As life expectancy increases across the world, more people are living longer but often with chronic pain, joint degeneration, mobility issues, and age-related diseases. Conventional treatments such as long-term medications or major surgeries are not always ideal for elderly patients due to higher risks, slower recovery, and multiple underlying health conditions. This has led to growing interest in stem cell therapy for elderly patients as a regenerative and minimally invasive treatment option.
Stem cell therapy focuses on repairing damaged tissues, reducing inflammation, and supporting natural healing rather than simply managing symptoms. For seniors and older adults, this approach can offer meaningful improvements in mobility, comfort, and overall quality of life when used appropriately.
This guide explains who can benefit from stem cell therapy in old age, how it works, safety considerations, expected outcomes, and what elderly patients should realistically expect before choosing this treatment.
Understanding Stem Cell Therapy and Aging
Stem cells are unique cells capable of self-renewal and differentiation into specialized cells such as bone, cartilage, muscle, or nerve cells. In regenerative medicine, these cells are used to support tissue repair and modulate inflammation.
As the body ages, its natural repair mechanisms slow down. The number and activity of native stem cells decrease, and tissues take longer to heal. This is why joint damage, spinal degeneration, and nerve-related conditions become more common in older adults.
Stem cell therapy in the aging population aims to supplement or stimulate these repair mechanisms, helping the body heal more effectively even at an advanced age.
Is There an Age Limit for Stem Cell Therapy?
One of the most common questions is whether there is an age limit for stem cell therapy. Chronological age alone does not determine eligibility. Many patients in their 60s, 70s, and even 80s have successfully undergone stem cell treatment.
What matters more is:
-
Overall health status
-
Severity and type of condition
-
Presence of uncontrolled chronic diseases
-
Functional goals and expectations
In clinical practice, stem cell therapy after 60 or 70 years is evaluated on a case-by-case basis. Elderly patients who are medically stable and have realistic expectations may still be good candidates.
Who Can Benefit from Stem Cell Therapy in Elderly Patients?
Stem cell therapy is not suitable for every senior, but it can benefit many older adults dealing with degenerative or inflammatory conditions.
Elderly Patients Most Likely to Benefit
Stem cell treatment may be appropriate for elderly patients who:
-
Have chronic joint or musculoskeletal pain
-
Experience reduced mobility due to degeneration
-
Are not ideal candidates for surgery
-
Have not responded well to medications or physiotherapy
-
Seek quality-of-life improvement rather than aggressive intervention
Conditions Commonly Treated in Seniors
Osteoarthritis and Joint Degeneration
Osteoarthritis and Joint Degeneration
-
Knee osteoarthritis
-
Hip arthritis
-
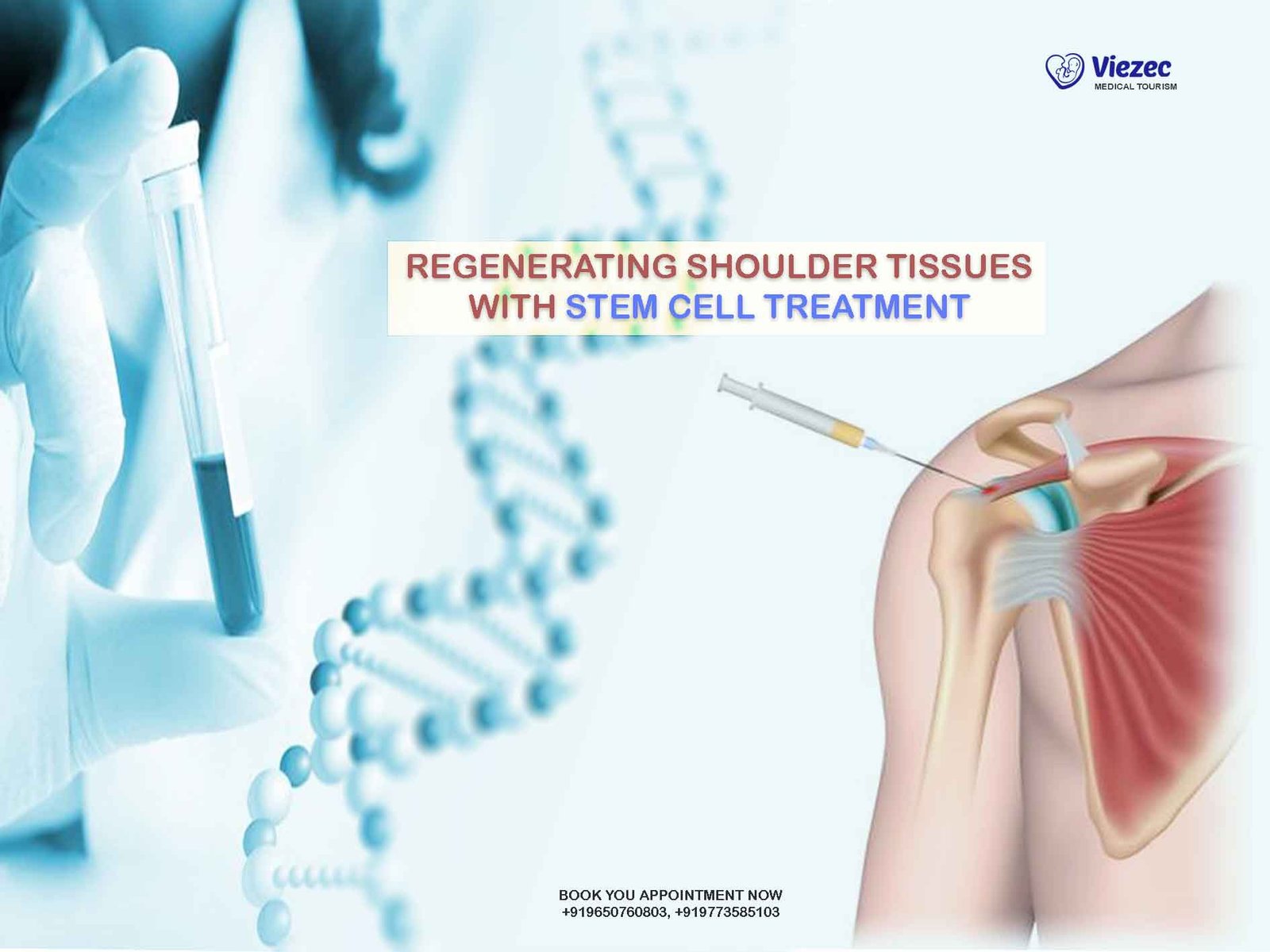
Shoulder degeneration
-
Ankle and small joint arthritis
Stem cell therapy for arthritis in elderly patients focuses on reducing inflammation, improving joint lubrication, and supporting cartilage health.
Spine and Disc Problems
-
Cervical and lumbar spondylosis
-
Chronic back or neck pain
Stem cell therapy for spinal degeneration in older adults may help relieve pain and improve function in selected cases.
Neurological and Post-Injury Conditions
-
Stroke rehabilitation support
-
Parkinson’s disease management
While not a cure, stem cell therapy for neurodegenerative conditions in elderly patients may support nerve repair and functional improvement in specific scenarios.
Soft Tissue and Tendon Injuries
-
Rotator cuff degeneration
-
Tendinitis and ligament wear
-
Muscle loss due to aging
Discover if Stem Cell Therapy Can Help You!
Book a Free Consultation with Our Experts at Viezec !
Who May Not Be a Suitable Candidate?
Not all elderly patients are eligible. Stem cell therapy may not be recommended for seniors with:
-
Active cancer or recent cancer history
-
Severe uncontrolled diabetes or heart disease
-
Active infections
-
Advanced organ failure
-
Certain autoimmune conditions without stabilization
A comprehensive medical evaluation is essential to ensure safety and realistic outcomes.
Types of Stem Cells Used for Elderly Patients
The choice of stem cell type depends on the patient’s condition, age, and treatment goals.
Autologous Stem Cells
These are derived from the patient’s own body, commonly from:
-
Bone marrow
-
Adipose (fat) tissue
Autologous stem cells are often preferred in elderly patients due to lower risk of immune reactions.
Allogeneic Stem Cells
These come from carefully screened donors. In older adults with reduced stem cell quality, donor-derived cells may sometimes be considered under strict medical protocols.
At centers like Viezec, treatment planning focuses on safety, ethical standards, and regulatory compliance, especially for senior patients.
Is Stem Cell Therapy Safe for Elderly Patients?
Safety is a primary concern when treating older adults. When performed in a controlled medical setting with proper screening, stem cell therapy is generally considered safe for elderly patients.
Safety Considerations Include:
-
Pre-treatment medical evaluation
-
Imaging and diagnostic tests
-
Review of medications
-
Monitoring during and after the procedure
Because stem cell therapy is minimally invasive, it typically involves fewer risks than surgery, such as infection, anesthesia complications, or prolonged hospitalization.
However, outcomes depend heavily on proper patient selection and experienced medical supervision.
What to Expect Before Stem Cell Therapy
Medical Assessment
Elderly patients undergo a detailed evaluation that may include:
-
Medical history review
-
Physical examination
-
Blood tests
-
Imaging such as MRI or X-ray
-
Functional assessment
This helps determine whether stem cell therapy is appropriate and which approach is most suitable.
Treatment Planning
The treatment plan is customized based on:
-
Age and overall health
-
Type and severity of condition
-
Expected functional improvement
Patients are informed about potential benefits, limitations, and recovery expectations.
Start Your Regenerative Journey Today!
Contact Viezec for Personalized Stem Cell Therapy Plan
The Stem Cell Therapy Procedure for Seniors
The procedure is usually performed on an outpatient basis.
Key Steps
-
Stem cell collection from bone marrow, fat tissue, or donor source
-
Processing and concentration of cells in a sterile environment
-
Targeted administration into the affected joint, tissue, or area
The procedure is minimally invasive and often completed within a few hours.
Recovery and Post-Treatment Expectations
Recovery Time
Recovery is generally quicker compared to surgery. Most elderly patients:
-
Resume light activities within a few days
-
Experience gradual improvement over weeks to months
When Results Appear
Stem cell therapy does not provide instant relief. Improvement often occurs progressively as inflammation reduces and tissue repair begins.
For seniors, noticeable improvement may take several weeks, depending on the condition and overall health.
Effectiveness of Stem Cell Therapy in Elderly Patients
Effectiveness varies based on:
-
Age-related tissue health
-
Severity of degeneration
-
Compliance with post-treatment care
Many elderly patients report:
-
Reduced pain
-
Improved joint function
-
Better mobility
-
Enhanced quality of life
It is important to understand that stem cell therapy aims to improve function and comfort, not reverse aging completely.
Managing Expectations in Older Adults
One of the most important aspects of treatment is expectation management. Stem cell therapy:
-
Is not a miracle cure
-
May not eliminate the need for future treatments
-
Works best in early to moderate degeneration
Clear communication ensures elderly patients make informed decisions.
Cost of Stem Cell Therapy for Elderly Patients
Cost depends on several factors:
-
Number of sessions required
-
Medical facility and expertise
In India, stem cell therapy is more affordable compared to many Western countries, making it attractive for international patients seeking advanced care. Centers like Viezec support global patients with structured treatment pathways and coordinated care.
Why India Is a Preferred Destination for Stem Cell Therapy
India has emerged as a key destination for regenerative medicine due to:
-
Experienced medical professionals
-
Advanced infrastructure
-
Cost-effective treatment options
-
Shorter waiting times
Elderly international patients often choose India for quality care combined with affordability.
Is Your Condition Eligible for Stem Cell Therapy?
Speak directly with our specialist.
Role of Follow-Up and Rehabilitation
Post-treatment care plays a vital role in outcomes. Elderly patients may benefit from:
-
Physiotherapy
-
Nutritional support
-
Regular follow-up assessments
These steps help maximize the benefits of stem cell therapy.
Frequently Ased Questions
Stem cell therapy is generally safe for elderly patients when performed after proper medical evaluation and in a controlled clinical setting. Safety depends on overall health, the condition being treated, and the type of stem cells used. Most treatments are minimally invasive and carry lower risk than surgical procedures.
There is no fixed upper age limit for stem cell therapy. Eligibility depends on medical fitness, severity of disease, and treatment goals rather than age alone. Many patients in their 60s, 70s, and older can still benefit if they are medically stable.
Results are gradual. Elderly patients may begin noticing improvement within a few weeks, with continued progress over several months. Healing timelines vary based on age, overall health, and the extent of tissue damage.
In selected cases, stem cell therapy may help delay or reduce the need for surgery, especially for joint and spine conditions. It is often considered when surgery carries higher risks or when patients prefer a less invasive treatment option.
Conditions with the best response in elderly patients include osteoarthritis, joint degeneration, chronic joint pain, spinal disc degeneration, and certain soft tissue injuries. Outcomes depend on disease stage and individual health factors.
Final Thoughts
Stem cell therapy represents a promising option for those seeking relief from degenerative conditions without the risks of major surgery. When used responsibly, it can improve mobility, reduce pain, and enhance quality of life for older adults.
However, success depends on careful patient selection, ethical medical practice, and realistic expectations. Elderly patients considering this therapy should seek experienced providers who prioritize safety, transparency, and individualized care.
With proper evaluation and guidance, stem cell therapy can be a meaningful part of a comprehensive treatment approach for seniors looking to stay active and independent longer.
List of References
Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation Feasible in Elderly Multiple Myeloma Patients — Study showing similar progression-free and overall survival between patients ≥65 and younger patients, indicating feasibility and comparable success in select elderly.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37739860/
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Outcomes in Patients ≥70 — Meta-analysis reporting survival, disease-free survival, and relapse rates in elderly patients receiving stem cell transplants, reflecting real-world transplant outcomes.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39755255/
Stem Cell Therapy Success Rates Hit ~78% in Diverse Conditions (General Research) — Overview of success rates across conditions showing significant quality-of-life improvements in many stem cell treatments and highlighting challenges like graft-versus-host disease.
https://globalrph.com/2025/03/stem-cell-therapy-success-rates-hit-78-new-research-reveals-breakthrough-results/
Autologous HSCT Safety & Efficacy in Elderly Multiple Myeloma — Retrospective evidence that autologous stem cell transplant can be safe and effective in patients ≥65, with substantial response rates and acceptable mortality.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30783208