KEY TAKEAWAYS
Stem cell therapy has shown promise in aiding locomotion recovery after spinal cord injuries by promoting nerve regeneration and reducing inflammation. Studies have demonstrated that certain stem cell types, particularly umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (U-MSCs), can significantly improve locomotor function and reduce pain in animal models. Furthermore, some clinical trials have reported positive outcomes, with patients regaining lost movement and sensation after stem cell treatment. These regenerative effects are believed to be driven by the stem cells’ ability to differentiate into neural cells and secrete neurotrophic factors. As research advances, stem cell therapy continues to offer hope for improved quality of life in individuals with spinal cord injuries.
What Is Locomotion Loss and Why It Happens After Spinal Cord Injury
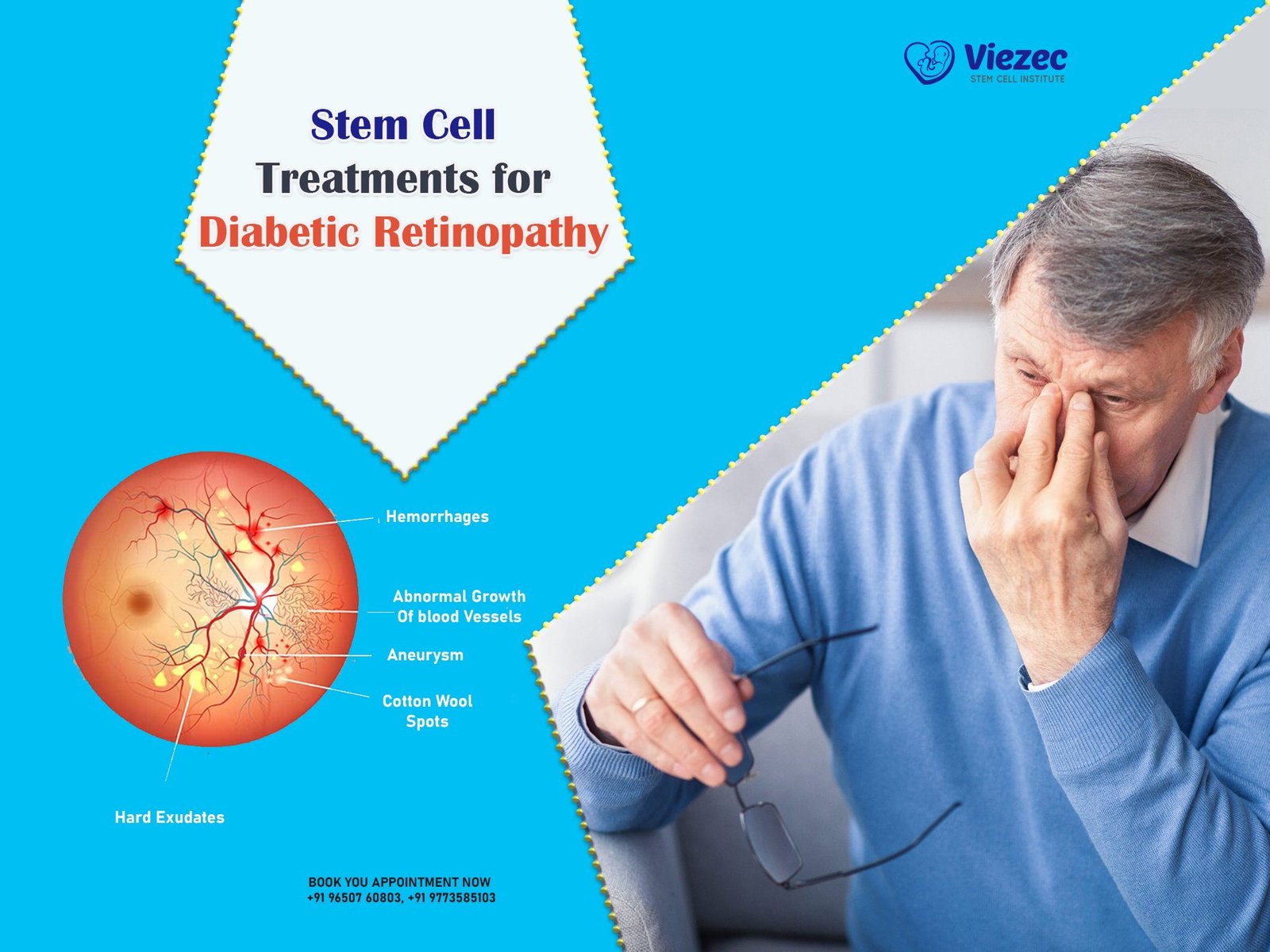
Locomotion loss refers to the impairment or complete loss of movement and mobility, typically affecting the legs or entire body. This condition is especially common after a spinal cord injury (SCI), where damage to the spinal nerves disrupts communication between the brain and muscles. When the spinal cord is injured, signals that control voluntary movement and reflexes can be blocked, leading to paralysis, weakness, or coordination difficulties depending on the severity and location of the injury.
Understanding Spinal Cord Damage and Its Impact on Mobility
The spinal cord is a vital part of the central nervous system that transmits messages from the brain to the rest of the body. When injured, even partially, the damage can impair the brain’s ability to send motor commands and receive sensory feedback. This disruption often leads to mobility loss, including difficulty walking, balancing, or controlling limb movements. The level of impairment depends on the injury’s location—higher injuries affect more of the body, while lower injuries may cause partial paralysis or loss of leg function. Spinal cord damage can also result in muscle stiffness, spasticity, and chronic pain.
Causes of Locomotor Dysfunction After Injury or Disease
Locomotor dysfunction can result from traumatic events like spinal cord injuries, strokes, or head trauma, as well as diseases such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, or muscular dystrophy. These conditions damage the pathways responsible for sending movement signals from the brain to the muscles. When these pathways are interrupted, muscle coordination becomes impaired. Additionally, inflammation, nerve degeneration, and scar tissue formation can further worsen the condition. Over time, this leads to reduced strength, loss of balance, or complete paralysis, affecting a person’s ability to perform daily tasks and reducing overall quality of life.
Introduction to Stem Cell Therapy for Movement Restoration
Stem cell therapy offers a revolutionary approach to restoring movement in individuals affected by spinal cord injuries, stroke, or neurodegenerative conditions. By harnessing the body’s natural repair mechanisms, stem cells help regenerate damaged nerve tissues and improve motor functions. This treatment has gained global attention for its potential to restore lost mobility, reduce inflammation, and support healing at the cellular level—making it a promising option in the field of regenerative medicine.
What Are Stem Cells and How Do They Work?
Stem cells are the body’s master cells with the unique ability to self-renew and transform into specialized cell types such as nerve, muscle, or bone cells. In the context of locomotion recovery, they target injured or degenerated tissues by migrating to damaged sites and releasing healing factors. These cells stimulate the repair of neurons, reduce inflammation, and support the formation of new neural pathways. Their regenerative and immunomodulatory properties are key to restoring mobility and improving neurological function over time.
Types of Stem Cells Used in Locomotion Recovery (MSC, NSC, etc.)
Several types of stem cells are utilized in movement restoration therapies. Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)—commonly derived from bone marrow, umbilical cord, or fat—are widely used due to their anti-inflammatory and tissue-regenerating abilities. Neural Stem Cells (NSCs) specifically target nerve repair and are crucial in spinal cord injury recovery. Additionally, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are gaining attention for their ability to become any cell type. Each cell type plays a unique role in promoting nerve healing and improving motor functions.
Mechanisms: How Stem Cells Help Restore Movement
Stem cell therapy supports movement recovery by targeting the root causes of motor dysfunction at the cellular level. These cells promote nerve regeneration, reduce damaging inflammation, and secrete healing proteins. Their multifunctional action allows restoration of neural pathways, which is essential for regaining lost mobility after spinal cord injury or neurological trauma.
Nerve Regeneration and Neuroplasticity
Stem cells can differentiate into nerve cells and support the repair of damaged neurons, which is vital for restoring locomotion. They also stimulate neuroplasticity—the brain and spinal cord’s ability to reorganize and form new neural connections. This adaptability is crucial for relearning movement patterns, improving coordination, and regaining voluntary motor control after injury.
Reduction of Inflammation and Scar Tissue
After spinal or neural injury, inflammation and scar formation can severely hinder recovery. Stem cells modulate the immune response by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines and promoting anti-inflammatory pathways. They also help limit glial scar formation, which otherwise blocks nerve signal transmission. This creates a more favorable environment for nerve repair and functional recovery.
Secretion of Growth Factors and Cytokines
One of the key benefits of stem cell therapy is the secretion of bioactive molecules such as growth factors, cytokines, and neurotrophic agents. These substances aid in tissue repair, stimulate blood vessel formation (angiogenesis), and enhance the survival and function of neurons. This biochemical support helps regenerate motor pathways and improves locomotion outcomes.
Best Stem Cell Sources for Locomotor Recovery
Stem cell therapy for locomotor recovery relies heavily on the source and type of stem cells used. The most effective options include umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), bone marrow stem cells, and adipose tissue stem cells. Each offers unique regenerative potential, safety, and compatibility for restoring movement and mobility.
Umbilical Cord-Derived MSCs
Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) are widely recognized for their strong regenerative and anti-inflammatory properties. These young, immunoprivileged cells are non-invasive to harvest and have a higher proliferation rate than adult stem cells. UC-MSCs promote nerve regeneration, modulate immune responses, and secrete neurotrophic factors essential for restoring locomotor function. Clinical studies have shown promising results in improving mobility and reducing symptoms in patients with spinal cord injuries and other neurological conditions. Their low risk of rejection makes them a preferred choice in many stem cell therapies.
Bone Marrow Stem Cells
Bone marrow-derived stem cells (BM-MSCs) have been used extensively in regenerative therapies for decades. They are harvested from the patient’s own hip bone through a minimally invasive procedure. BM-MSCs possess strong capabilities for differentiation into nerve and support cells, making them useful in repairing damaged spinal tissues. Their ability to reduce inflammation and support axonal regrowth contributes significantly to locomotor recovery. Although their regenerative potential may slightly decline with age, BM-MSCs remain a reliable and personalized treatment option for improving movement and function after neurological damage.
Adipose Tissue Stem Cells
Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) are harvested from body fat through liposuction and offer an abundant, easily accessible source of mesenchymal stem cells. These cells exhibit powerful regenerative effects and have been studied for their role in promoting nerve repair and reducing inflammation. ADSCs are especially valued for their ability to secrete growth factors that enhance cellular healing in injured tissues. Their use in locomotion recovery is gaining popularity due to the minimally invasive extraction process and their robust healing properties. Many clinical applications now include ADSCs for musculoskeletal and neurological rehabilitation.
Treatment Procedure: What Patients Can Expect
Stem cell therapy for locomotion recovery is a multi-step process tailored to each patient’s condition and needs. From initial diagnosis to post-treatment rehabilitation, every phase is carefully monitored by medical professionals. Patients can expect a seamless experience, including evaluation, stem cell harvesting or sourcing, transplantation, and structured follow-up care for optimal outcomes.
Diagnosis and Eligibility for Stem Cell Therapy
Before beginning treatment, patients undergo a thorough evaluation that includes imaging tests like MRI or CT scans, neurological assessments, and medical history reviews. This helps determine the severity of locomotor impairment and whether the patient qualifies for stem cell therapy. Factors such as age, overall health, injury duration, and type of spinal damage are considered. Only those with realistic therapeutic potential are recommended for the procedure, ensuring the highest chances of a successful outcome.
Harvesting, Processing, and Delivery of Stem Cells
Stem cells are either harvested from the patient’s own body—typically bone marrow or adipose tissue—or obtained from donor sources such as umbilical cord tissue. After collection, the cells are purified and processed in a sterile lab to enhance their regenerative properties. The prepared cells are then delivered into the affected area via injection, often guided by imaging techniques like fluoroscopy or ultrasound to ensure precision and safety throughout the procedure.
Recovery Time and Post-Treatment Guidelines
Recovery varies by patient but is generally swift, especially since stem cell therapy is minimally invasive. Most patients can resume light activities within a few days, though physical therapy may be recommended to support rehabilitation. Follow-up visits are crucial to monitor progress and assess nerve response. Patients are advised to avoid heavy exertion, maintain hydration, and follow all post-procedure care instructions to maximize the regenerative benefits and support optimal healing.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy for Mobility Impairment
Stem cell therapy offers a groundbreaking approach to improving mobility in patients with spinal cord injuries and other neurological disorders. By targeting damaged nerve tissues and promoting natural healing, it can significantly enhance motor function, reduce pain, and improve daily mobility. The benefits often extend beyond physical improvements, supporting emotional and mental well-being too.
Improved Muscle Control and Coordination
One of the most promising benefits of stem cell therapy is enhanced muscle control and coordination. By regenerating damaged nerve pathways, stem cells help restore the communication between the brain and muscles. This restoration allows patients to regain voluntary movement, improve posture, and perform tasks with greater precision. With consistent therapy and physical rehabilitation, many patients show significant improvements in balance, gait, and coordination, especially those with incomplete spinal injuries. These changes can be life-changing, offering renewed hope for functional independence and social reintegration.
Reduced Spasticity and Chronic Pain
Spasticity and chronic pain are common complications after spinal cord injuries and neurological disorders. Stem cell therapy can help alleviate these symptoms by modulating the inflammatory response and repairing nerve tissue. Many patients report reduced muscle stiffness, decreased spasms, and less dependency on pain medication after treatment. This improvement occurs as stem cells regulate abnormal nerve firing and promote healthier muscle tone. By addressing the root cause of discomfort, stem cell therapy can greatly enhance physical comfort and allow for better participation in rehabilitation and daily activities.
Enhanced Quality of Life and Independence
Beyond physical improvements, stem cell therapy can dramatically enhance a patient’s overall quality of life. As mobility, coordination, and pain levels improve, individuals often regain a sense of freedom and confidence. This can lead to increased social interaction, emotional well-being, and reduced caregiver dependency. Simple activities like walking independently, dressing, or returning to work become achievable goals. For many, the therapy is not just a medical treatment—it’s a pathway to reclaiming autonomy, self-esteem, and hope for a more active and fulfilling future.
Who Can Benefit from Stem Cell Therapy for Locomotion?
Stem cell therapy is an emerging regenerative solution for individuals facing mobility challenges due to neurological damage or disease. It offers new hope by restoring function, reducing inflammation, and supporting nerve repair. Patients with spinal injuries, stroke aftermath, or degenerative disorders can see measurable improvements in locomotion, strength, and overall quality of life.
Patients with Spinal Cord Injury
Individuals suffering from spinal cord injuries often face partial or complete loss of motor function. Stem cell therapy can help by regenerating damaged nerve tissues and promoting communication between the brain and limbs. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), especially those derived from umbilical cords or bone marrow, have shown encouraging results in clinical trials by improving motor function, muscle tone, and reducing spasticity. These treatments aim to restore mobility and independence, particularly in patients with incomplete injuries who still retain some sensory or motor function.
Individuals with Stroke-Induced Motor Loss
Stroke survivors frequently experience weakness, paralysis, or coordination issues on one side of the body. Stem cell therapy holds promise by repairing brain tissue damaged during the stroke and reactivating dormant neural pathways. Studies show that neural stem cells and MSCs can aid in recovery by enhancing neuroplasticity and supporting the growth of new neural connections. When combined with physical therapy, patients may regain strength, improve coordination, and boost their functional independence—especially if treatment begins during the subacute or early chronic phase post-stroke.
People with Neurodegenerative or Autoimmune Motor Conditions
Patients with conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), or Parkinson’s disease may benefit from stem cell therapy as a way to slow progression and restore lost motor abilities. These therapies work by reducing inflammation, repairing neural damage, and modulating immune system activity. MSCs and neural precursor cells are often used to stabilize symptoms and promote mobility. While not a cure, stem cell therapy may improve walking ability, reduce fatigue, and enhance quality of life when conventional treatments have limited effectiveness.
Why Choose Viezec for Stem Cell Locomotion Treatment?
Viezec stands out as a trusted leader in stem cell-based locomotion recovery, offering cutting-edge therapies backed by years of experience and clinical excellence. Our focus on safety, innovation, and patient outcomes makes us the preferred destination for individuals seeking improved mobility through regenerative medicine.
Our Expertise in Regenerative Medicine
At Viezec, our team comprises leading experts in stem cell research and regenerative medicine with extensive experience in treating spinal cord injuries and movement disorders. We stay updated with the latest advancements to provide scientifically validated therapies. From diagnosis to recovery, our physicians, researchers, and care professionals collaborate to deliver effective, research-backed treatments that aim to restore motor function and enhance quality of life.
State-of-the-Art Facilities and Patient-Centered Care
Our advanced treatment centers are equipped with modern laboratories, sterile processing units, and image-guided injection systems to ensure precision and safety. We prioritize a patient-centered approach, providing a warm and supportive environment from consultation to follow-up. Each patient is treated with empathy, respect, and clear communication to ensure a smooth and comfortable healing experience.
Personalized Treatment Plans and Post-Care Support
Every patient at Viezec receives a tailored treatment strategy based on their condition, injury severity, and medical history. Our multidisciplinary team designs a comprehensive care plan that includes rehabilitation and long-term follow-up. Post-treatment, we offer continuous support, physical therapy guidance, and progress monitoring to maximize outcomes and promote sustained locomotor recovery.