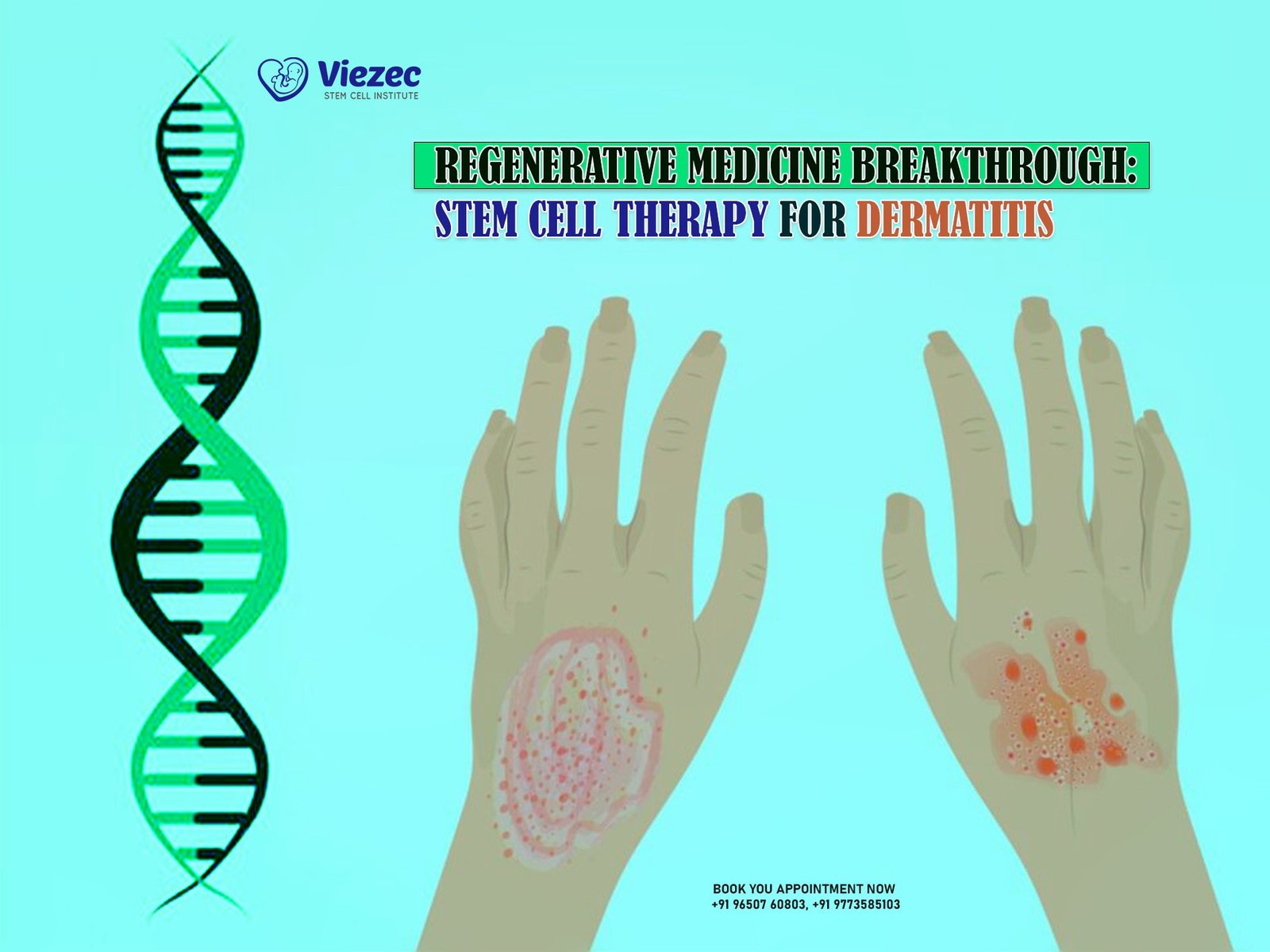
Stem cell therapy holds significant promise as a groundbreaking approach for managing and treating depression, including cases that are resistant to traditional treatments. Research suggests that stem cells, especially mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), have the potential to stimulate neurogenesis, repair damaged neural networks, and restore neurotransmitter balance—critical factors in the pathophysiology of depression. This emerging treatment modality not only offers hope for individuals with chronic depression but also paves the way for more personalized, effective therapies in the future, providing a new avenue for patients who have struggled with conventional treatments. As studies continue to evolve, the possibilities for stem cell therapy in mental health are expanding, offering exciting prospects for long-term relief and recovery.
What is Depression and How Does It Affect the Brain?
Depression is a mental health condition that affects many aspects of a person’s life, often leading to prolonged feelings of sadness, disinterest in activities, and difficulty managing daily responsibilities. This condition doesn’t just impact emotions—it also has a profound effect on brain function, particularly in areas related to mood, thought patterns, and behavior.
How Depression Affects the Brain:
-
Neurotransmitters: Imbalances in key neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine are strongly linked to depression, disrupting the brain’s ability to regulate mood and other functions, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
-
Brain Structure:
-
Hippocampus: This area, crucial for memory and learning, may shrink in individuals with depression, leading to difficulties with memory retention.
-
Prefrontal Cortex: This region, which governs attention, decision-making, and emotional control, can experience reduced activity and structural changes.
-
-
Brain Connectivity: Depression can interfere with communication between various brain regions, impacting the processing of information and emotional regulation.
-
Gray Matter: Research suggests that depression can lead to a reduction in gray matter in certain brain areas, which may increase susceptibility to future depressive episodes.
-
Neuroplasticity: The brain’s ability to adapt and form new connections may be hindered in depression, slowing recovery and the brain’s ability to respond to new challenges.
Understanding the impact of depression on the brain is critical for developing more effective treatment strategies and supporting individuals through their recovery journey.
The Science Behind Stem Cell Therapy and Its Impact on Mental Health
Stem cell therapy is rapidly gaining recognition as a potential breakthrough treatment for a variety of mental health conditions, including depression, schizophrenia, and PTSD. By leveraging the regenerative power of stem cells, this innovative therapy focuses on healing and rejuvenating the brain, offering new hope for those suffering from these complex disorders. The goal is to:
-
Repair Damaged Brain Tissue: Stem cells have the ability to regenerate and repair damaged areas in the brain, offering the potential to restore lost function.
-
Balance Neurotransmitter Activity: Stem cells can help regulate neurotransmitter levels, addressing imbalances that often contribute to mental health issues.
-
Enhance Neuroplasticity: Stem cells promote neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to form new neural connections, which can improve cognitive function and emotional regulation.
How Stem Cells Promote Neurogenesis and Brain Repair
Stem cells can promote neurogenesis and brain repair by replacing damaged neurons, secreting factors that support neuronal survival and growth, and modulating the brain’s immune response. They can also stimulate the brain’s own repair mechanisms by attracting endogenous neural stem cells to the injury site.
Here’s a more detailed explanation:
-
Replacing Damaged Neurons:
Stem cells, particularly neural stem cells (NSCs), have the ability to differentiate into neurons and other brain cells. In cases of brain injury or disease, stem cells can be transplanted into the damaged area, where they replace lost or damaged neurons. This replacement can help restore function and structure to the affected brain region. -
Supporting Neuronal Survival and Growth:
Stem cells release various growth factors and cytokines that enhance the survival, growth, and differentiation of existing neurons. These factors help create an environment conducive to neuronal regeneration and plasticity. For instance, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been shown to secrete factors that promote axon regeneration and neurogenesis.
In the future, ongoing research into stem cell therapies for neurodegenerative diseases promises further breakthroughs in effectively restoring lost cognitive functions and enhancing recovery in patients.
The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in Treating Depression
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) present a promising potential for addressing depression, thanks to their immunomodulatory and neurotrophic properties. Research indicates that MSCs can reduce depressive symptoms in animal models by modulating inflammatory responses, fostering neurogenesis, and impacting neurotransmitter systems. Encapsulated MSCs, in particular, have shown increased effectiveness in improving cell survival and stimulating neurotrophic factor production. This innovative approach could pave the way for novel treatments, especially for patients suffering from depression that has not responded to conventional therapies. Further clinical studies are necessary to confirm their efficacy in humans and refine treatment protocols.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): A Breakthrough in Depression Treatment
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) represent a major breakthrough in depression treatment. These cells are created by reprogramming adult cells back to a stem cell-like state, providing an abundant supply of brain cells. iPSCs are used for personalized models, enabling researchers to study depression in a more targeted way and test potential treatments. This revolutionary approach could offer new therapeutic options for depression, especially for patients who haven’t benefited from traditional therapies.
Can Stem Cells Address Treatment-Resistant Depression?
Stem cell therapy is emerging as a promising solution for patients with treatment-resistant depression (TRD). For individuals who haven’t found relief through traditional treatments, stem cells offer the potential to target the underlying causes of depression at a cellular level. By focusing on brain tissue repair and regenerating damaged areas, stem cells can promote long-term healing.
This innovative approach may also help restore neurotransmitter balance, a key factor in depression. Stem cells have the ability to address these imbalances, which are often difficult to correct with conventional therapies. As a result, stem cell therapy presents a hopeful alternative for those who have not responded to other treatments, offering the possibility of lasting improvement and better quality of life.
Neurotransmitter Imbalance and How Stem Cells Help Restore Balance
Neurotransmitter imbalances are central to many depressive disorders. Stem cells can help restore balance by generating new neurons and improving communication between brain cells. This process enhances the production of essential neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which are crucial for mood regulation. Stem cells’ ability to repair damaged brain circuits may provide a lasting solution to neurotransmitter imbalances in depression.
Is Stem Cell Therapy a Viable Alternative to Traditional Depression Treatments?
Patients considering stem cell therapy for depression can anticipate a tailored treatment plan designed to address their specific needs. The process begins with an in-depth evaluation to assess the suitability for stem cell therapy. During this initial consultation, the healthcare provider will review the patient’s medical history, conduct necessary tests, and discuss the potential benefits and risks of the procedure. Based on the evaluation, stem cells may be administered through injections directly into targeted areas of the brain to promote healing and regeneration of brain tissue.
The results of stem cell therapy vary from patient to patient. While some individuals may experience significant improvements in mood and overall well-being in a relatively short period, others may require a few months to notice the full effects. Since this treatment aims to heal the brain at a cellular level, the process is gradual, and long-term benefits may take time to manifest. Patients will have regular follow-up consultations to monitor their progress, ensure that the therapy is effective, and address any potential side effects. These ongoing assessments help maximize the chances of a successful outcome and provide reassurance to patients throughout their recovery.
Stem Cell Therapy vs. Conventional Treatments: Which Is More Effective?
Stem cell therapy offers a promising alternative to conventional depression treatments, such as antidepressants or psychotherapy.
-
Stem Cells: Target the biological causes of depression, such as neurotransmitter imbalance and brain damage.
-
Conventional Treatments: Primarily focus on symptom management and often require ongoing medication.
While stem cells offer long-term healing potential, traditional treatments may still be necessary for short-term symptom relief. As research continues, a combined approach may prove most effective for many patients.
The Safety and Risks of Stem Cell Therapy in Mental Health
Stem cell therapy in mental health treatments carries some risks, though these are generally low when the procedure is performed in a clinical setting.
-
Potential Risks: Infections, immune rejection, and inflammation.
-
Safety Measures: Patients are thoroughly screened before treatment to minimize these risks.
Though promising, stem cell therapy is still under research, and ongoing studies aim to refine protocols to ensure patient safety.
How Stem Cell Therapy Is Revolutionizing the Treatment of Depression
Stem cell therapy is revolutionizing depression treatment by offering a cellular approach to healing the brain. By promoting neurogenesis and improving neurotransmitter function, stem cells go beyond symptom management to address the underlying biological causes of depression. This innovative approach holds the potential to change the way we treat mental health disorders, offering long-term relief and improving the quality of life for chronic depression sufferers.
What You Need to Know Before Considering Stem Cell Therapy for Depression
Before opting for stem cell therapy, patients should carefully consider several factors:
-
Eligibility: A thorough consultation and medical evaluations will determine if stem cells are a viable option.
-
Treatment Plan: Personalized plans are designed to address individual needs.
-
Potential Outcomes: While promising, results can vary, and patience is necessary as benefits may take time to become evident.
-
Risks: It’s essential to be aware of potential side effects and discuss these risks with a qualified healthcare provider.
How Stem Cell Therapy Offers Hope for Chronic Depression Sufferers
For individuals suffering from chronic depression, stem cell therapy provides a promising alternative that addresses the underlying causes of their condition. Traditional treatments, such as medications and therapy, may offer temporary relief but often fail to provide long-term solutions. In contrast, stem cell therapy works at a deeper level, focusing on regenerating damaged brain cells and restoring the delicate balance of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which play a key role in mood regulation. By targeting the root causes of depression, stem cells offer the potential for more sustained improvements in mental health.
Additionally, stem cell therapy promotes neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to form new neural connections. This process is crucial for enhancing cognitive function and emotional resilience, offering lasting improvements in both mood and mental clarity. For those who have struggled with chronic depression for years and have not found relief through traditional methods, stem cell therapy offers a beacon of hope. This innovative treatment could help break the cycle of ongoing symptoms, providing a pathway to better mental health and an improved quality of life for many who have long felt trapped by their condition.
Promise and Potential of Stem Cells in Mental Health Treatment
Stem cells hold immense promise in transforming mental health treatments by targeting the root causes of disorders like depression. They have the potential to repair damaged brain tissue, restore neurotransmitter balance, and regenerate neurons, leading to sustainable improvements in mental well-being. As ongoing research uncovers more about their efficacy, stem cell therapy could become an integral part of mental health care. This revolutionary approach offers new hope for individuals who have struggled with treatment-resistant conditions, providing an alternative that addresses the underlying biological mechanisms, potentially offering long-term relief and better outcomes.
Getting Started: How to Pursue Stem Cell Therapy for Depression
To begin your journey with stem cell therapy for depression, the first step is to schedule a consultation with a healthcare provider specializing in regenerative medicine, like Viezec. Our team will conduct a comprehensive evaluation, including medical screenings and assessments, to create a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs. Choosing a reputable clinic with expertise in stem cell therapies is crucial for ensuring the treatment is both safe and effective. At Viezec, we prioritize patient safety and provide clear guidance on the potential benefits and risks. Take the first step toward potentially transformative care by contacting us today to learn more about how stem cell therapy can help alleviate depression and improve your quality of life.