Infertility remains a significant concern for couples worldwide, affecting approximately 15% of reproductive-aged couples. While infertility can arise from various factors, male infertility contributes to nearly half of all cases. Azoospermia, characterized by the absence of sperm in the ejaculate, presents a particularly challenging obstacle to achieving conception. However, recent advancements in stem cell therapy offer promising prospects for managing this condition.
Definition of Azoospermia
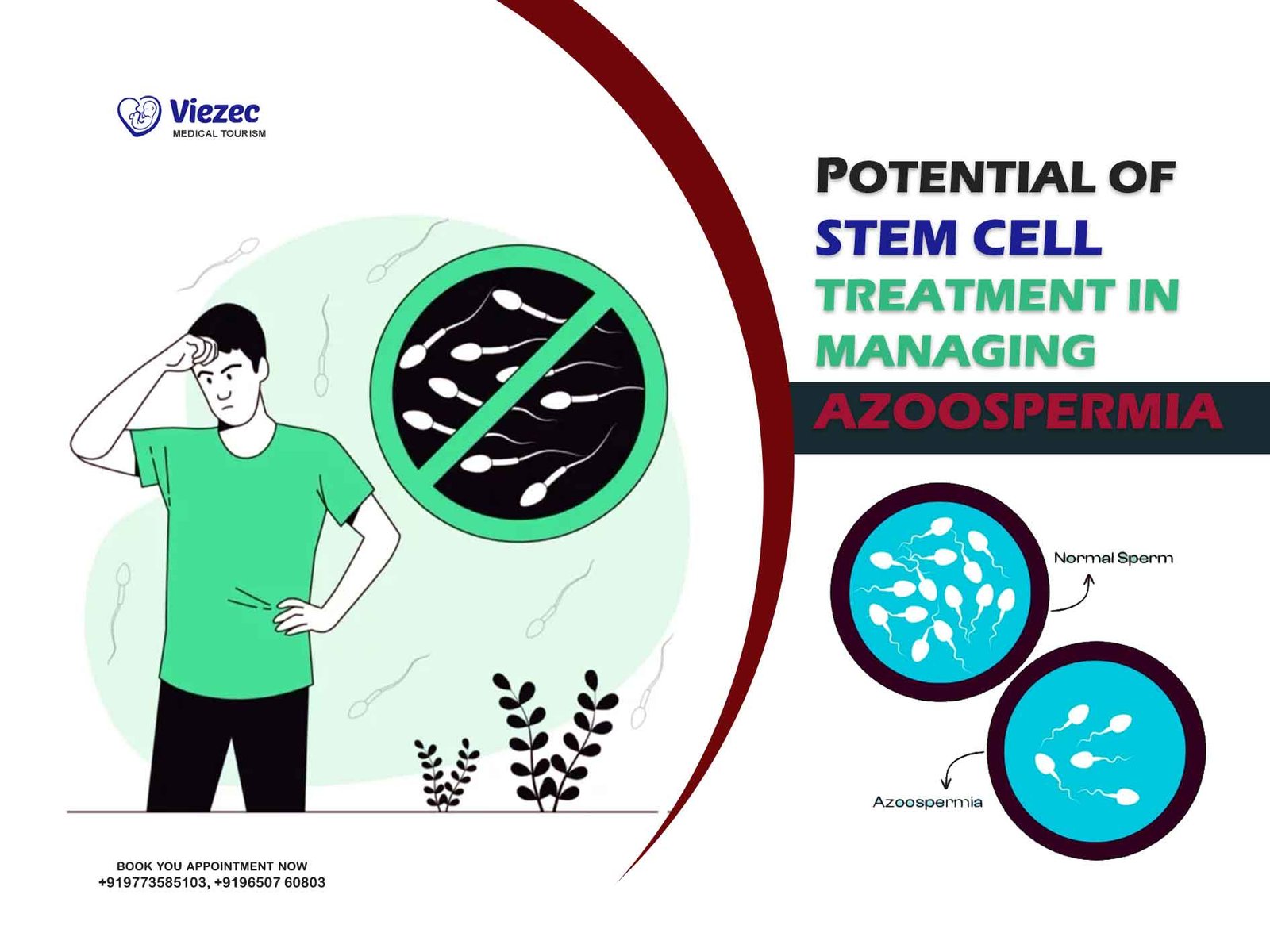
Azoospermia, a condition affecting approximately 1% of the male population, is diagnosed when no sperm are found in the ejaculate upon microscopic examination. This absence of sperm can result from either obstructive or non-obstructive factors, presenting distinct challenges in diagnosis and treatment.
Importance of Fertility in Men
Fertility plays a crucial role in family planning and reproductive health. For many men, the inability to father a child can lead to emotional distress and strain on relationships. Addressing male infertility not only fulfills the desire for parenthood but also contributes to overall well-being and quality of life.
Overview of Current Treatment Options
Traditional treatments for azoospermia include surgical interventions, hormone therapy, and assisted reproductive techniques such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). While these approaches can be effective in certain cases, they may not address the underlying causes of azoospermia or carry significant risks and limitations.
Understanding Azoospermia
Types of Azoospermia (Obstructive vs. Non-obstructive)
Azoospermia can be classified into obstructive and non-obstructive categories based on the underlying pathology. Obstructive azoospermia occurs when there is a physical blockage preventing the release of sperm into the ejaculate, while non-obstructive azoospermia results from impaired sperm production within the testes.
Causes and Risk Factors
Various factors can contribute to the development of azoospermia, including genetic abnormalities, hormonal imbalances, infections, environmental exposures, and lifestyle factors such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for determining the most appropriate treatment approach.
Diagnostic Procedures for Azoospermia
Diagnosing azoospermia typically involves a comprehensive evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, semen analysis, hormonal assessments, and imaging studies such as scrotal ultrasound. Additionally, genetic testing may be indicated to identify potential chromosomal abnormalities or mutations associated with infertility.
Stem Cell Therapy: Basics
What are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells with the remarkable ability to differentiate into various cell types and self-renew indefinitely. They hold tremendous potential for regenerative medicine and tissue repair due to their regenerative and immunomodulatory properties.
Types of Stem Cells Relevant to Azoospermia Treatment
Several types of stem cells have been investigated for their potential in treating azoospermia, including spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs), embryonic stem cells (ESCs), induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Each type offers unique advantages and challenges in terms of safety, efficiency, and ethical considerations.
Mechanisms of Action in Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy holds promise for treating azoospermia through various mechanisms, including differentiation into mature sperm cells, promotion of endogenous spermatogenesis, modulation of the local microenvironment, and immunomodulation to reduce inflammation and tissue damage.
Stem Cell Therapy in Azoospermia: Preclinical Studies
Animal Models and Experimental Designs
Preclinical studies using animal models have provided valuable insights into the feasibility and efficacy of stem cell-based approaches for treating azoospermia. These studies often employ rodent models, such as mice and rats, to investigate the safety and therapeutic potential of stem cell transplantation in restoring spermatogenesis.
Key Findings and Outcomes
Several preclinical studies have demonstrated the ability of stem cells to differentiate into functional sperm cells and restore fertility in animal models of azoospermia. These findings offer promising proof-of-concept evidence for the translational potential of stem cell therapy in human patients.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the encouraging results from preclinical studies, several challenges and limitations must be addressed before stem cell therapy can be widely implemented in clinical practice. These include concerns related to safety, efficacy, long-term outcomes, ethical considerations, and regulatory approval.
Clinical Applications of Stem Cell Therapy
Case Studies and Clinical Trials
Clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapy for azoospermia are currently underway, with several promising case studies demonstrating positive outcomes in selected patients. These trials aim to establish the feasibility and therapeutic potential of stem cell transplantation in restoring fertility in men with azoospermia.
Efficacy and Safety Assessments
Assessing the efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy in clinical settings requires rigorous monitoring and evaluation of various parameters, including sperm production, sperm quality, reproductive hormone levels, testicular function, and potential adverse effects. Long-term follow-up is essential to determine the durability and sustainability of treatment outcomes.
Long-term Outcomes and Follow-up Studies
Longitudinal studies tracking the long-term outcomes of stem cell therapy in azoospermia patients are essential for evaluating its efficacy, durability, and safety over time. These studies can provide valuable insights into the potential benefits and limitations of stem cell-based approaches in addressing male infertility.
Directions and Challenges
Potential Advancements in Stem Cell Research for Azoospermia
Future research in stem cell biology and regenerative medicine holds promise for overcoming current limitations and further improving the efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy for azoospermia. Advancements in cell culture techniques, genetic engineering, and biomaterials may enhance the efficiency of sperm production and transplantation.
Regulatory Considerations and Ethical Implications
Navigating regulatory pathways and addressing ethical concerns are paramount in advancing stem cell therapy for azoospermia from preclinical research to clinical application. Clear guidelines and standards are needed to ensure patient safety, informed consent, ethical use of stem cells, and equitable access to treatment.
Addressing Remaining Hurdles and Uncertainties
Despite significant progress, several challenges and uncertainties remain in the development and implementation of stem cell therapy for azoospermia. These include optimizing cell delivery methods, improving engraftment and survival of transplanted cells, minimizing immune rejection, and ensuring reproducibility and scalability of treatment protocols.
Comparative Analysis: Stem Cell Therapy vs. Traditional Treatments
Comparing Effectiveness and Side Effects
Comparing the effectiveness and side effects of stem cell therapy with traditional treatments for azoospermia is essential for informing clinical decision-making and optimizing patient outcomes. While traditional treatments such as surgical interventions and hormonal therapy may offer immediate relief, stem cell therapy holds the potential for long-term restoration of fertility.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Conducting a cost-benefit analysis can help assess the economic implications of adopting stem cell therapy as a treatment option for azoospermia. While stem cell therapy may initially entail higher upfront costs, its potential to offer sustained benefits and reduce the need for repeated interventions may justify its long-term economic value.
Patient Perspectives and Preferences
Understanding patient perspectives, preferences, and priorities is crucial for tailoring treatment approaches to individual needs and preferences. Factors such as treatment efficacy, safety, convenience, cost, and ethical considerations play a significant role in patient decision-making regarding the choice of treatment for azoospermia.
Multidisciplinary Approaches in Azoospermia Management
Integration of Stem Cell Therapy with Other Treatment Modalities
Adopting a multidisciplinary approach to azoospermia management involves integrating stem cell therapy with other treatment modalities, such as surgical interventions, hormone therapy, and assisted reproductive techniques. Collaborative efforts among urologists, reproductive endocrinologists, stem cell researchers, and other healthcare professionals are essential for optimizing patient care and outcomes.
Role of Urologists, Reproductive Endocrinologists, and Stem Cell Researchers
Urologists play a central role in diagnosing and treating azoospermia, offering expertise in surgical interventions and male reproductive health. Reproductive endocrinologists specialize in hormonal imbalances and assisted reproductive techniques, while stem cell researchers contribute expertise in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
Holistic Care for Azoospermia Patients
Providing holistic care for azoospermia patients involves addressing not only their physical health but also their psychological, emotional, and social well-being. Counseling, support groups, and fertility preservation options can help patients cope with the challenges of infertility and make informed decisions about their treatment journey.
Promising Trends and Emerging Technologies
Advancements in Tissue Engineering for Male Infertility
Tissue engineering approaches hold promise for generating functional sperm cells in vitro for transplantation or assisted reproduction. By mimicking the complex microenvironment of the testes, tissue-engineered constructs can support spermatogenesis and provide an alternative source of sperm for azoospermia patients.
Gene Editing Techniques and Their Potential Applications
Advancements in gene editing techniques, such as CRISPR-Cas9, offer new opportunities for correcting genetic mutations associated with male infertility. By targeting specific genes implicated in azoospermia, gene editing technologies may enable precise interventions to restore normal spermatogenesis and improve fertility outcomes.
Personalized Medicine Approaches in Azoospermia Treatment
Personalized medicine approaches, including genetic screening, molecular profiling, and tailored treatment strategies, can optimize the management of azoospermia based on individual patient characteristics and underlying genetic factors. By customizing treatment plans to each patient’s unique needs, personalized medicine holds the potential to improve treatment outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Stem cell therapy represents a promising frontier in the management of azoospermia, offering potential benefits such as sperm production, tissue regeneration, and immunomodulation. While significant progress has been made in preclinical and clinical studies, several challenges and uncertainties remain, necessitating further research, collaboration, and innovation to realize the full potential of stem cell therapy in addressing male infertility. By integrating stem cell therapy with other treatment modalities and adopting a multidisciplinary approach, healthcare professionals can provide comprehensive care for azoospermia patients and improve their chances of achieving parenthood and fulfilling their reproductive aspirations.