Intracerebral hemorrhage is one of the most severe forms of stroke, often leading to long-term disability or life-threatening complications. It occurs when a blood vessel ruptures inside the brain, causing bleeding within brain tissue and disrupting vital neurological functions. Despite advances in emergency care and neurosurgery, conventional treatment options for intracerebral hemorrhage mainly focus on stabilizing the patient rather than repairing the damaged brain tissue.
In recent years, stem cell treatment for intracerebral hemorrhage patients has emerged as a promising regenerative approach. This advanced therapy aims to support brain repair, reduce inflammation, and enhance neurological recovery beyond what traditional methods can offer. As research continues to evolve, patients and families are increasingly exploring stem cell therapy as a potential option for post-hemorrhagic recovery.
This page provides a detailed, evidence-based overview of intracerebral hemorrhage, current treatment limitations, how stem cell therapy works, potential benefits, safety considerations, and what patients should realistically expect.
Understanding Intracerebral Hemorrhage
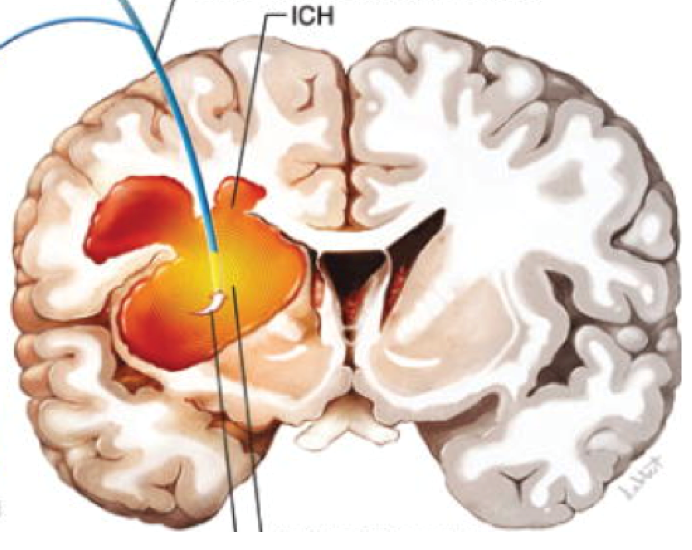
Intracerebral hemorrhage, often abbreviated as ICH, is a type of hemorrhagic stroke caused by bleeding directly into the brain parenchyma. The accumulation of blood increases intracranial pressure, damages surrounding neurons, and interrupts blood supply to critical brain regions.
Common Causes of Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Several underlying conditions can increase the risk of ICH, including:
-
Chronic high blood pressure
-
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy
-
Head trauma
-
Blood clotting disorders
-
Overuse of anticoagulant or antiplatelet medications
-
Brain tumors or vascular malformations
The severity of intracerebral hemorrhage varies depending on the size and location of the bleed, as well as the patient’s age and overall health.
Symptoms and Long-Term Impact
Symptoms of intracerebral hemorrhage often develop suddenly and may worsen rapidly. These can include:
-
Severe headache
-
Sudden weakness or paralysis on one side of the body
-
Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
-
Loss of balance or coordination
-
Altered consciousness or coma
Even after survival, many patients experience long-term neurological deficits such as impaired mobility, cognitive decline, speech difficulties, and emotional changes. Recovery is often slow and incomplete, highlighting the need for advanced therapeutic approaches.
Limitations of Conventional Treatment
Standard treatment for intracerebral hemorrhage focuses on acute management and preventing further damage. This may involve:
-
Blood pressure control
-
Surgical evacuation of the hematoma in selected cases
-
Medications to reduce brain swelling
-
Intensive rehabilitation therapies
While these interventions are critical for survival, they do not regenerate damaged brain tissue. Neurons lost due to hemorrhage are not naturally replaced, which limits functional recovery for many patients.
This gap in treatment outcomes has driven interest in regenerative medicine, particularly stem cell therapy.
What Is Stem Cell Therapy?
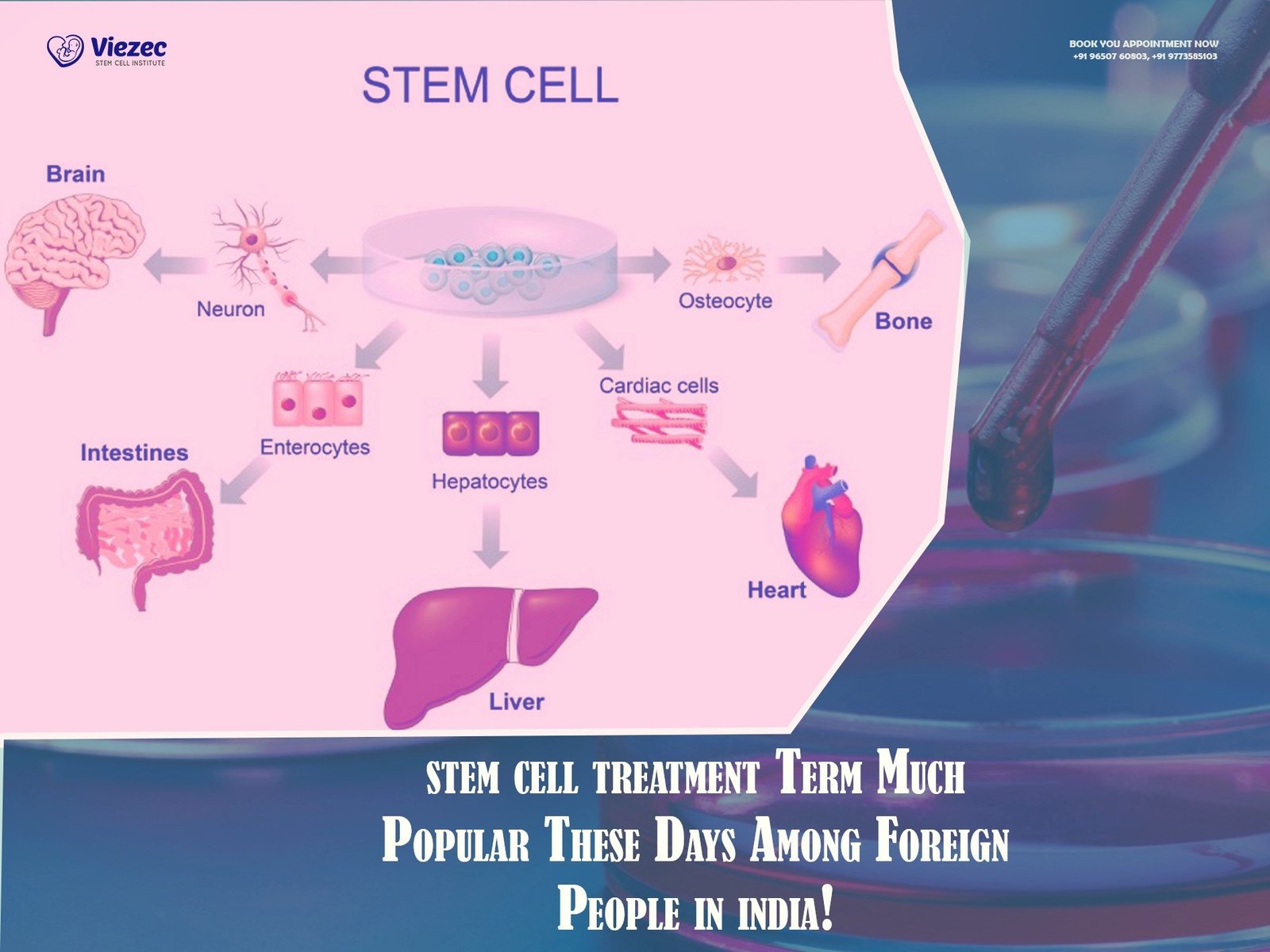
Stem cell therapy is a regenerative medical approach that uses specialized cells capable of self-renewal and differentiation into various cell types. In neurological conditions, stem cells are studied for their ability to support repair processes within the central nervous system.
Rather than acting as a direct cure, stem cell treatment works by creating a supportive environment for healing. It influences inflammation, cell survival, and neural signaling, which are critical factors in recovery after brain injury.
Discover if Stem Cell Therapy Can Help You!
Book a Free Consultation with Our Experts at Viezec !
How Stem Cell Treatment Works for Intracerebral Hemorrhage
In the context of intracerebral hemorrhage, stem cell therapy is believed to work through multiple mechanisms:
Neuroprotection
Stem cells release bioactive molecules that help protect surviving neurons from secondary injury caused by inflammation and oxidative stress.
Reduction of Inflammation
Post-hemorrhagic inflammation plays a major role in worsening brain damage. Stem cells modulate the immune response, helping to limit harmful inflammation.
Promotion of Angiogenesis
Stem cells can stimulate the formation of new blood vessels, improving oxygen and nutrient delivery to damaged brain regions.
Support for Neural Repair
Although full neuronal replacement remains a challenge, stem cells support synaptic remodeling and neural network reorganization, which are essential for functional recovery.
Types of Stem Cells Used in Therapy
Several types of stem cells are being studied and used in clinical applications for intracerebral hemorrhage:
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
MSCs are the most commonly used cells due to their safety profile and immunomodulatory properties. They are typically derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, or umbilical cord tissue.
Neural Stem Cells
These cells have the potential to differentiate into neurons and glial cells. Their use is mainly limited to research and controlled clinical settings.
Autologous vs Allogeneic Cells
Autologous stem cells are derived from the patient’s own body, reducing the risk of immune rejection. Allogeneic cells come from screened donors and are processed under strict quality standards.
The choice of stem cell type depends on patient condition, clinical protocols, and regulatory considerations.
Potential Benefits of Stem Cell Treatment for ICH Patients
Stem cell therapy does not promise instant recovery, but it offers several potential benefits when integrated with rehabilitation:
-
Improvement in motor function and coordination
-
Enhanced speech and cognitive abilities
-
Reduction in muscle spasticity
-
Better quality of life and independence
-
Slower progression of secondary brain damage
Clinical observations suggest that patients who receive stem cell therapy during the recovery phase may experience more meaningful functional gains compared to rehabilitation alone.
Timing of Stem Cell Therapy
The timing of treatment plays a crucial role in outcomes. Stem cell therapy is typically considered during the subacute or chronic phase of intracerebral hemorrhage, once the patient is medically stable.
Early intervention may help limit secondary injury, while later treatment can still support neuroplasticity and functional recovery. Each case requires individualized assessment.
Start Your Regenerative Journey Today!
Contact Viezec for Personalized Stem Cell Therapy Plan
Safety and Ethical Considerations
Safety is a primary concern in any advanced therapy. Stem cell treatment for intracerebral hemorrhage is generally considered safe when performed under proper medical supervision and ethical standards.
Key safety measures include:
-
Use of clinically tested stem cell sources
-
Strict screening and processing protocols
-
Careful patient selection
-
Continuous monitoring during and after treatment
Serious adverse events are rare when therapy is conducted responsibly. Patients should avoid unverified clinics making exaggerated claims.
Scientific Evidence and Ongoing Research
Preclinical studies and early-phase clinical trials have shown encouraging results in improving neurological outcomes after intracerebral hemorrhage. Research indicates improvements in motor recovery, reduced brain edema, and enhanced neural repair mechanisms.
However, large-scale randomized trials are still ongoing. Stem cell therapy should be viewed as an evolving treatment option supported by growing scientific evidence rather than a guaranteed cure.
Role of Rehabilitation Alongside Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell treatment is most effective when combined with structured rehabilitation programs. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and cognitive training help translate biological improvements into functional gains.
The regenerative effects of stem cells may enhance the brain’s responsiveness to rehabilitation, leading to better long-term outcomes.
Patient Eligibility and Evaluation
Not every intracerebral hemorrhage patient is an ideal candidate for stem cell therapy. Eligibility depends on factors such as:
-
Age and overall health
-
Severity and location of the hemorrhage
-
Time since stroke
-
Presence of other medical conditions
A comprehensive medical evaluation is essential to determine suitability and expected benefits.
Is Your Condition Eligible for Stem Cell Therapy?
Speak directly with our specialist.
Stem Cell Treatment in India
India has emerged as a key destination for advanced regenerative therapies due to experienced clinicians, established research infrastructure, and cost-effective treatment options. Indian centers follow defined clinical protocols and ethical guidelines for stem cell applications.
Viezec, based in India, plays a supportive role in connecting patients with reliable information and structured treatment pathways related to regenerative medicine. By focusing on patient education and transparency, Viezec helps individuals make informed decisions about stem cell therapy options.
What Patients Should Expect
Stem cell treatment is a process rather than a single event. Patients should have realistic expectations:
-
Gradual improvement over months
-
Results vary from person to person
-
Therapy complements but does not replace rehabilitation
-
Continuous follow-up is essential
Clear communication between patients, caregivers, and medical teams is vital for successful outcomes.
Cost Considerations
The cost of stem cell treatment for intracerebral hemorrhage varies based on factors such as stem cell type, treatment protocol, hospitalization needs, and rehabilitation support. While costs may appear significant, many patients consider the potential for improved independence and quality of life when evaluating long-term value.
Choosing the Right Guidance
Due to the complexity of stem cell therapy, patients should seek guidance from credible, experience-driven platforms. Viezec assists patients by providing medically reviewed information and helping them navigate treatment options within India’s evolving regenerative medicine landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
Stem cell treatment has shown promising results in supporting neurological recovery after intracerebral hemorrhage. It works by reducing inflammation, protecting surviving brain cells, and promoting repair mechanisms. While it is not a cure, many patients experience improvements in motor function, cognition, and overall quality of life when therapy is combined with rehabilitation.
Stem cell therapy is usually considered after the patient becomes medically stable. This may be during the subacute or chronic recovery phase. Early evaluation is important because timing, severity of the hemorrhage, and overall health influence potential outcomes.
When performed under proper medical protocols, stem cell therapy is generally considered safe. Most patients experience minimal side effects such as mild fever or temporary discomfort. Serious complications are rare when cells are sourced, processed, and administered responsibly.
Stem cell therapy does not replace emergency treatment, surgery, or rehabilitation. It is used as a supportive regenerative approach. The best outcomes are seen when stem cell treatment is combined with physical therapy, speech therapy, and neurological rehabilitation.
Patients in India should seek information from credible, medically guided platforms and avoid clinics making unrealistic claims. Viezec help patients understand evidence-based stem cell therapy options and guide them toward informed, ethical treatment decisions.
Final Thoughts
Intracerebral hemorrhage remains a devastating neurological condition with limited regenerative treatment options. Stem cell therapy represents a significant step forward by addressing the underlying damage rather than only managing symptoms.
While it is not a miracle cure, stem cell treatment for intracerebral hemorrhage patients offers hope for improved recovery, better functional outcomes, and enhanced quality of life when delivered responsibly and combined with rehabilitation.
Patients considering this therapy should rely on evidence-based information, realistic expectations, and guidance from trusted platforms like Viezec to make informed decisions about their recovery journey.
List of References
Current Status and Progress in Stem Cell Therapy for ICH – review summarizing developmental history, transplantation strategies, enhancement methods, and barriers to clinical translation.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38001353/
Stem Cell Therapy: A Promising Method for ICH – review of therapeutic mechanisms (neurogenesis, anti-inflammation) and the need for more clinical evidence.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29871521/
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy Clinical Trial (Mayo Clinic) – current interventional Phase 1 study investigating safety/feasibility of MSC therapy in recent spontaneous ICH.
https://www.mayo.edu/research/clinical-trials/cls-20379665
Preclinical Meta-Analysis of Stem Cell Transplantation in ICH – shows behavioral and structural improvements, highlights administration routes and timing effects, cautioning study quality.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26409481/
Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Improve Neurological Outcomes in ICH Model – rodent evidence that intravenous stem cell delivery can ameliorate cognitive and motor deficits (preclinical success).
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006899318306681