Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is a complex neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the brain, leading to motor and non-motor symptoms. While conventional therapies provide symptomatic relief, they often fail to address the underlying pathology. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in exploring innovative treatments that target disease-modifying mechanisms, neuroprotection, and personalized approaches. This article delves into the latest advancements in PD research and the potential of emerging therapies to revolutionize patient care.
Understanding Parkinson’s Disease
Definition and Symptoms
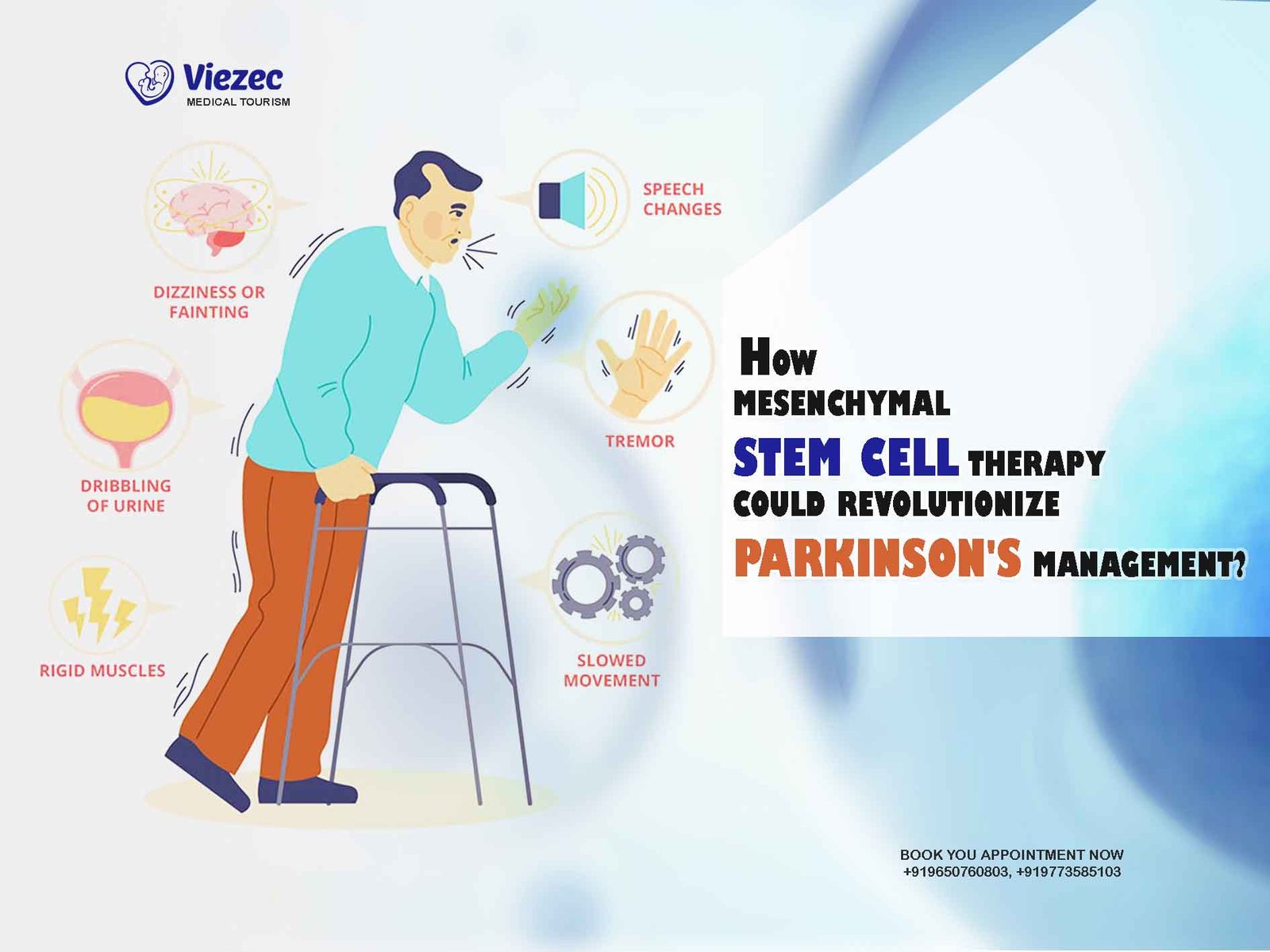
Parkinson’s Disease is a chronic and progressive movement disorder that affects millions worldwide. Its hallmark motor symptoms include tremors, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability. Non-motor symptoms such as cognitive impairment, mood disturbances, and autonomic dysfunction significantly impact patients’ quality of life.
Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disease
The pathophysiology of PD involves the accumulation of misfolded alpha-synuclein protein aggregates, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction. These factors contribute to neuronal degeneration in the substantia nigra region of the brain, leading to dopamine depletion and subsequent motor impairment.
Current Treatment Challenges
Despite significant advancements, current PD treatments primarily focus on symptom management and fail to halt disease progression. Moreover, long-term use of dopaminergic medications often results in motor complications such as dyskinesias and motor fluctuations, posing treatment challenges for clinicians.
Conventional Therapies for Parkinson’s
Dopamine Replacement Therapy
The cornerstone of PD management involves dopamine replacement therapy, primarily through the administration of levodopa, a precursor to dopamine. While effective in alleviating motor symptoms, prolonged use is associated with diminished efficacy and the development of motor fluctuations.
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
Deep Brain Stimulation involves the surgical implantation of electrodes into specific brain regions, such as the subthalamic nucleus or globus pallidus, to modulate abnormal neural activity. DBS offers significant symptom relief for patients with advanced PD, particularly those experiencing medication-refractory motor fluctuations.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in improving mobility, balance, and motor function in individuals with PD. Rehabilitation interventions, including exercise programs, gait training, and occupational therapy, help optimize functional independence and enhance overall well-being.
Emerging Role of Stem Cell Therapy
Introduction to Stem Cells
Stem cells possess the unique ability to self-renew and differentiate into various cell types, making them promising candidates for regenerative medicine. In the context of PD, stem cell therapy aims to replace lost dopaminergic neurons, restore neuronal circuitry, and promote neuroregeneration.
Potential of Stem Cells in Parkinson’s Treatment
Preclinical studies have demonstrated the therapeutic potential of various stem cell sources, including embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells, and mesenchymal stem cells, in PD models. Stem cell transplantation holds promise for reversing motor deficits, enhancing dopamine production, and fostering neural repair.
Clinical Trials and Research Findings
Several clinical trials have been conducted to assess the safety, efficacy, and long-term outcomes of stem cell-based therapies in PD patients. While initial results are encouraging, challenges such as immune rejection, tumorigenicity, and graft survival remain to be addressed for widespread clinical implementation.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite considerable progress, stem cell therapy faces several challenges, including ethical considerations, standardization of protocols, and scalability for large-scale production. Additionally, the optimal route of administration, timing of intervention, and patient selection criteria warrant further investigation.
Future Directions in Stem Cell Research
Future research efforts aim to optimize stem cell-based approaches through the development of novel delivery methods, genetic engineering techniques, and biomaterial scaffolds. Collaborative endeavors between scientists, clinicians, and regulatory agencies are essential to accelerate the translation of stem cell therapies from bench to bedside.
Neuroprotective Strategies
Overview of Neuroprotection
Neuroprotective strategies aim to preserve existing neurons, mitigate disease progression, and prevent further neurodegeneration in PD. These approaches target underlying pathological mechanisms, including oxidative stress, inflammation, protein aggregation, and excitotoxicity.
Drug-based Neuroprotection
Numerous pharmacological agents, such as antioxidants, anti-inflammatory drugs, and neurotrophic factors, have shown neuroprotective properties in preclinical models of PD. However, translating these findings into clinical practice remains challenging due to issues related to bioavailability, target specificity, and off-target effects.
Non-pharmacological Neuroprotection Approaches
In addition to pharmacotherapy, non-pharmacological interventions such as lifestyle modifications, dietary supplements, and environmental modifications play a crucial role in promoting neuroprotection and disease resilience. Physical exercise, cognitive stimulation, and stress management techniques have been shown to exert beneficial effects on brain health and function.
Gene Therapy Innovations
Gene Editing Techniques
Recent advancements in gene editing technologies, including CRISPR-Cas9 and viral vector-mediated gene delivery systems, offer unprecedented opportunities for precise manipulation of the genome. Gene therapy holds immense potential for correcting genetic mutations, regulating gene expression, and modulating disease pathways in PD.
Target Genes for Parkinson’s Treatment
Several target genes implicated in PD pathogenesis, such as alpha-synuclein, LRRK2, Parkin, and PINK1, serve as promising candidates for gene-based interventions. Strategies aimed at reducing protein aggregation, enhancing protein clearance mechanisms, and restoring cellular homeostasis hold promise for disease modification in PD.
Clinical Applications and Progress
Clinical trials evaluating gene therapy approaches for PD have shown encouraging results in terms of safety, tolerability, and preliminary efficacy. Gene delivery vectors, dosing regimens, and patient selection criteria are actively being optimized to maximize therapeutic outcomes and minimize adverse events.
Immunotherapy for Parkinson’s
Role of the Immune System in Parkinson’s
Growing evidence suggests that neuroinflammation and immune dysregulation contribute to neurodegeneration in PD. The activation of microglia, infiltration of peripheral immune cells, and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines exacerbate neuronal damage and exacerbate disease progression.
Immunomodulatory Therapies
Immunotherapy aims to modulate the immune response, suppress neuroinflammation, and promote neuroprotection in PD. Strategies such as monoclonal antibodies, cytokine inhibitors, and immune cell-based therapies hold promise for mitigating inflammatory processes and preserving neuronal integrity.
Challenges and Potential
Despite the potential benefits of immunotherapy, several challenges, including blood-brain barrier penetration, target specificity, and immune-related adverse effects, need to be addressed. Moreover, patient heterogeneity, disease stage, and biomarker identification pose significant challenges for personalized immunomodulatory approaches.
Nutritional Interventions and Lifestyle Modifications
Impact of Diet on Parkinson’s Disease
Emerging evidence suggests that dietary factors play a critical role in modulating PD risk and progression. Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, has been associated with a reduced risk of PD and improved motor function in affected individuals.
Exercise and Physical Activity Recommendations
Regular physical exercise is essential for maintaining mobility, balance, and overall health in individuals with PD. Aerobic exercise, strength training, and balance exercises can improve motor symptoms, enhance cardiovascular fitness, and reduce the risk of falls.
Holistic Approaches to Management
In addition to dietary modifications and exercise, holistic approaches such as stress reduction techniques, mindfulness practices, and social engagement can positively impact PD outcomes. Integrative therapies, including yoga, tai chi, and massage therapy, promote relaxation, alleviate symptoms, and improve quality of life.
Personalized Medicine Approaches
Biomarkers in Parkinson’s Disease
The identification of reliable biomarkers is critical for early diagnosis, disease monitoring, and treatment stratification in PD. Biomarkers encompass various molecular, imaging, and clinical measures that reflect disease pathology, progression, and response to therapy.
Tailored Treatment Strategies
Personalized medicine aims to customize treatment plans based on individual patient characteristics, including genetic predisposition, biomarker profiles, and clinical phenotypes. Precision medicine approaches enable targeted interventions, optimal dosing regimens, and enhanced therapeutic outcomes for PD patients.
Integration of Technology for Personalization
Advancements in digital health technologies, wearable devices, and telemedicine platforms facilitate remote monitoring, real-time data collection, and personalized interventions in PD care. Machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence tools enable data analysis, predictive modeling, and treatment optimization for individuals with PD.
Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM)
Herbal Remedies and Supplements
Many individuals with PD use complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) approaches, including herbal remedies, dietary supplements, and traditional therapies, to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. However, evidence supporting the efficacy and safety of CAM modalities in PD remains limited.
Acupuncture and Traditional Therapies
Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice, has gained popularity as a complementary therapy for PD management. Acupuncture treatments target specific acupoints to restore energy balance, alleviate pain, and enhance overall well-being in affected individuals.
Evidence and Considerations
While some CAM modalities may provide symptomatic relief and adjunctive support, their efficacy and safety require further scientific validation through rigorous clinical trials and systematic reviews. Healthcare providers should engage in open dialogue with patients regarding CAM usage and ensure informed decision-making in PD management.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations in Parkinson’s Research
Ethical Dilemmas in Clinical Trials
Ethical considerations in PD research encompass issues such as informed consent, risk-benefit assessment, patient autonomy, and confidentiality. Balancing the pursuit of scientific knowledge with the protection of human subjects’ rights and welfare is paramount in conducting ethically sound clinical trials.
Patient Rights and Informed Consent
Respecting patient autonomy and ensuring informed consent are fundamental principles of ethical research conduct. Patients must be fully informed about study objectives, procedures, risks, and alternatives to make voluntary decisions regarding their participation in clinical trials.
Regulatory Frameworks and Oversight
Regulatory agencies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of investigational therapies for PD. Regulatory oversight, Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines, and ethical review processes safeguard research participants and uphold scientific integrity.
Future Directions and Collaborative Efforts
Multidisciplinary Research Initiatives
Addressing the complex challenges of PD requires multidisciplinary collaboration among scientists, clinicians, industry partners, advocacy groups, and government agencies. Integrated research efforts encompass basic science, translational research, clinical trials, and implementation science to accelerate therapeutic innovations.
Patient Advocacy and Community Engagement
Empowering patients, caregivers, and advocacy organizations as partners in research and healthcare decision-making fosters patient-centered approaches and enhances research relevance and impact. Community engagement initiatives, educational outreach programs, and support networks facilitate knowledge dissemination, resource mobilization, and policy advocacy in the PD community.
Global Collaborations and Partnerships
Global collaboration and knowledge sharing are essential for advancing PD research, promoting equity in access to care, and addressing disparities in healthcare delivery. International consortia, research networks, and collaborative platforms facilitate data sharing, harmonization of research standards, and collective efforts to conquer PD worldwide.
In conclusion, the landscape of Parkinson’s Disease research and treatment is rapidly evolving, fueled by innovative discoveries, collaborative endeavors, and patient-centered approaches. While significant challenges remain, the collective efforts of scientists, clinicians, policymakers, and stakeholders offer hope for a future where effective therapies halt disease progression, improve quality of life, and ultimately cure Parkinson’s Disease.