Tinnitus is a complex auditory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is commonly described as a persistent ringing, buzzing, hissing, or whistling sound in the ears, even when no external sound source is present. For some individuals, tinnitus is a mild inconvenience. For others, it becomes a chronic condition that interferes with concentration, sleep, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life.
Despite advances in audiology and neurology, tinnitus remains one of the most challenging conditions to treat. Conventional therapies often focus on symptom management rather than addressing the underlying biological damage. This limitation has driven growing interest in regenerative medicine, particularly the potential of stem cell therapy in tinnitus management.
Stem cell research has opened new possibilities for repairing damaged auditory structures, restoring neural function, and targeting the root causes of tinnitus rather than masking symptoms. While still an evolving field, early findings suggest that stem cell therapy could reshape how tinnitus is treated in the future.
This article explores the science, mechanisms, current research, benefits, limitations, and future outlook of stem cell therapy for tinnitus, with a clear, patient-focused approach.
Understanding Tinnitus: Why It Is So Difficult to Treat
Tinnitus is not a disease itself. It is a symptom of an underlying issue within the auditory system or the brain. This is one of the primary reasons it is so difficult to manage with a single treatment approach.
Common Causes of Tinnitus
Tinnitus can develop due to several factors, including:
-
Damage to cochlear hair cells
-
Sensorineural hearing loss
-
Noise-induced acoustic trauma
-
Age-related degeneration of auditory pathways
-
Inflammation or oxidative stress in the inner ear
-
Auditory nerve damage
-
Changes in brain signal processing
In many cases, tinnitus persists even after the initial trigger has resolved. This suggests that structural or neurological damage remains unaddressed.
Limitations of Conventional Tinnitus Treatments
Standard tinnitus management options include:
-
Sound therapy
-
Hearing aids
-
Cognitive behavioral therapy
-
Tinnitus retraining therapy
-
Medications for associated anxiety or sleep disturbances
While these approaches can reduce distress, they do not repair damaged inner ear cells or regenerate auditory nerve tissue. As a result, patients often continue to experience symptoms long term.
This gap in treatment effectiveness has led researchers to explore regenerative therapies, including stem cell-based approaches.
What Is Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cell therapy is a form of regenerative medicine that uses the body’s own repair mechanisms to restore damaged tissues. Stem cells have the unique ability to self-renew and differentiate into specialized cell types.
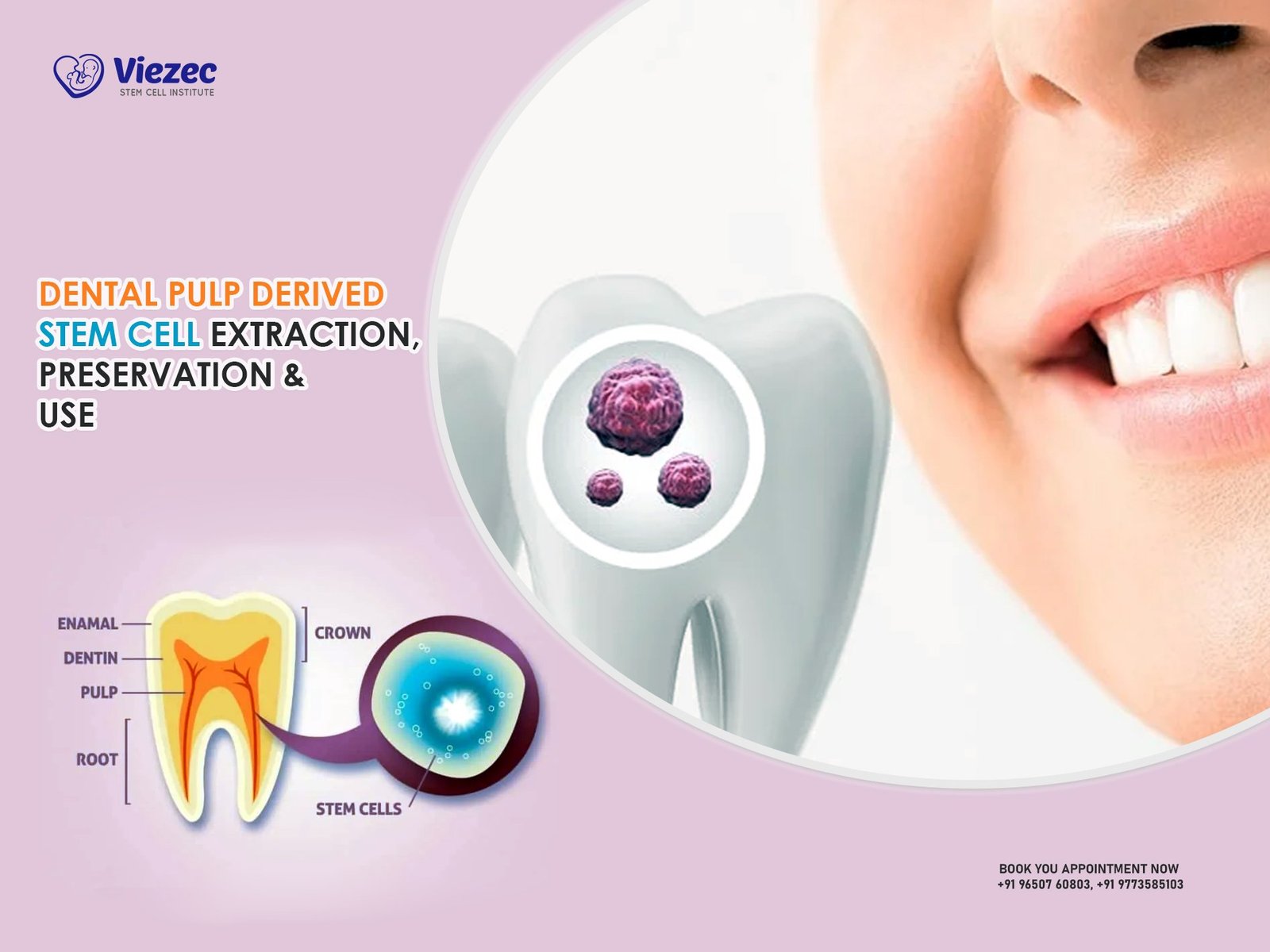
Types of Stem Cells Relevant to Hearing Disorders
Several types of stem cells are being studied for tinnitus and hearing loss:
Among these, mesenchymal stem cells are most commonly explored due to their regenerative, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties.
Discover if Stem Cell Therapy Can Help You!
Book a Free Consultation with Our Experts at Viezec !
Why Stem Cells Matter in Tinnitus Management
Tinnitus often arises from irreversible damage to cochlear hair cells or auditory nerve pathways. Unlike other tissues, these structures have very limited natural regenerative capacity.
Stem cell therapy offers a potential method to:
-
Promote regeneration of damaged inner ear cells
-
Support auditory nerve repair
-
Reduce inflammation contributing to tinnitus
-
Improve neural signaling in the auditory pathway
Rather than suppressing symptoms, stem cell therapy aims to address biological dysfunction.
How Stem Cell Therapy May Work for Tinnitus
Stem cell therapy for tinnitus is based on several key biological mechanisms. While research is ongoing, scientists have identified multiple pathways through which stem cells may contribute to tinnitus management.
Regeneration of Cochlear Hair Cells
Cochlear hair cells play a critical role in converting sound vibrations into electrical signals. Damage to these cells is one of the most common causes of tinnitus.
Stem cells may support hair cell regeneration by:
-
Differentiating into hair-cell-like structures
-
Releasing growth factors that stimulate repair
-
Enhancing survival of remaining healthy cells
This approach targets the structural origin of tinnitus in many patients.
Auditory Nerve Repair
Damage to the auditory nerve disrupts communication between the ear and the brain, leading to abnormal neural activity perceived as tinnitus.
Stem cell therapy may help by:
-
Supporting neural regeneration
-
Improving nerve signal conduction
-
Reducing nerve inflammation
This mechanism is particularly relevant for tinnitus associated with sensorineural hearing loss.
Modulation of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress in the inner ear can worsen tinnitus symptoms.
Mesenchymal stem cells are known to:
-
Reduce inflammatory cytokines
-
Promote tissue healing
-
Improve cellular environment
This anti-inflammatory effect may contribute to symptom reduction even when structural regeneration is limited.
Neuroplasticity and Brain Signal Regulation
Tinnitus is not only an ear condition. It also involves changes in how the brain processes sound.
Stem cells may influence neuroplasticity by:
-
Supporting healthy neural connections
-
Reducing abnormal auditory cortex activity
-
Encouraging balanced signal processing
This central nervous system impact is an important area of ongoing research.
Current Research on Stem Cell Therapy for Tinnitus
Stem cell therapy for tinnitus is still considered an emerging and investigational approach. Most evidence comes from preclinical studies, early-stage clinical trials, and research on hearing loss rather than tinnitus alone.
Preclinical Studies
Animal studies have demonstrated:
-
Partial regeneration of cochlear hair cells
-
Improved auditory nerve function
-
Reduction in tinnitus-like behaviors
These findings provide a scientific foundation for human research.
Early Clinical Investigations
Human studies remain limited but promising. Some early trials and observational studies have reported:
-
Improvement in tinnitus severity scores
-
Better hearing thresholds in select patients
-
Reduction in associated symptoms such as ear fullness
However, results vary depending on the cause of tinnitus, treatment protocol, and patient health.
Ongoing Clinical Trials
Research continues worldwide to evaluate:
-
Optimal stem cell type
-
Best delivery methods
-
Safety and long-term outcomes
-
Patient selection criteria
As evidence grows, clearer clinical guidelines are expected to emerge.
Start Your Regenerative Journey Today!
Contact Viezec for Personalized Stem Cell Therapy Plan
Who May Benefit from Stem Cell Therapy for Tinnitus
Stem cell therapy is not suitable for all tinnitus patients. Outcomes depend heavily on the underlying cause and disease stage.
Potential Candidates
Patients who may benefit include those with:
-
Noise-induced tinnitus
-
Sensorineural hearing loss-related tinnitus
-
Chronic tinnitus linked to inner ear damage
-
Tinnitus associated with inflammation or nerve injury
Patients with Limited Benefit
Stem cell therapy may be less effective for:
-
Tinnitus caused by temporary ear infections
-
Tinnitus linked to jaw disorders or vascular issues
-
Psychogenic tinnitus without structural damage
A thorough medical evaluation is essential before considering regenerative treatment.
Safety Considerations and Ethical Aspects
Safety is a critical concern in any regenerative therapy.
Safety Profile of Stem Cell Therapy
When performed using established protocols, stem cell therapy is generally well tolerated. Potential risks include:
-
Mild injection-site discomfort
-
Temporary inflammation
-
Variable treatment response
Serious adverse events are rare when therapy is administered under proper medical supervision.
Importance of Medical Oversight
Patients should seek care from reputable regenerative medicine providers that follow ethical guidelines, informed consent processes, and evidence-based protocols.
Viezec, based in India, emphasize patient education, transparent consultation, and responsible application of regenerative therapies.
Stem Cell Therapy vs Conventional Tinnitus Management
Understanding how stem cell therapy differs from traditional treatments helps patients make informed decisions.
Conventional Approaches
-
Focus on coping strategies
-
Manage symptoms rather than causes
-
Require long-term use
-
Limited biological repair
Stem Cell-Based Approach
-
Targets underlying tissue damage
-
Aims for regeneration and healing
-
Potential for long-term improvement
-
Still evolving and not a guaranteed cure
In many cases, regenerative therapy may complement rather than replace conventional management.
The Role of Regenerative Medicine Clinics in India
India has become an important hub for regenerative medicine research and clinical application. Advances in stem cell science, combined with growing clinical expertise, have expanded treatment possibilities for complex conditions like tinnitus.
Centers such as Viezec focus on integrating scientific evidence, patient-specific assessment, and ethical regenerative practices. While tinnitus treatment using stem cells remains investigational, structured clinical frameworks help ensure safety and transparency.
Patients considering such therapies should engage in detailed consultations to understand realistic outcomes and limitations.
Is Your Condition Eligible for Stem Cell Therapy?
Speak directly with our specialist.
Challenges and Limitations of Stem Cell Therapy for Tinnitus
Despite its promise, stem cell therapy is not without challenges.
Scientific Limitations
-
Incomplete understanding of tinnitus mechanisms
-
Variability in patient response
-
Limited large-scale clinical trials
Practical Considerations
-
Treatment availability varies by region
-
Cost may be higher than conventional therapy
-
Results may take time to become noticeable
These factors highlight the need for continued research and patient education.
Making an Informed Decision as a Patient
Patients exploring stem cell therapy for tinnitus should approach the process thoughtfully.
Key Questions to Consider
-
What is the underlying cause of my tinnitus?
-
Is there evidence supporting regenerative therapy for my condition?
-
What are the realistic outcomes?
-
What risks and limitations exist?
Reputable providers, including Viezec, prioritize detailed assessments and patient education before recommending regenerative options.
Frequently Asked Questions
Stem cell therapy is not currently considered a permanent cure for tinnitus. Research suggests it may help reduce symptoms by supporting inner ear repair, auditory nerve regeneration, and inflammation control. Results vary depending on the cause of tinnitus and individual patient factors.
Stem cell therapy works by targeting damaged cochlear hair cells, auditory nerves, and inflammatory processes linked to tinnitus. Stem cells release growth factors that support tissue repair and improve neural signaling within the auditory system.
When performed under proper medical supervision using established protocols, stem cell therapy is generally considered safe. Most reported side effects are mild and temporary. Long-term safety continues to be evaluated through ongoing clinical research.
Patients with tinnitus related to sensorineural hearing loss, noise exposure, or inner ear damage may be better candidates. A detailed medical evaluation is essential to determine whether stem cell therapy is appropriate for an individual case.
Some patients may notice gradual changes within a few weeks to months after treatment. Improvements often depend on the severity of tinnitus, underlying cause, and the body’s regenerative response. Immediate results should not be expected.
Conclusion
Tinnitus remains a complex and often frustrating condition with limited conventional treatment success. Stem cell therapy represents a promising frontier in tinnitus management by addressing biological damage within the auditory system rather than merely masking symptoms.
While research is still evolving, early findings suggest potential benefits in cochlear hair cell regeneration, auditory nerve repair, inflammation reduction, and neural signal modulation. Stem cell therapy is not a guaranteed cure, and it is not suitable for every patient. However, it offers hope for individuals with tinnitus linked to structural or neurological damage.
As regenerative medicine continues to advance, stem cell-based approaches may become an important component of comprehensive tinnitus care. Patients should seek evidence-based guidance, realistic expectations, and medically supervised treatment pathways when considering this emerging option.
List of References
Stem Cell Therapy for Inner Ear & Hearing Disorders (animal success data: hair cell & neuron differentiation) – shows high success rates in animal studies (up to ~82% hair cell differentiation, 100% auditory neuron differentiation). PubMed: Stem‑cell therapy for hearing loss review (differentiation success)
Current Status of Stem Cell Therapeutics for Hearing Loss (preclinical & early clinical) – stem cell therapies for hearing loss are under research; no FDA-approved stem cell treatments yet, indicating early stage.
Harvard Health: current clinical trial status stem cells for hearing
Regenerative Cell Therapy First-In-Human Trial (Rincell-1) – first human clinical trial of regenerative cell therapy targeting auditory neurons has been approved, showing current translational progress.
University of Sheffield: first‑in‑human regenerative cell therapy trial for hearing loss
Stem Cell Therapy for Inner Ear: Progress & Challenges (review) – discusses the ongoing research challenges and long-term hurdles in making stem cell therapy a reality (context for tinnitus/hearing regeneration).
PMC review: inner ear stem cell therapy advances & barriers
Systematic Hearing Regeneration Review (cochlear hair cell, nerve restoration) – broader look at stem cells for congenital hearing loss with notes on moderate improvements in early human contexts and ongoing needs for large trials.
Stem Cell Therapy: systematic review for cochlear regeneration