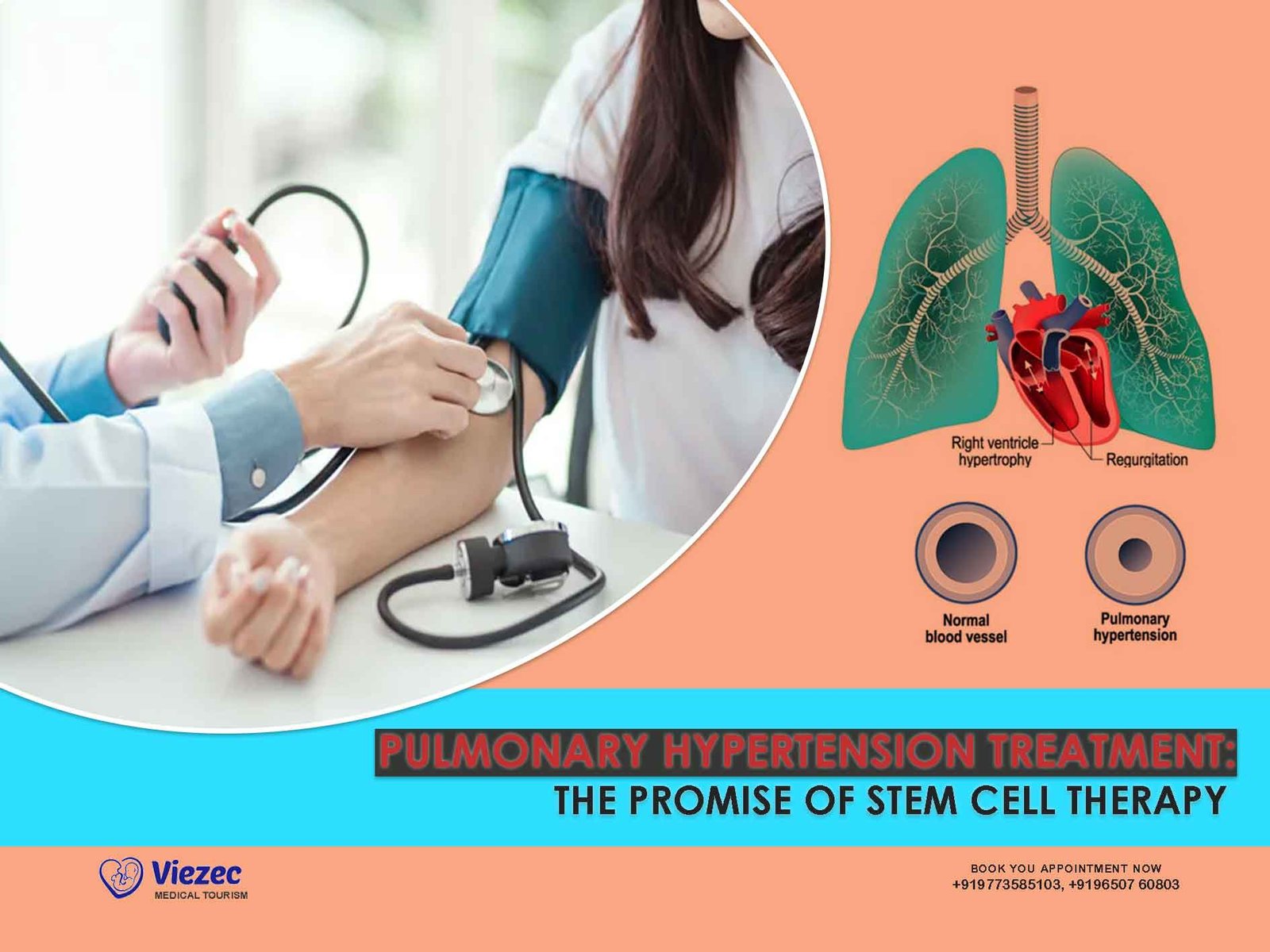
Stem cell therapy has been investigated as a potential treatment for cardiovascular diseases, such as heart failure, myocardial infarction, and peripheral artery disease. Stem cells derived from bone marrow or umbilical cord blood can be delivered directly to the heart or blood vessels to promote angiogenesis, improve cardiac function, and enhance tissue perfusion.
Autoimmune Disorders
Stem cell therapy has shown promise in treating autoimmune disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus. Hematopoietic stem cells obtained from bone marrow or peripheral blood can be used to reset the immune system, suppress autoimmune responses, and induce tolerance in affected individuals.
Considerations for Stem Cell Therapy
Safety and Efficacy
While stem cell therapy holds great promise for treating a variety of medical conditions, it’s essential to recognize that not all stem cell therapies are created equal. Safety and efficacy should be top priorities when considering stem cell treatment, and patients should seek treatment from reputable providers with a track record of success and adherence to regulatory standards.
Regulation and Oversight
Stem cell therapy is a rapidly evolving field with varying degrees of regulation and oversight depending on the country or region. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates stem cell products and therapies to ensure safety, efficacy, and compliance with established standards and guidelines.
Informed Consent
Before undergoing stem cell therapy, patients should receive comprehensive information about the treatment, including its potential risks, benefits, and alternatives. Informed consent is essential for ensuring that patients understand the nature of the treatment and can make well-informed decisions about their healthcare options.
Cost and Accessibility
Stem cell therapy can be costly, and insurance coverage may vary depending on the specific treatment and provider. Patients should consider the financial implications of stem cell therapy and explore alternative treatment options or financing options if necessary. Accessibility to stem cell therapy may also be limited by geographic location, availability of qualified providers, and regulatory constraints.
Stem cell therapy offers exciting possibilities for treating a wide range of medical conditions, leveraging the regenerative potential of stem cells to promote tissue repair, regeneration, and healing. Whether utilizing a patient’s own stem cells or donor-derived cells, stem cell therapy holds promise for revolutionizing healthcare and improving patient outcomes. However, it’s essential to approach stem cell therapy with caution, considering factors such as safety, efficacy, regulation, and informed consent. By staying informed and working with qualified healthcare providers, patients can navigate the evolving landscape of stem cell therapy and make informed decisions about their healthcare options.