Stem cell-based therapy has emerged as a promising frontier in the field of medical science, offering revolutionary solutions for treating a wide array of human diseases. Stem cells possess unique properties, including self-renewal and differentiation capabilities, making them invaluable tools in regenerative medicine and disease management. This article explores the transformative potential of stem cell-based therapy in revolutionizing the treatment landscape for various human diseases.
Understanding Stem Cells
What Are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells with the remarkable ability to develop into specialized cell types. They serve as the building blocks of the human body, playing a crucial role in embryonic development, tissue repair, and regeneration. Stem cells can be broadly categorized into two main types: embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and adult stem cells.
Types of Stem Cells
- Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs): These stem cells are derived from the inner cell mass of blastocysts, which are early-stage embryos. ESCs are pluripotent, meaning they have the potential to differentiate into any cell type in the body. This remarkable versatility makes them valuable for research and therapeutic purposes.
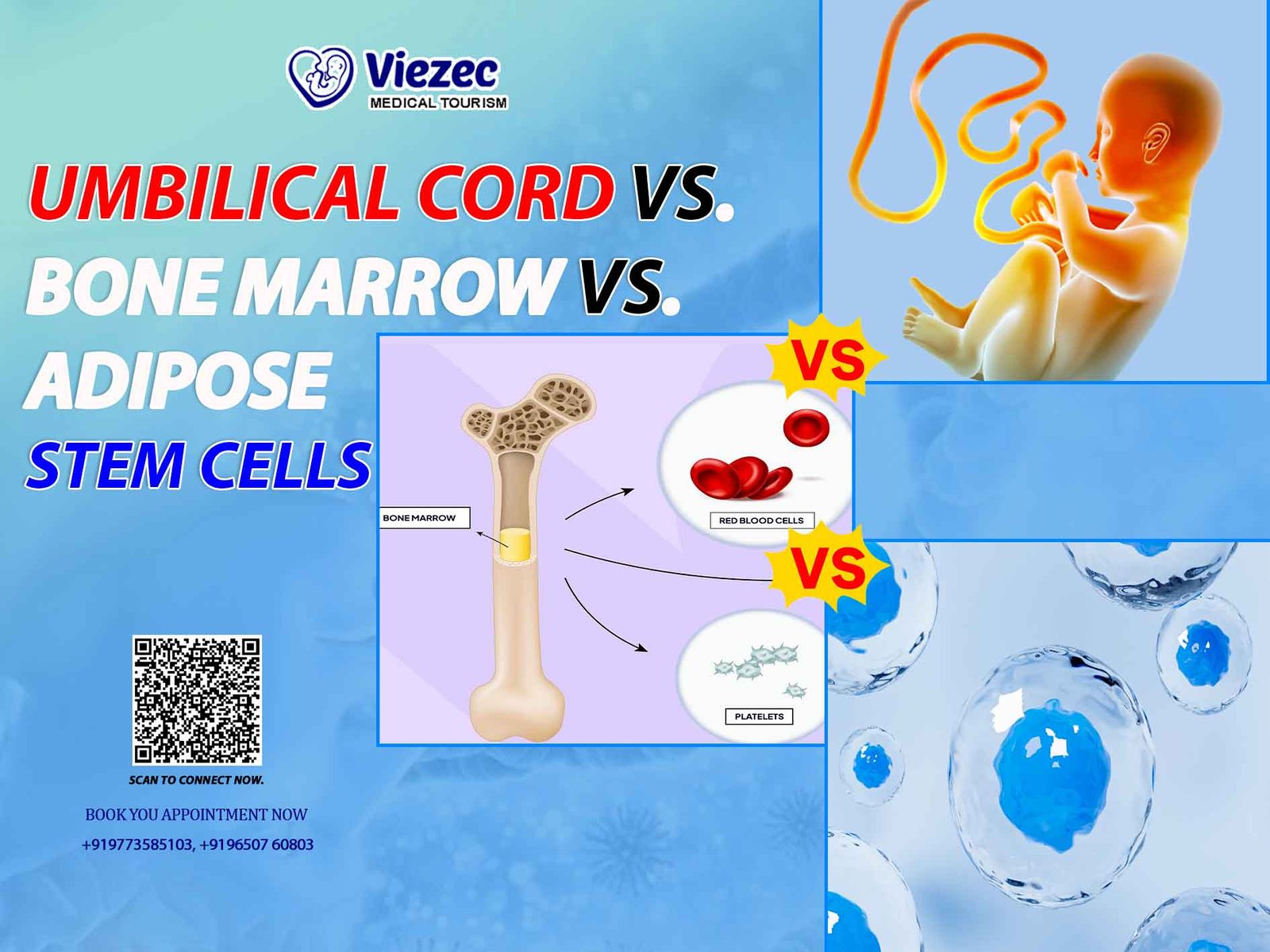
- Adult Stem Cells: Also known as somatic or tissue-specific stem cells, these cells are found in various tissues and organs throughout the body. Unlike ESCs, adult stem cells are multipotent or sometimes unipotent, meaning they can differentiate into a limited range of cell types. Examples include hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow and mesenchymal stem cells in the adipose tissue.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
In addition to ESCs and adult stem cells, scientists have developed a third category of stem cells known as induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). These cells are generated by reprogramming adult somatic cells, such as skin cells, to revert to a pluripotent state. iPSCs exhibit characteristics similar to ESCs and hold significant potential for personalized medicine and disease modeling.
Applications of Stem Cell-Based Therapy
Regenerative Medicine
One of the most promising applications of stem cell-based therapy is in regenerative medicine, where stem cells are used to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs. This approach offers hope for patients suffering from degenerative diseases, traumatic injuries, and congenital defects. By harnessing the regenerative potential of stem cells, researchers aim to restore normal tissue function and improve patient outcomes.
Disease Modeling and Drug Discovery
Stem cells provide a valuable tool for modeling human diseases in the laboratory setting. By generating disease-specific cell lines from patient-derived iPSCs, researchers can study the underlying mechanisms of various disorders, screen potential therapeutics, and develop personalized treatment strategies. This approach has the potential to revolutionize drug discovery and accelerate the development of novel therapies for a wide range of diseases.
Immunotherapy
Stem cell-based immunotherapy involves harnessing the immune-modulating properties of stem cells to treat autoimmune diseases, cancer, and other conditions characterized by dysfunctional immune responses. Mesenchymal stem cells, in particular, have been studied for their ability to suppress inflammation, modulate immune cell activity, and promote tissue repair. Immunotherapy approaches using stem cells hold promise for achieving long-term remission and improving the quality of life for patients with immune-mediated disorders.
Clinical Advances in Stem Cell Therapy
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has been performed for decades to treat various hematological disorders, including leukemia, lymphoma, and aplastic anemia. During HSCT, stem cells obtained from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood are infused into the patient to restore healthy blood cell production. This procedure has saved countless lives and serves as a cornerstone of stem cell therapy in clinical practice.
Cartilage Regeneration
Osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease characterized by cartilage deterioration, affects millions of people worldwide and poses a significant healthcare burden. Stem cell-based approaches offer potential solutions for cartilage regeneration and joint repair. Researchers are investigating the use of mesenchymal stem cells, either alone or in combination with biomaterial scaffolds, growth factors, and other therapeutic agents, to promote cartilage healing and alleviate osteoarthritis symptoms.
Neurological Disorders
Neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and spinal cord injury, present formidable challenges due to their complex nature and limited treatment options. Stem cell-based therapies hold promise for repairing damaged neural tissue, restoring lost function, and improving neurological outcomes. Clinical trials involving the transplantation of neural stem cells, ESC-derived neurons, and iPSC-derived dopaminergic cells have shown encouraging results, paving the way for future advancements in the field of neuroregeneration.
Safety and Efficacy
Ensuring the safety and efficacy of stem cell-based therapies is paramount for their successful translation into clinical practice. Challenges such as immune rejection, tumor formation, and unintended differentiation must be addressed through rigorous preclinical testing and well-designed clinical trials. Additionally, optimizing cell manufacturing processes, standardizing quality control measures, and developing reliable delivery methods are critical for maximizing therapeutic outcomes and minimizing risks associated with stem cell therapy.
Personalized Medicine
The advent of iPSC technology has opened new avenues for personalized medicine, where patient-specific stem cells can be used to tailor treatments to individual genetic makeup and disease characteristics. By leveraging iPSC-derived cell models, clinicians can predict drug responses, identify optimal treatment regimens, and optimize therapeutic outcomes for each patient. As our understanding of stem cell biology continues to deepen and technology advances, personalized stem cell-based therapies are poised to revolutionize healthcare delivery and improve patient care across diverse medical specialties.
Make an informed Decision
Stem cell-based therapy represents a paradigm shift in modern medicine, offering unprecedented opportunities for treating human diseases and improving patient outcomes. From regenerative medicine and disease modeling to immunotherapy and personalized medicine, the applications of stem cells are vast and far-reaching. While significant challenges remain, the transformative potential of stem cell-based therapies cannot be overstated. By harnessing the regenerative power of stem cells and translating scientific discoveries into clinical innovations, we have the potential to revolutionize the way we prevent, diagnose, and treat diseases, ushering in a new era of healthcare excellence and human well-being.