Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) pose a significant challenge in clinical management due to their chronic and debilitating nature. They are a common complication of diabetes mellitus and often result from peripheral neuropathy, peripheral arterial disease, and impaired wound healing. Traditional treatment modalities such as debridement, offloading, and wound dressings are important, but they may not always suffice, particularly in cases of non-healing ulcers. Stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising approach for managing DFUs by harnessing the regenerative potential of various stem cell types. This article explores different stem cell varieties utilized in diabetic foot ulcer management and their effectiveness in promoting wound healing.
Understanding Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetic foot ulcers are open sores or wounds that commonly occur on the feet of individuals with diabetes. They typically develop as a result of a combination of factors including neuropathy, peripheral vascular disease, foot deformities, and trauma. Neuropathy, in particular, leads to diminished sensation, making patients unaware of minor injuries or pressure points that can eventually progress into ulcers. Moreover, peripheral arterial disease compromises blood flow to the extremities, impairing the body’s ability to deliver nutrients and oxygen to the affected tissue, further complicating the healing process. These ulcers often become chronic and can lead to severe complications such as infection, gangrene, and even amputation if left untreated.
Role of Stem Cells in Wound Healing
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells with the ability to self-renew and differentiate into various cell types. They play a crucial role in tissue regeneration and repair processes. When deployed to the site of injury, stem cells exert their therapeutic effects through several mechanisms, including:
- Differentiation: Stem cells can differentiate into specialized cell types such as keratinocytes, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells, which are essential for skin regeneration and angiogenesis.
- Paracrine Signaling: Stem cells secrete various growth factors, cytokines, and chemokines that modulate inflammation, promote angiogenesis, and stimulate local cell proliferation and migration.
- Immunomodulation: Stem cells regulate the immune response at the wound site, suppressing excessive inflammation and promoting a more conducive environment for healing.
- Extracellular Matrix Remodeling: Stem cells contribute to the remodeling of the extracellular matrix, facilitating tissue repair and regeneration.
Harnessing these mechanisms, stem cell therapy offers a promising approach for enhancing wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers.
Plan Your Stem Cell Therapy Procedure in India
Types of Stem Cells Used in Diabetic Foot Ulcer Management
Several types of stem cells have been investigated for their efficacy in treating diabetic foot ulcers. Each type possesses unique characteristics and potential advantages for wound healing. The following are some of the commonly studied stem cell varieties:
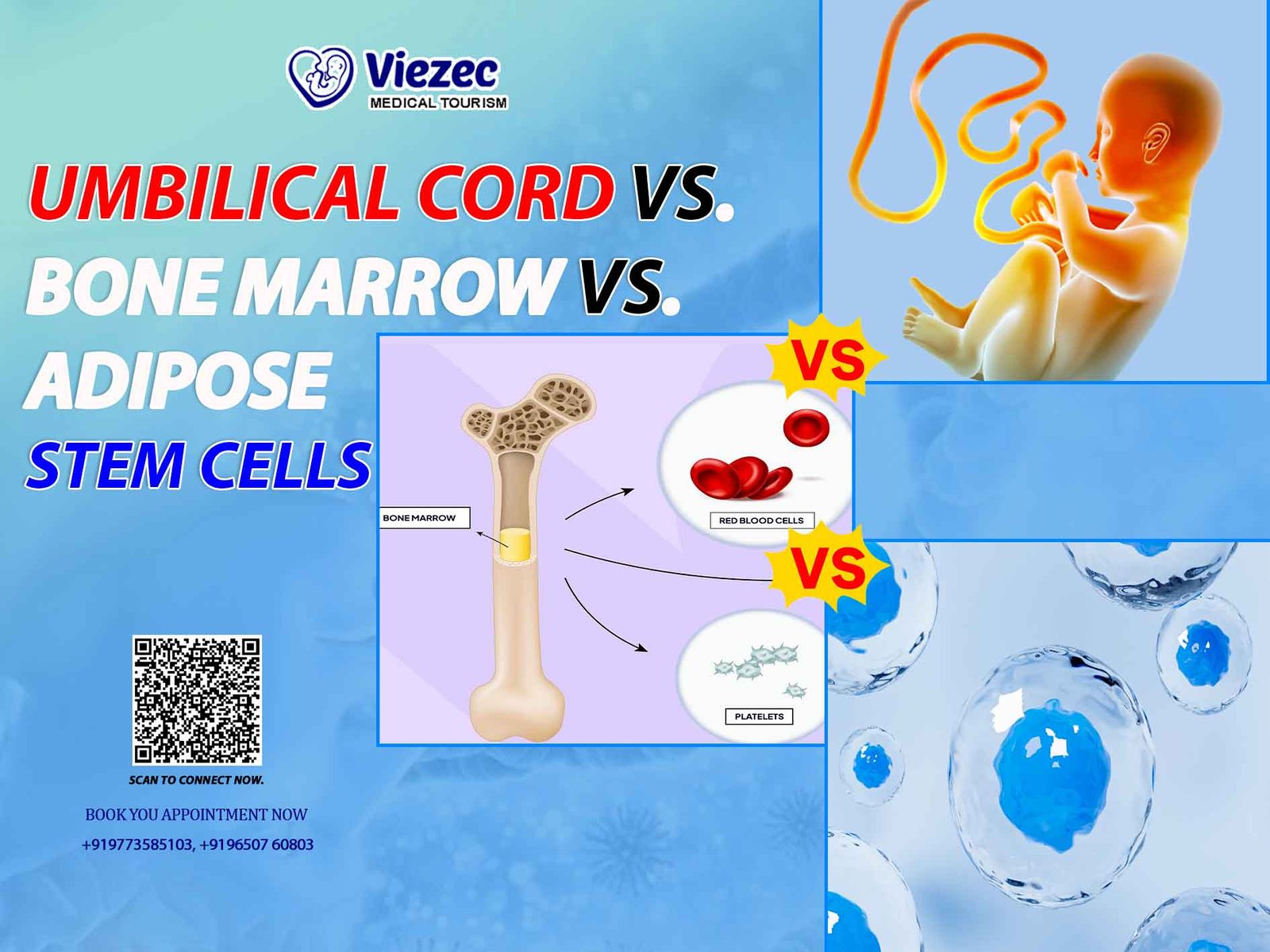
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
MSCs are multipotent stromal cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types, including osteoblasts, adipocytes, and chondrocytes. They are commonly isolated from bone marrow, adipose tissue, umbilical cord blood, and other sources. MSCs have gained significant attention in diabetic foot ulcer management due to their immunomodulatory properties and ability to promote tissue repair.
Advantages of MSCs:
- Immunomodulation: MSCs suppress inflammation and modulate immune responses, creating a conducive environment for wound healing.
- Angiogenic Potential: MSCs secrete pro-angiogenic factors, promoting the formation of new blood vessels and improving tissue perfusion.
- Paracrine Effects: MSCs secrete a wide range of growth factors and cytokines that facilitate wound healing processes.
Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs)
ADSCs are a type of MSCs isolated from adipose tissue. They are abundant and easily accessible, making them an attractive option for regenerative therapies. ADSCs have demonstrated promising results in promoting wound healing and tissue regeneration in diabetic foot ulcers.
Advantages of ADSCs:
- Abundant Source: Adipose tissue is readily available and can yield large quantities of ADSCs with minimal donor site morbidity.
- Angiogenic Properties: ADSCs secrete pro-angiogenic factors that stimulate neovascularization, enhancing blood flow to the wound site.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: ADSCs modulate the inflammatory response, reducing tissue damage and promoting a healing environment.
Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells (BMSCs)
BMSCs are multipotent stem cells found in the bone marrow. They have the capacity to differentiate into various cell lineages, including osteoblasts, chondrocytes, and adipocytes. BMSCs have been investigated for their therapeutic potential in diabetic foot ulcer management.
Advantages of BMSCs:
- Osteogenic Potential: BMSCs can differentiate into osteoblasts, contributing to bone regeneration and repair in cases of osteomyelitis associated with diabetic foot ulcers.
- Immunomodulation: Similar to other MSCs, BMSCs exert immunomodulatory effects, dampening inflammation and promoting tissue healing.
- Paracrine Signaling: BMSCs secrete trophic factors that support tissue regeneration and angiogenesis.
Umbilical Cord-Derived Stem Cells
Umbilical cord-derived stem cells, including mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) and endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs), are obtained from the umbilical cord tissue and blood, respectively. These stem cells possess unique properties that make them attractive candidates for diabetic foot ulcer therapy.
Advantages of Umbilical Cord-Derived Stem Cells:
- Immunomodulatory Effects: UC-MSCs exhibit potent immunomodulatory properties, suppressing inflammatory responses and promoting tissue repair.
- Angiogenic Potential: EPCs have angiogenic properties, enhancing blood vessel formation and improving tissue perfusion in ischemic wounds.
- Younger Donor Age: Umbilical cord-derived stem cells are obtained from neonatal tissues, which may confer advantages in terms of potency and proliferative capacity compared to adult-derived stem cells.
Clinical Efficacy of Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Numerous clinical studies have evaluated the efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy in the management of diabetic foot ulcers. While results vary across studies, there is growing evidence supporting the beneficial effects of stem cell-based interventions in promoting wound healing and reducing ulcer-related complications.
Clinical Trials Using Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
Several clinical trials have investigated the use of MSCs, including ADSCs and BMSCs, for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. These trials have reported improvements in wound healing rates, reduction in ulcer size, and enhanced tissue regeneration following MSC therapy. For example, a randomized controlled trial by Wu et al. demonstrated that treatment with autologous ADSCs significantly accelerated wound closure and improved vascularization in patients with diabetic foot ulcers compared to conventional therapy alone.
Clinical Trials Using Umbilical Cord-Derived Stem Cells
Clinical studies employing umbilical cord-derived stem cells, particularly UC-MSCs and EPCs, have also shown promising results in diabetic foot ulcer management. In a prospective study by Li et al., intramuscular injection of allogeneic UC-MSCs led to substantial improvements in wound healing and limb salvage rates in patients with critical limb ischemia and diabetic foot ulcers. Similarly, a phase I/II clinical trial by Lu et al. demonstrated the safety and efficacy of intramuscular injection of allogeneic UC-MSCs in promoting wound healing and improving tissue perfusion in patients with diabetic foot ulcers.
Challenges and Future Directions
While stem cell therapy holds immense promise for the management of diabetic foot ulcers, several challenges and considerations need to be addressed to optimize its clinical translation and efficacy.
Regulatory Considerations
Regulatory frameworks governing the use of stem cell-based therapies vary across jurisdictions and may pose challenges in terms of standardization, quality control, and approval processes.
Optimization of Delivery Methods
Optimal delivery methods for stem cell transplantation, including route of administration, cell dosage, and timing, need to be further optimized to maximize therapeutic outcomes and ensure long-term safety.
Patient Heterogeneity
The heterogeneity of diabetic foot ulcers and patient populations underscores the need for personalized treatment approaches tailored to individual patient characteristics and wound profiles.
Long-Term Safety and Efficacy
Long-term safety and efficacy data are crucial for establishing the sustained therapeutic benefits of stem cell therapy and assessing potential risks such as tumorigenesis and immunogenicity.
Cost-Effectiveness
The cost-effectiveness of stem cell-based interventions relative to conventional treatments warrants careful evaluation to ensure accessibility and affordability for patients and healthcare systems.
Contact us for free online appointment
Make an informed Decision
Stem cell therapy represents a promising paradigm in diabetic foot ulcer management, offering potential advantages in promoting wound healing, tissue regeneration, and limb salvage. Various stem cell varieties, including MSCs, ADSCs, BMSCs, and umbilical cord-derived stem cells, have demonstrated efficacy in preclinical and clinical studies. While challenges remain in terms of regulatory, logistical, and safety considerations, ongoing research efforts hold the promise of advancing stem cell-based therapies towards routine clinical practice, thereby improving outcomes for patients with diabetic foot ulcers.
Through harnessing the regenerative potential of stem cells, clinicians may usher in a new era of personalized and effective treatments for this debilitating complication of diabetes mellitus.
Related post:-
Exploring Stem Cell Treatments for Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Promise of Stem Cell Therapies in Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment